(x2+y2-5)2-4(x2y2+4xy+4)
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


a: \(x^2+4x+4=x^2+2\cdot x\cdot2+2^2=\left(x+2\right)^2\)
b: \(4x^2-4x+1=\left(2x\right)^2-2\cdot2x\cdot1+1^2=\left(2x-1\right)^2\)
c: \(2x-1-x^2\)
\(=-\left(x^2-2x+1\right)=-\left(x-1\right)^2\)
d: \(x^2+x+\dfrac{1}{4}=x^2+2\cdot x\cdot\dfrac{1}{2}+\left(\dfrac{1}{2}\right)^2=\left(x+\dfrac{1}{2}\right)^2\)
e: \(9-x^2=3^2-x^2=\left(3-x\right)\left(3+x\right)\)
g: \(\left(x+5\right)^2-4x^2=\left(x+5+2x\right)\left(x+5-2x\right)\)
\(=\left(5-x\right)\left(5+3x\right)\)
h: \(\left(x+1\right)^2-\left(2x-1\right)^2\)
\(=\left(x+1+2x-1\right)\left(x+1-2x+1\right)\)
\(=3x\left(-x+2\right)\)
i: \(=x^2y^2-4xy+4-3\)
\(=\left(xy-2\right)^2-3=\left(xy-2-\sqrt{3}\right)\left(xy-2+\sqrt{3}\right)\)
k: \(=y^2-\left(x-1\right)^2\)
\(=\left(y-x+1\right)\left(y+x-1\right)\)
l: \(=x^3+3\cdot x^2\cdot2+3\cdot x\cdot2^2+2^3=\left(x+2\right)^3\)
m: \(=\left(2x\right)^3-3\cdot\left(2x\right)^2\cdot y+3\cdot2x\cdot y^2-y^3=\left(2x-y\right)^3\)

a) \(x^4+2x^3-4x-4=\left(x^4+2x^3+x^2\right)-\left(x^2+4x+4\right)\)
\(=\left(x^2+x\right)^2-\left(x+2\right)^2=\left(x^2+x-x-2\right)\left(x^2+x+x+2\right)\)
\(=\left(x^2-2\right)\left(x^2+2x+2\right)\)
a) Ta có: \(x^4+2x^3-4x-4\)
\(=\left(x^4+2x^3+x^2\right)-\left(x^2+4x+4\right)\)
\(=\left(x^2+x\right)^2-\left(x+2\right)^2\)
\(=\left(x^2+x-x-2\right)\left(x^2+x+x+2\right)\)
\(=\left(x^2-2\right)\cdot\left(x^2+2x+2\right)\)

a) (x - y)(x + y + 3). b) (x + y - 2xy)(2 + y + 2xy).
c) x 2 (x + l)( x 3 - x 2 + 2). d) (x – 1 - y)[ ( x - 1 ) 2 + ( x - 1 ) y + y 2 ].

a) Áp dụng HĐT 1 thu được ( 2 x + y ) 2 .
b) Áp dụng HĐT 3 với A = 2x + l; B = x - l thu được
[(2x +1) + (x -1)] [(2x +1) - (x -1)] rút gọn thành 3x(x + 2).
c) Ta có: 9 - 6x + x 2 - y 2 = ( 3 - x ) 2 - y 2 = (3 - x - y)(3 -x + y).
d) Ta có: -(x + 2) + 3( x 2 - 4) = -{x + 2) + 3(x + 2)(x - 2)
= (x + 2) [-1 + 3(x - 2)] = (x + 2)(3x - 7).

a) \(3x\left(2x-y\right)+5y\left(y-2x\right)\)
\(=3x\left(2x-y\right)-5y\left(2x-y\right)\)
\(=\left(3x-5y\right)\left(2x-y\right)\)
b) \(\left(x-5\right)^2-9\left(x+y\right)^2\)
\(=\left(x-5\right)^2-3^2\left(x+y\right)^2\)
\(=\left(x-5\right)^2-\left(3x+3y\right)^2\)
\(=\left(x-5+3x+3y\right)\left(x-5-3x-3y\right)\)
\(=\left(4x+3y-5\right)\left(-2x-3y-5\right)\)
a: \(3x\left(2x-y\right)+5y\left(y-2x\right)=\left(2x-y\right)\left(3x-5y\right)\)
e: \(x^2-10x+24=\left(x-4\right)\left(x-6\right)\)

Trả lời:
Phương trình hoành độ giao điểm (P) và (d) ta có:
\(-x^2=2x+m-1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2+2x+m-1=0\)(1)
Ta có: \(\Delta=2^2-4.1.\left(m-1\right)\)
\(=4-4m+4\)
\(=8-4m\)
Để phương trình (1) có 2 nghiệm phân biệt \(\Leftrightarrow\Delta>0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow8-4m>0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4m< 8\)
\(\Leftrightarrow m< 2\)
\(\Rightarrow\)Phương trình (1) có 2 nghiệm phân biệt
\(\Rightarrow\)(d) cắt (P) tại 2 diểm phân biệt \(A\left(x_1,y_1\right);B\left(x_2,y_2\right)\)
Áp dụng Vi-ét \(\hept{\begin{cases}x_1+x_2=-2\left(1\right)\\x_1.x_2=m-1\left(2\right)\end{cases}}\)
Ta có \(y_1=-x_1^2\); \(y_2=-x_2^2\)
Theo đề bài:
\(x_1.y_1-x_2.y_2-x_1.x_2=4\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x_1.\left(-x_1^2\right)-x_2.\left(-x_2^2\right)-x_1.x_2=4\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-x_1^3+x_2^3-x_1.x_2=4\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-\left(x_1^3-x_2^3\right)-\left(m-1\right)=4\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-\left(x_1-x_2\right).\left(x_1^2+x_1.x_2+x_2^2\right)-\left(m-1\right)=4\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-\left(x_1-x_2\right)\left[\left(x_1+x_2\right)^2-2x_1.x_2+x_1.x_2\right]-\left(m-1\right)=4\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-\left(x_1-x_2\right).\left[\left(x_1+x_2\right)^2-x_1.x_2\right]-\left(m-1\right)=4\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-\left(x_1-x_2\right).\left[\left(-2\right)^2-m+1\right]-\left(m-1\right)=4\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-\left(x_1-x_2\right).\left(4-m+1\right)=4+m-1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-\left(x_1-x_2\right).\left(3-m\right)=m+3\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-\left(x_1-x_2\right)=\frac{m+3}{3-m}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x_1-x_2=\frac{m+3}{m-3}\)(3)
Từ (1) (3) ta có: \(\hept{\begin{cases}x_1+x_2=-2\\x_1-x_2=\frac{m+3}{m-3}\end{cases}}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}2x_1=-2+\frac{m+3}{m-3}=\frac{9-m}{m-3}=-\left(m+3\right)\\x_1+x_2=-2\end{cases}}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}x_1=\frac{-\left(m+3\right)}{2}\\x_2=\frac{m-1}{2}\end{cases}}\)
Thay x1, x2 vào (2) ta có
\(x_1.x_2=m-1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\frac{-\left(m+3\right)}{2}.\frac{m-1}{2}=m-1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\frac{-\left(m+3\right)}{2}=2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-\left(m+3\right)=4\)
\(\Leftrightarrow m+3=-4\)
\(\Leftrightarrow m=-7\)(TM)
Vậy \(m=-7\) thì thỏa mãn bài toán
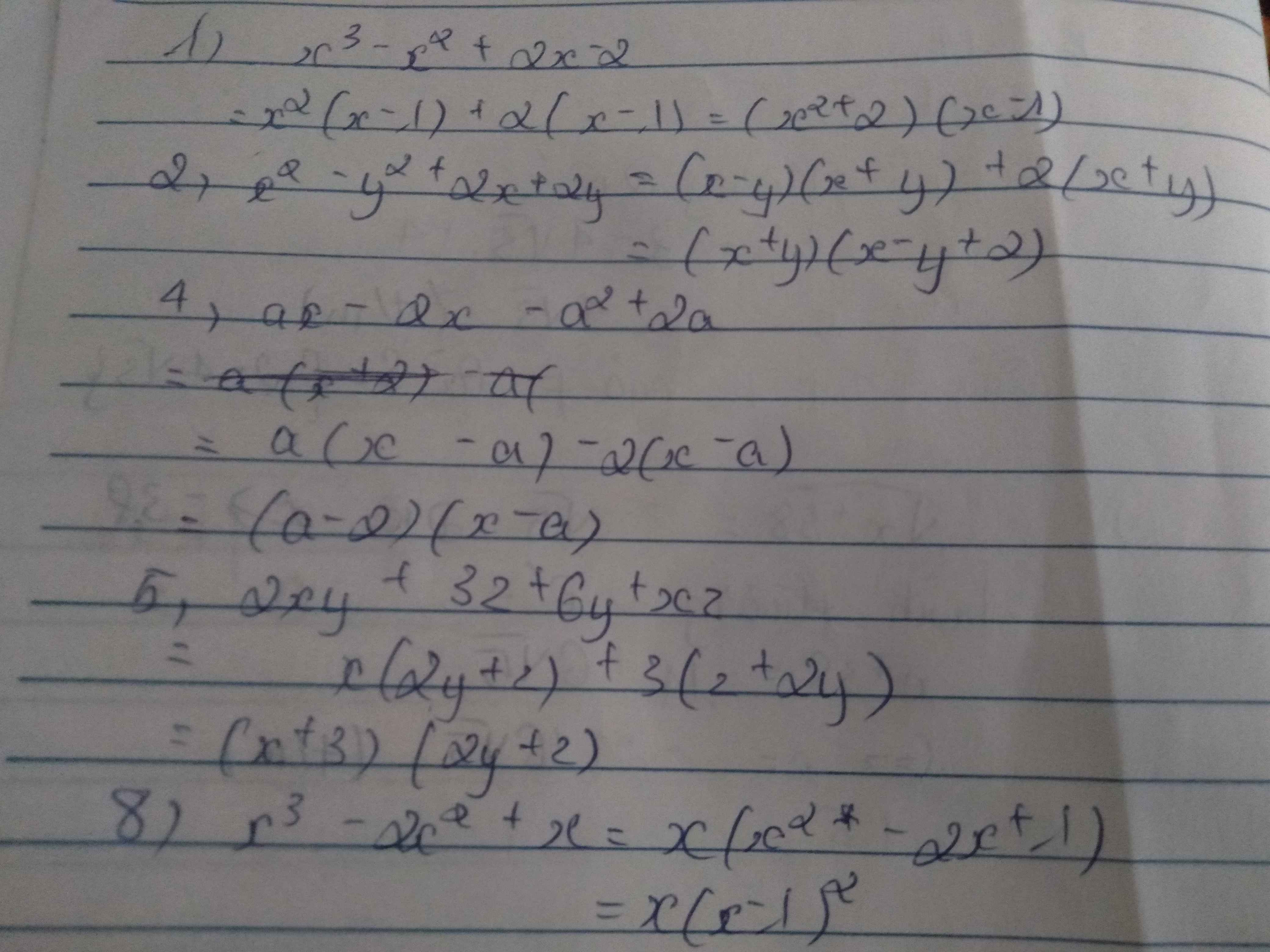
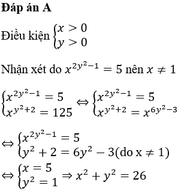
\(=\left(x^2+y^2-5\right)^2-4\left(xy+2\right)^2\\ =\left(x^2+y^2-5-2xy-4\right)\left(x^2+y^2-5+2xy+4\right)\\ =\left[\left(x-y\right)^2-9\right]\left[\left(x+y\right)^2-1\right]\\ =\left(x-y-3\right)\left(x-y+3\right)\left(x+y-1\right)\left(x+y+1\right)\)