(4x-7)2=(x-1)2
Tìm x
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


Để A là số nguyên thì \(2x-1\in\left\{1;-1;5;-5\right\}\)
hay \(x\in\left\{1;0;3;-2\right\}\)

Bài 2:
a: Ta có: \(2\left(5x-8\right)-3\left(4x-5\right)=4\left(3x-4\right)+11\)
\(\Leftrightarrow10x-16-12x+15=12x-16+11\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-14x=-4\)
hay \(x=\dfrac{2}{7}\)
b: Ta có: \(2x\left(6x-2x^2\right)+3x^2\left(x-4\right)=8\)
\(\Leftrightarrow12x^2-4x^3+3x^3-12x^2=8\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^3=-8\)
hay x=-2
Bài 1:
a: Ta có: \(I=x\left(y^2-xy^2\right)+y\left(x^2y-xy+x\right)\)
\(=xy^2-x^2y^2+x^2y^2-xy^2+xy\)
\(=xy\)
=1
b: Ta có: \(K=x^2\left(y^2+xy^2+1\right)-\left(x^3+x^2+1\right)\cdot y^2\)
\(=x^2y^2+x^3y^2+x^2-x^3y^2-x^2y^2-y^2\)
\(=x^2-y^2\)
\(=\dfrac{1}{4}-\dfrac{1}{4}=0\)

Để hệ có nghiệm duy nhất thì \(\dfrac{2m}{8}\ne\dfrac{1}{m}\)
=>\(m^2\ne4\)
=>\(m\notin\left\{2;-2\right\}\)
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}2mx+y=2\\8x+my=m+2\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}2m^2\cdot x+my=2m\\8x+my=m+2\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x\left(2m^2-8\right)=m-2\\y=2-2mx\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{m-2}{2m^2-8}=\dfrac{1}{2\left(m+2\right)}\\y=2-\dfrac{2m}{2\left(m+2\right)}=2-\dfrac{m}{m+2}=\dfrac{2m+4-m}{m+2}=\dfrac{m+4}{m+2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
4x+3y=7
=>\(\dfrac{4}{2\left(m+2\right)}+\dfrac{3\left(m+4\right)}{m+2}=7\)
=>\(\dfrac{2+3\left(m+4\right)}{m+2}=7\)
=>7(m+2)=2+3m+12
=>7m+14=3m+14
=>4m=0
=>m=0(nhận)

{ x2 - [ 62 - ( 82 - 9.7)3 - 7.5]3 - 5.3 }3 = 1
{ x2 + [ 36 - (64 - 63)3 - 35]3 - 15}3 = 1
[ x2 - ( 36 - 13 - 35 ) - 15 ]3 = 1
[ x2 - ( 36 - 1 - 35 ) - 15]3 = 1
[ x2 - ( 35 - 35 ) - 15]3 = 1
[ x2 - 0 - 15]3 = 1
( x2 - 15 )3 = 1
<=> ( x2 - 15)3 = 13
=> x2 - 15 = 1
<=> x2 = 16
=> x = 4

\(\left(3x+1\right)^2=9\left(x-2\right)^2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow9x^2+6x+1=9\left(x^2-4x+4\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow9x^2+6x+1=9x^2-36x+36\)
\(\Leftrightarrow9x^2+6x+1-9x^2+36x-36=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow42x-35=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow42x=35\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{35}{42}=\dfrac{5}{6}\)
Vậy: \(S=\left\{\dfrac{5}{6}\right\}\)

\(\Delta=\left[-2\left(m-1\right)\right]^2-4\left(m-2\right)\left(m+1\right)\)
\(=4m^2-8m+4-4\left(m^2+m-2m-2\right)\)
\(=4m^2-8m+4-4m^2+4m+8\)
\(=-4m+12\)
Để pt có 2 nghiệm thì \(\Delta>0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-4m+12>0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow m< 3\)
Theo hệ thức Vi-ét, ta có:\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x_1+x_2=\dfrac{2m-2}{m+1}\\x_1x_2=\dfrac{m-2}{m+1}\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\dfrac{1}{x_1}+\dfrac{1}{x_2}=\dfrac{7}{4}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{x_1+x_2}{x_1x_2}=\dfrac{7}{4}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{2m-2}{m+1}:\dfrac{m-2}{m+1}=\dfrac{7}{4}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{2m-2}{m-2}=\dfrac{7}{4}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow8m-8=7m-14\)
\(\Leftrightarrow m=-6\left(tm\right)\)
Vậy \(m=-6\)

\(\Leftrightarrow a\cdot\dfrac{13}{15}=\dfrac{28}{13}:2=\dfrac{14}{13}\)
=>\(a=\dfrac{14}{13}:\dfrac{13}{15}=\dfrac{210}{169}\)

Lời giải:
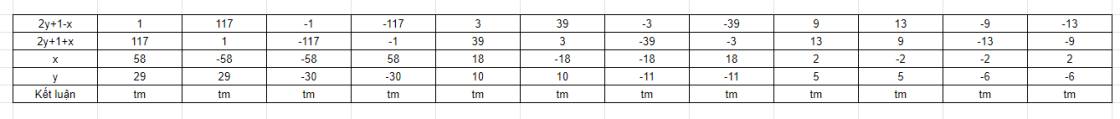
$117=(2y+1)^2-x^2=(2y+1-x)(2y+1+x)$
Vì $x,y$ nguyên nên $2y+1-x, 2y+1+x$ nguyên. Do đó ta có bảng sau:
`(4x-7)^2 = (x-1)^2`
TH1 :
`->4x-7=x-1`
`->4x-x=7-1`
`->3x=6`
`->x=2`
TH2 ;
`->4x-7=-x+1`
`->4x+x=7+1`
`->5x=8`
`->x=8/5`
Vậy `x=2` hoặc `x=8/5`