giúp mik câu này với huhu
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


\(x^{10}=1^x\\ =>x^{10}=1\\ =>x^{10}=\left(\pm1\right)^{10}\\ =>x=\pm1\)
Vậy: ...

ΔABC cân tại A
=>\(\widehat{BAC}=180^0-2\cdot\widehat{ABC}=100^0\)
AD là phân giác góc ngoài tại đỉnh A
=>\(\widehat{CAD}=\dfrac{180^0-\widehat{BAC}}{2}=40^0\)
=>\(\widehat{CAD}=\widehat{ACB}\left(=40^0\right)\)
mà hai góc này là hai góc ở vị trí so le trong
nên AD//BC

Đặt: \(\dfrac{1}{2x-y}=a;\dfrac{1}{x+y}=b\left(2x\ne y;x\ne-y\right)\)
Hpt trở thành:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}3a-6b=1\\a-b=0\end{matrix}\right. \Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}3a-6a=1\\a=b\end{matrix}\right.\\ \Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}-3a=1\\a=b\end{matrix}\right. \Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}a=-\dfrac{1}{3}\\b=a=-\dfrac{1}{3}\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(=>\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{1}{2x-y}=\dfrac{1}{-3}\\\dfrac{1}{x+y}=\dfrac{1}{-3}\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}2x-y=-3\\x+y=-3\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}3x=-6\\x+y=-3\end{matrix}\right.\\ \Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{-6}{3}=-2\\-2+y=-3\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=-2\\y=-3+2=-1\end{matrix}\right.\)

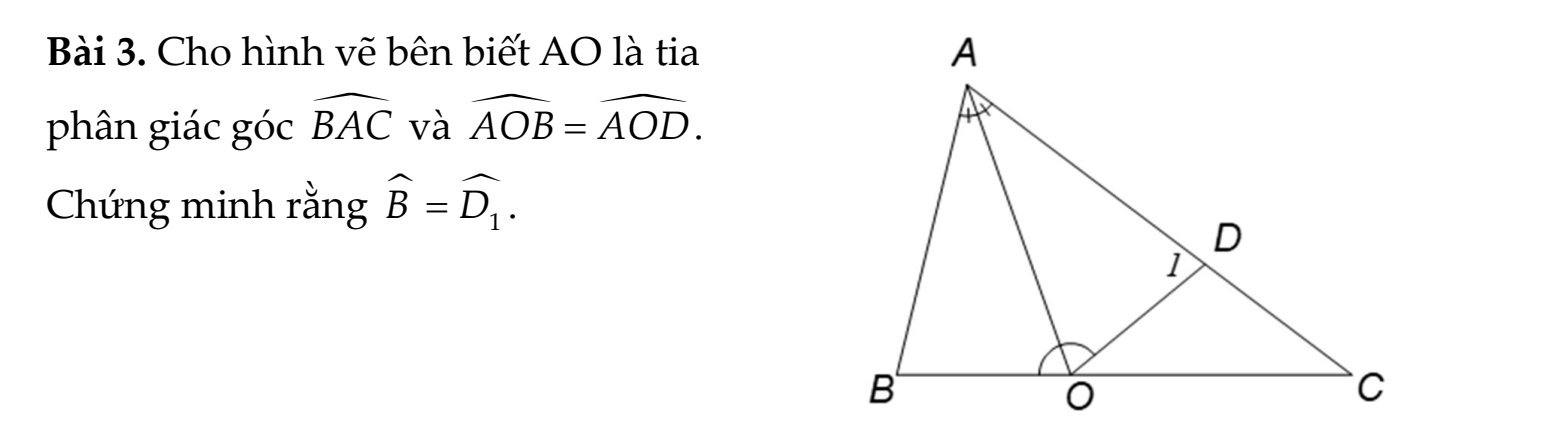
Xét 2 ΔABO và ΔADO ta có:
\(\widehat{BAO}=\widehat{DAO}\) (AD là phân giác của góc BAC)
\(OA\) chung
\(\widehat{AOB}=\widehat{AOD}\left(gt\right)\)
\(=>\Delta ABO=\Delta ADO\left(g.c.g\right)\)
\(=>\widehat{B}=\widehat{D_1}\) (hai góc tương ứng)

a) 575-(6x+70)=455
6x+70=575-455
6x+70=120
6x=120-70
6x=50
x=50:6
x=\(\dfrac{25}{3}\) \(\notinℕ\)
Vậy không có giá trị tự nhiên x thỏa mãn đề
b) 315+(125-x)=435
125-x=435-315
125-x=120
x=125-120
x=5 (nhận)
c) 3x+28=88
3x=88-28
3x=60
x=60:3
x=20
\(a.575-\left(6\cdot x+70\right)=455\\ =>6\cdot x+70=575-455\\ =>6\cdot x+70=120\\ =>6\cdot x=120-70\\ =>6\cdot x=50\\ =>x=\dfrac{50}{6}=\dfrac{25}{3}\left(L\right)\\ b.315+\left(125-x\right)=435\\ =>125-x=435-315=125\\ =>x=125-125=0\\ c.3\cdot x+28=88\\ =>3\cdot x=88-28\\ =>3\cdot x=60\\ =>x=\dfrac{60}{3}=20\\ x-105:21=15\\ =>x-5=15\\ =>x=15+5=20\\ e.\left(x-105\right):21=15\\ =>x-105=21\cdot15\\ =>x-105=315\\ =>x=315+105\\ =>x=420\)

Đặt: \(3x^2-5x-7=0\)
\(\Delta=\left(-5\right)^2-4\cdot3\cdot\left(-7\right)=109>0\)
\(x_1=\dfrac{-\left(-5\right)+\sqrt{109}}{2\cdot3}=\dfrac{5+\sqrt{109}}{6}\)
\(x_2=\dfrac{-\left(-5\right)-\sqrt{109}}{2\cdot3}=\dfrac{5-\sqrt{109}}{6}\)
=> \(3x^2-5x-7=\left(x-\dfrac{5+\sqrt{109}}{6}\right)\left(x-\dfrac{5-\sqrt{109}}{6}\right)\)

\(x^4+2x^2-3\\ =\left(x^4-x^2\right)+\left(3x^2-3\right)\\ =x^2\left(x^2-1\right)+3\left(x^2-1\right)\\ =\left(x^2-1\right)\left(x^2+3\right)\\ =\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)\left(x^2+3\right)\)
\(x^4+2x^2-3\)
\(=x^4+3x^2-x^2-3\)
\(=x^2\left(x^2+3\right)-\left(x^2+3\right)=\left(x^2+3\right)\left(x^2-1\right)\)
\(=\left(x^2+3\right)\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)\)

a/ Dựng \(AH\perp BC\left(H\in BC\right)\)
Xét tg vuông ACH có
\(\cos C=\dfrac{CH}{AC}=\dfrac{CH}{b}\Rightarrow CH=b\cos C\)
Xét tg vuông ABH có
\(\cos B=\dfrac{BH}{AB}=\dfrac{BH}{c}\Rightarrow BH=c\cos B\)
\(\Rightarrow CH+BH=BC=a=b\cos C+c\cos B\)
b/
Đặt \(\widehat{BAH}=\alpha;\widehat{CAH}=\beta\)
\(\Rightarrow\cos A=\cos\left(\alpha+\beta\right)=\cos\alpha\cos\beta-\sin\alpha\sin\beta=\)
\(=\dfrac{AH}{c}.\dfrac{AH}{b}-\dfrac{BH}{c}.\dfrac{CH}{b}=\dfrac{AH^2-BH.CH}{bc}=\)
\(=\dfrac{2AH^2-2BH.CH}{2bc}=\dfrac{c^2-BH^2+b^2-CH^2-2BH.CH}{2bc}=\)
\(=\dfrac{b^2+c^2-\left(BH+CH\right)^2}{2bc}=\dfrac{b^2+c^2-a^2}{2bc}\)

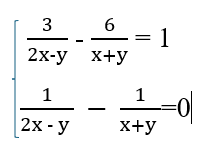
Xét ΔABC vuông tại A có \(\widehat{ABC}+\widehat{ACB}=90^0\)
=>\(2\cdot\left(\widehat{OBC}+\widehat{OCB}\right)=90^0\)
=>\(\widehat{OBC}+\widehat{OCB}=45^0\)
Xét ΔOBC có \(\widehat{BOC}+\widehat{OBC}+\widehat{OCB}=180^0\)
=>\(\widehat{BOC}+45^0=180^0\)
=>\(\widehat{BOC}=135^0\)