3^10x15^5/25^3x9^7
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


a/
$\frac{1}{x}+\frac{1}{y}=\frac{1}{5}$
$\Rightarrow \frac{x+y}{xy}=\frac{1}{5}$
$\Rightarrow 5(x+y)=xy$
$\Rightarrow 5x+5y-xy=0$
$\Rightarrow x(5-y)+5y=0$
$\Rightarrow x(5-y)-5(5-y)=-25$
$\Rightarrow (x-5)(5-y)=-25$
$\Rightarrow (x-5)(y-5)=25$
Do $x,y$ nguyên nên $x-5,y-5$ nguyên. Mà tích $(x-5)(y-5)=25$ nên xảy ra các TH sau đây:
TH1: $x-5=1, y-5=25\Rightarrow x=6; y=30$
TH2: $x-5=-1, y-5=-25\Rightarrow x=4; y=-20$
TH3: $x-5=25, y-5=1\Rightarrow x=30; y=6$
TH4: $x-5=-25, y-5=-1\Rightarrow x=-20; y=4$
TH5: $x-5=5, y-5=5\Rightarrow x=10; y=10$
TH6: $x-5=-5, y-5=-5\Rightarrow x=0; y=0$
b/
$\frac{2}{x}+\frac{1}{y}=3$
$\Rightarrow \frac{x+2y}{xy}=3$
$\Rightarrow x+2y=3xy$
$\Rightarrow 3xy-x-2y=0$
$\Rightarrow x(3y-1)-2y=0$
$\Rightarrow 3x(3y-1)-6y=0$
$\Rightarrow 3x(3y-1)-2(3y-1)=2$
$\Rightarrow (3x-2)(3y-1)=2$
Do $x,y$ nguyên nên $3x-2, 3y-1$ cũng là số nguyên. Mà tích của chúng bằng 2 nên ta xét các TH sau:
TH1: $3x-2=1, 3y-1=2\Rightarrow x=y=1$
TH2: $3x-2=2, 3y-1=1\Rightarrow x=\frac{4}{3}$ (loại)
TH3: $3x-2=-1, 3y-1=-2\Rightarrow x=\frac{1}{3}$ (loại)
TH4: $3x-2=-2, 3y-1=-1\Rightarrow x=y=0$ (loại do $x,y\neq 0$)
Vậy $x=y=1$

Gọi số hạng thứ nhất là a thì số hạng thứ hai là \(\dfrac{2}{5}\cdot a\), số hạng thứ ba là \(\dfrac{2}{5}\cdot a+\dfrac{7}{4}\), số hạng thứ tư là \(\dfrac{1}{5}\cdot a\).
Khi đó, ta được:
\(a+\dfrac{2}{5}\cdot a+\dfrac{2}{5}\cdot a+\dfrac{7}{4}+\dfrac{1}{5}\cdot a=\dfrac{57}{4}\\ \Leftrightarrow2a+\dfrac{7}{4}=\dfrac{57}{4}\\ \Leftrightarrow2a=\dfrac{50}{4}\\ \Leftrightarrow a=\dfrac{25}{4}\)
Vậy số hạng thứ nhất là \(\dfrac{25}{4}\), số hạng thứ hai là \(\dfrac{5}{2}\), số hạng thứ ba là \(\dfrac{17}{4}\), số hạng thứ tư là \(\dfrac{5}{4}\).
Ta được: \(14\dfrac{1}{4}=\dfrac{25}{4}+\dfrac{5}{2}+\dfrac{17}{4}+\dfrac{5}{4}\)

Gọi 17 số đó là \(a_1,a_2,...,a_{17}\left(a_i\inℚ,i=\overline{1,17}\right)\)
Theo đề bài, ta có:
\(a_1=a_2^3+a_3^3+a_4^3+...+a_{17}^3\)
\(a_2=a_1^3+a_3^3+a_4^3+...+a_{17}^3\)
Trừ theo vế 2 hệ thức này, ta được:
\(a_1-a_2=a_2^3-a_1^3\)
\(\Leftrightarrow a_1-a_2+a_1^3-a_2^3=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(a_1-a_2\right)\left[\left(a_1-a_2\right)^2+1\right]=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}a_1=a_2\\\left(a_1-a_2\right)^2+1=0\left(loại\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
Như vậy ta có \(a_1=a_2\)
Chứng minh tương tự, ta thu được \(a_1=a_2=...=a_{17}\)
Thế vào hệ thức đầu tiên trong 2 hệ thức trên, ta có:
\(a_1=17a_1^3\)
\(\Leftrightarrow a_1\left(17a_1^2-1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}a_1=0\\a_1=\dfrac{\sqrt{17}}{17}\left(loạivìa_1\inℚ\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy \(\left(a_1,a_2,...,a_{17}\right)=\left(0,0,...,0\right)\) là bộ 17 số duy nhất thỏa mãn ycbt.

\(\dfrac{x-2y}{z-y}=-5\Rightarrow\dfrac{x-2y}{y-z}=5\\ \Rightarrow x-2y=5\left(y-z\right)\\ \Rightarrow x-2y=5y-5z\\ \Rightarrow x+5z=7y\)
Ta có:
\(\dfrac{1}{7}\cdot\dfrac{x-2z}{y-z}=\dfrac{x-2z}{7\left(y-z\right)}=\dfrac{x-2z}{7y-7z}\\ =\dfrac{x-2z}{x+5z-7z}=\dfrac{x-2z}{x-2z}=1\)
\(\Rightarrow\dfrac{x-2z}{y-z}=1:\dfrac{1}{7}=7\)

1) \(x^2-4=x^2-2^2=\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)\)
2) \(1-4x^2=1-\left(2x\right)^2=\left(1-2x\right)\left(1+2x\right)\)
3) \(4x^2-9=\left(2x\right)^2-3^2=\left(2x-3\right)\left(2x+3\right)\)
4) \(9-25x^2=3^2-\left(5x\right)^2=\left(3-5x\right)\left(3+5x\right)\)
5) \(4x^2-25=\left(2x\right)^2-5^2=\left(2x-5\right)\left(2x+5\right)\)
6) \(9x^2-36=\left(3x\right)^2-6^2=\left(3x-6\right)\left(3x+6\right)\)
7) \(\left(3x\right)^2-y^2=\left(3x+y\right)\left(3x-y\right)\)
8) \(x^2-\left(2y\right)^2=\left(x+2y\right)\left(x-2y\right)\)
9) \(\left(2x\right)^2-y^2=\left(2x-y\right)\left(2x+y\right)\)

\(3x-\dfrac{3}{5}=\dfrac{-7}{10}\\ 3x=\dfrac{-7}{10}+\dfrac{3}{5}\\ 3x=\dfrac{-7}{10}+\dfrac{6}{10}\\ 3x=\dfrac{-1}{10}\\ x=\dfrac{-1}{30}\)
___________________
\(\dfrac{2}{3}+\dfrac{1}{3}:x=\dfrac{3}{5}\\ \dfrac{1}{3}:x=\dfrac{3}{5}-\dfrac{2}{3}\\ \dfrac{1}{3}:x=\dfrac{9}{15}-\dfrac{10}{15}\\ \dfrac{1}{3}:x=\dfrac{-1}{15}\\ x=\dfrac{1}{3}:\dfrac{-1}{15}\\ x=-5\)
\(3x-\dfrac{3}{5}=-\dfrac{7}{10}\)
\(3x\) \(=-\dfrac{7}{10}+\dfrac{3}{5}\)
\(3x\) \(=-\dfrac{1}{10}\)
\(x\) \(=-\dfrac{1}{10}:3\)
\(x\) \(=-\dfrac{1}{30}\)
Vậy \(x=-\dfrac{1}{30}\)
\(\dfrac{2}{3}+\dfrac{1}{3}:x=\dfrac{3}{5}\)
\(\dfrac{1}{3}:x=\dfrac{3}{5}-\dfrac{2}{3}\)
\(\dfrac{1}{3}:x=-\dfrac{1}{15}\)
\(x=\dfrac{1}{3}:-\dfrac{1}{15}\)
\(x=-5\)
Vậy \(x=-5\)

\(\left(\dfrac{2}{7}-\dfrac{9}{4}\right)-\left(-\dfrac{3}{7}+\dfrac{5}{4}\right)-\left(\dfrac{2}{4}-\dfrac{9}{7}\right)\)
\(=\dfrac{2}{7}-\dfrac{9}{4}+\dfrac{3}{7}-\dfrac{5}{4}-\dfrac{2}{4}+\dfrac{9}{7}\)
\(=\left(\dfrac{2}{7}+\dfrac{3}{7}+\dfrac{9}{7}\right)-\left(\dfrac{9}{4}+\dfrac{5}{4}+\dfrac{2}{4}\right)\)
\(=2-4\)
\(=-2\)

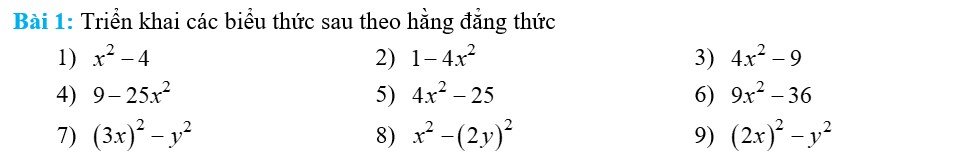

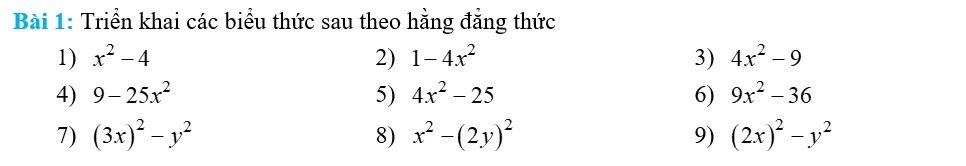
Bạn bấm vào biểu tượng để nhập các công thức toán học cho rõ ràng nhé!
để nhập các công thức toán học cho rõ ràng nhé!
Vd:\(3^{10}\)
\(\dfrac{3^{10}\cdot15^5}{25^3\cdot9^7}=\dfrac{3^{10}\cdot\left(3\cdot5\right)^5}{\left(5^2\right)^3\cdot\left(3^2\right)^7}=\dfrac{3^{10}\cdot3^5\cdot5^5}{5^6\cdot3^{14}}\)
\(=\dfrac{3^{15}}{5\cdot3^{14}}=\dfrac{3}{5}\)