Cho hai đường thẳng d1: y=2x-3 và d2: y=-3x+7
a, vẽ d1, d2 trên cùng 1 hệ trục tọa độ
b, tìm tọa độ giao điểm của d1 và d2
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

a: 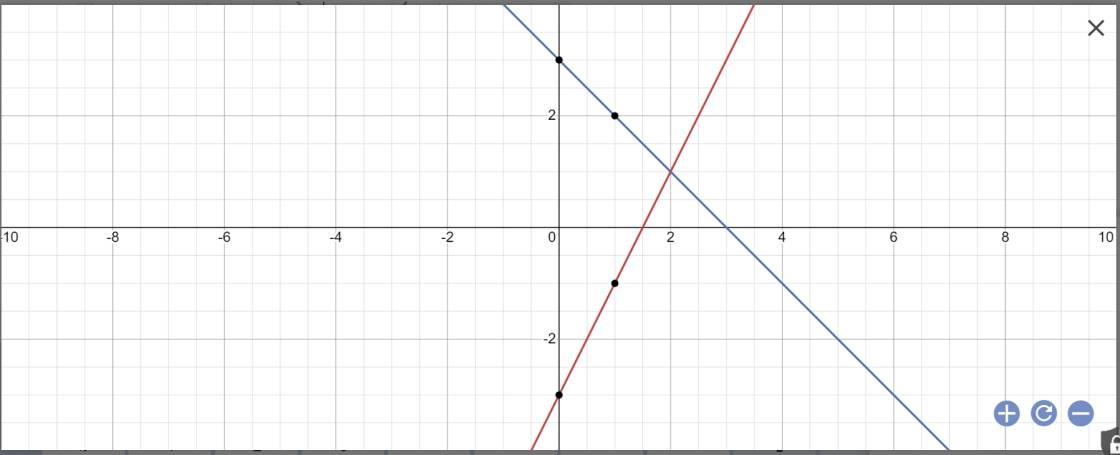
b: Phương trình hoành độ giao điểm là:
2x-3=3-x
=>3x=6
=>x=6/3=2
Thay x=2 vào y=3-x, ta được:
\(y=3-2=1\)

\(b,\) PT hoành độ giao điểm: \(3x+2=x-2\Leftrightarrow x=-2\Leftrightarrow y=-4\Leftrightarrow A\left(-2;-4\right)\)
Vậy \(A\left(-2;-4\right)\) là tọa độ giao điểm

b, PT giao điểm (d3) và (d1) là \(\dfrac{1}{3}x+3=2x-2\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{5}{3}x=5\Leftrightarrow x=3\Leftrightarrow y=4\Leftrightarrow A\left(3;4\right)\)
PT giao điểm (d3) và (d2) là \(\dfrac{1}{3}x+3=-\dfrac{4}{3}x-2\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{5}{3}x=-5\Leftrightarrow x=-3\Leftrightarrow y=2\Leftrightarrow B\left(-3;2\right)\)

\(b,\) Tọa độ giao điểm 2 đường thẳng là:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=-2x+4\\y=x+1\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x+1=-2x+4\\y=x+1\end{matrix}\right.\\ \Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=1\\y=2\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow A\left(1;2\right)\)
Tọa độ giao điểm 2 đường thẳng với trục hoành là
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=0\\\left[{}\begin{matrix}y=-2x+4\\y=x+1\end{matrix}\right.\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=0\\\left[{}\begin{matrix}4-2x=0\\x+1=0\end{matrix}\right.\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=0\\\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=2\\x=-1\end{matrix}\right.\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow B\left(2;0\right),C\left(-1;0\right)\)

a, HS Tự làm
b, Tìm được C(–2; –3) là tọa độ giao điểm của d 1 và d 2
c, Kẻ OH ⊥ AB (CH ⊥ Ox)
S A B C = 1 2 C H . A B = 9 4 (đvdt)
a, bạn tự vẽ nhé
b, Hoành độ giao điểm thỏa mãn phương trình
\(2x-3=-3x+7\Leftrightarrow5x=10\Leftrightarrow x=2\)
Thay vào ptđt d1 ta được : \(y=4-3=1\)
Vậy d1 cắt d2 tại A(2;1)