\(\dfrac{x-17}{33}\)+\(\dfrac{x-21}{29}_{ }\)+\(\dfrac{x}{25}\)=4
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


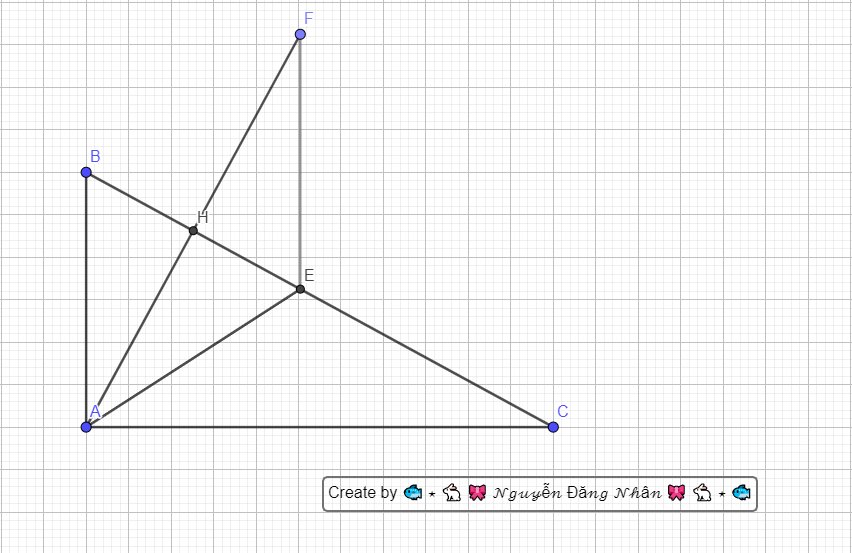
a)
Xét 2 tám giác AHB và AHE có:
\(\widehat{AHB}=\widehat{AHE}=90^o\) (giả thiết)
\(BH=HE\)
\(AH\): cạnh chung:
\(\Rightarrow\Delta AHB=\Delta AHE\)
b)
\(\widehat{B}=\widehat{E}\) (vì \(\Delta AHB=\Delta AHE\)) nên ABE là tam giác đều (không cần dữ kiện C=30 độ)
c) Xét 2 tam giác AHB và FHE có:
\(AH=FH\) (giả thiết)
\(\widehat{AHB}=\widehat{FHE}\) (góc đối đỉnh)
\(HB=HE\)
\(\Rightarrow\Delta AHB=\Delta FHE\left(c.g.c\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow\widehat{BAH}=\widehat{EFH}\)
\(\Rightarrow EF//AB\) (2 góc so le trong bằng nhau)
a) xét △ABH và △AHE có :
AH là cạnh chung
AHE = ABH = 90 độ
EH = BH
Vậy △AHB = △AHE ( c.g.c)
b)
Ta có A + B + C = 180 độ
=> B= 180 - A - C= 180 - 90 - 30 = 60 độ
Ta có EAB + B + AEB = 180
=> AEB + EAB = 180 - 60 =120 độ
Vì △AEH = △ABH ( chứng minh câu a)
=> AEB = ABE = 60 độ
Ta có BAE + AEB =120 độ
=> EAB = 120 - 60 =60 độ
=> △ABE là tam giác đều

\(\left(\dfrac{1}{5}\right)^{25}\cdot\left(\dfrac{1}{5}\right)^{30}\)
\(=\left(\dfrac{1}{5}\right)^{25+30}\)
\(=\left(\dfrac{1}{5}\right)^{55}\)
\(\left(\dfrac{1}{16}\right)^3:\left(\dfrac{1}{8}\right)^2\)
\(=\left[\left(\dfrac{1}{2}\right)^4\right]^3:\left[\left(\dfrac{1}{2}\right)^3\right]^2\)
\(=\left(\dfrac{1}{2}\right)^{12}:\left(\dfrac{1}{2}\right)^6\)
\(=\left(\dfrac{1}{2}\right)^{12-6}=\left(\dfrac{1}{2}\right)^6\)
\(\left(x^3\right)^2:\left(x^2\right)^3\)
\(=x^{3\cdot2-2\cdot3}\)
\(=x^0=1\)

\(\left(\dfrac{1}{3}+\dfrac{1}{6}\right)\cdot2^{x+4}-2^x=2^{13}-2^{10}\)
\(\Rightarrow\dfrac{1}{2}\cdot2^{x+4}-2^x=2^{13}-2^{10}\)
\(\Rightarrow2^{x+3}-2^x=2^{13}-2^{10}\)
\(\Rightarrow x+3=13;x+0=10\)
\(\Rightarrow x=10\)
(\(\dfrac{1}{3}\) +\(\dfrac{1}{6}\) ) . 2x+4 - 2x = 213 - 210
(\(\dfrac{2}{6}\) + \(\dfrac{1}{6}\)) . \(2^{x+4}\) - \(2^x\) = 8192 - 1024
\(\dfrac{3}{6}\) . 2x . \(2^4\) -\(2^x\) = 7168
8 . 2x - 2x . 1 = 7168
2x . ( 8 - 1 ) = 7168
2x . 7 = 7168
2x = 7168 : 7
2x = 1024
2x = \(2^{10}\)
⇒ x = 10

`@` `\text {Ans}`
`\downarrow`
\((6x-5)(x+8)-(3x-1)(2x+3)-9(4x-3)\)
`= 6x(x+8) - 5(x+8) - [ 3x(2x+3) - 2x - 3] - 36x + 27`
`= 6x^2 + 48x - 5x - 40 - (6x^2 + 9x - 2x - 3) - 36x + 27`
`= 6x^2 + 48x - 5x - 40 - (6x^2 + 7x - 3) - 36x + 27`
`= 6x^2 + 48x - 5x - 40 - 6x^2 - 7x + 3 - 36x + 27`
`= (6x^2 - 6x^2) + (48x - 5x - 7x - 36x) + (-40 + 3 + 27)`
`= 0 + 0 - 10`
`= - 10`
Vậy, giá trị của biểu thức không phụ thuộc vào giá trị của biến

32 < 211 < 128 ( xem lại đề bài em nhé)
4< 2N < 216
\(\dfrac{4}{2}< \) N < \(\dfrac{216}{2}\)
2 < N < 108
vì N \(\in\) Z nên N \(\in\) { 3; 4; 5; 6; 7;...; 107}

`@` `\text {Ans}`
`\downarrow`
`-1/27 = ( (-1)^3/(-3)^3) =(-1/3)^3`
`8/729 = ( (2^3)/(9^3) ) = (2/9)^3`
`16/685 = ( (4^2)/( \sqrt {685}) ) = (4/(\sqrt {685}) )^2`


(\(x\) + 1)2 = \(\dfrac{4}{25}\)
(\(x+1\))2 = (\(\dfrac{2}{5}\))2
\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x+1=-\dfrac{2}{5}\\x+1=\dfrac{2}{5}\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{2}{5}-1\\x=-\dfrac{2}{5}-1\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-\dfrac{3}{5}\\x=-\dfrac{7}{5}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy \(x\in\){ \(-\dfrac{7}{5}\) ; - \(\dfrac{3}{5}\)}
`@` `\text {Ans}`
`\downarrow`
`(x+1)^2 = 4/25`
`=> (x+1)^2 = (+-2/5)^2`
`=>`\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x+1=\dfrac{2}{5}\\x+1=-\dfrac{2}{5}\end{matrix}\right.\)
`=>`\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{2}{5}-1\\x=-\dfrac{2}{5}-1\end{matrix}\right.\)
`=>`\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-\dfrac{3}{5}\\x=-\dfrac{7}{5}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy, `x \in {-3/5; -7/5}.`
\(\dfrac{x-17}{33}+\dfrac{x-21}{29}+\dfrac{x}{25}=4\)
\(\dfrac{x-17}{33}+\dfrac{x-21}{29}+\dfrac{x}{25}-4=0\)
\(\dfrac{\left(x-17\right)\times725}{33\times725}+\dfrac{\left(x-21\right)\times825}{29\times825}+\dfrac{x\times957}{25\times957}-\dfrac{4\times23925}{23925}=0\)
\(725x-12325+825x-17325+957x-95700=0\)
\(2507x-125350=0\)
\(2507x=125350\)
\(x=50\)
Nếu mà theo cách x - 50 = 0 thì bạn theo cách này nha:
\(\dfrac{x-17}{33}+\dfrac{x-21}{29}+\dfrac{x}{25}=4\)
\(\dfrac{x-17}{33}+\dfrac{x-21}{29}+\dfrac{x}{25}-4=0\)
\(\dfrac{x-17}{33}-1+\dfrac{x-21}{29}-1+\dfrac{x}{25}-2=0\)
\(\dfrac{x-50}{33}+\dfrac{x-50}{29}+\dfrac{x-50}{25}=0\)
\(\left(x-50\right)\left(\dfrac{1}{33}+\dfrac{1}{29}+\dfrac{1}{5}\right)=0\)
Vì \(\dfrac{1}{33}+\dfrac{1}{29}+\dfrac{1}{25}>0\)
=> \(x-50=0\)
=> \(x=50\)