Cho f(x)= log 5 ( sin x ) , x ∈ ( 0 ; π / 2 ) . Tính f'(x)
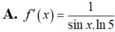
![]()
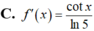
![]()
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

3.
\(f\left(x+\frac{\pi}{3}\right)=cos\left(x+\frac{\pi}{3}\right)\Rightarrow f'\left(x+\frac{\pi}{3}\right)=-sin\left(x+\frac{\pi}{3}\right)\)
\(f'\left(x-\frac{\pi}{6}\right)=-sin\left(x-\frac{\pi}{6}\right)\)
\(f'\left(0\right)=-sin\left(0\right)=0\)
\(2f'\left(x+\frac{\pi}{3}\right).f'\left(x-\frac{\pi}{6}\right)=2sin\left(x+\frac{\pi}{3}\right)sin\left(x-\frac{\pi}{6}\right)\)
\(=cos\left(\frac{\pi}{2}\right)-cos\left(2x+\frac{\pi}{6}\right)=-cos\left(2x+\frac{\pi}{6}\right)\)
\(f'\left(0\right)-f\left(2x+\frac{\pi}{6}\right)=0-cos\left(2x+\frac{\pi}{6}\right)=-cos\left(2x+\frac{\pi}{6}\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow2f'\left(x+\frac{\pi}{3}\right)f'\left(x-\frac{\pi}{6}\right)=f'\left(0\right)-f\left(2x+\frac{\pi}{6}\right)\) (đpcm)
4.
\(y=3\left(sin^4x+cos^4x\right)-2\left(sin^6x+cos^6x\right)\)
\(=3\left(sin^2x+cos^2x\right)^2-6sin^2x.cos^2x-2\left(sin^2x+cos^2x\right)^3+6sin^2x.cos^2x\left(sin^2x+cos^2x\right)\)
\(=3-2=1\)
\(\Rightarrow y'=0\) ; \(\forall x\)
5.
\(y=\left(\frac{sinx}{1+cosx}\right)^3=\left(\frac{sinx\left(1-cosx\right)}{1-cos^2x}\right)^3=\left(\frac{sinx\left(1-cosx\right)}{sin^2x}\right)^3=\left(\frac{1-cosx}{sinx}\right)^3\)
\(y'=3\left(\frac{1-cosx}{sinx}\right)^2\left(\frac{sin^2x-cosx\left(1-cosx\right)}{sin^2x}\right)=3\left(\frac{1-cosx}{sinx}\right)^2\left(\frac{1-cosx}{sin^2x}\right)=\frac{3\left(1-cosx\right)^3}{sin^4x}\)
\(\Rightarrow y'.sinx-3y=\frac{3\left(1-cosx\right)^3}{sin^3x}-3\left(\frac{1-cosx}{sinx}\right)^3=0\) (đpcm)

\(a,\left(0,3\right)^{x-3}=1\\ \Leftrightarrow x-3=0\\ \Leftrightarrow x=3\\ b,5^{3x-2}=25\\ \Leftrightarrow3x-2=2\\ \Leftrightarrow3x=4\\ \Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{4}{3}\\ c,9^{x-2}=243^{x+1}\\ \Leftrightarrow3^{2x-4}=3^{5x+5}\\ \Leftrightarrow2x-4=5x+5\\ \Leftrightarrow3x=-9\\ \Leftrightarrow x=-3\)
d, Điều kiện: \(x>-1;x\ne0\)
\(log_{\dfrac{1}{x}}\left(x+1\right)=-3\\ \Leftrightarrow x+1=x^3\\ x\simeq1,325\left(tm\right)\)
e, Điều kiện: \(x>\dfrac{5}{3}\)
\(log_5\left(3x-5\right)=log_5\left(2x+1\right)\\ \Leftrightarrow3x-5=2x+1\\ \Leftrightarrow x=6\left(tm\right)\)
f, Điều kiện: \(x>\dfrac{1}{2}\)
\(log_{\dfrac{1}{7}}\left(x+9\right)=log_{\dfrac{1}{7}}\left(2x-1\right)\\ \Leftrightarrow x+9=2x-1\\ \Leftrightarrow x=10\left(tm\right)\)

Giả sử \(f\left(x\right)\) có bậc k \(\Rightarrow f'\left(x\right)\) có bậc \(k-1\) và \(f''\left(x\right)\) có bậc \(k-2\)
\(\Rightarrow f''\left(x\right)+3x^2-5\) có bậc lớn nhất bằng \(max\left\{k-2;2\right\}\)
\(\Rightarrow k-1=max\left\{k-2;2\right\}\Rightarrow k-1=2\) (do \(k-1\ne k-2\) với mọi k)
\(\Rightarrow f\left(x\right)\) là đa thức bậc 3 có dạng: \(y=ax^3+bx^2+cx-5\) với \(a\ne0\)
\(3ax^2+2bx+c=6ax+2b+3x^2-5\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3ax^2+2bx+c=3x^2+6ax+2b-5\)
Đồng nhất 2 vế: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}3a=3\\2b=6a\\c=2b-5\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}a=1\\b=3\\c=1\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow f\left(x\right)=x^3+3x^2+x-5\)
Đặt \(sin^2x=t\Rightarrow0\le t\le1\)
\(f\left(t\right)=0\Leftrightarrow t^3+3t^2+t-5=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(t-1\right)\left(t^2+4t+5\right)=0\Rightarrow t=1\)
\(\Rightarrow sin^2x=1\Leftrightarrow cosx=0\)
\(\Rightarrow x=\frac{\pi}{2}+k\pi\)
\(\Rightarrow\frac{\pi}{2}+k\pi\le2020\Rightarrow k\le\frac{4040-\pi}{2\pi}\)
\(\Rightarrow k_{max}=642\Rightarrow x_{max}=\frac{\pi}{2}+642\pi\)

Chọn B.
Ta có: 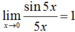 ; f(0) = a + 2.
; f(0) = a + 2.
Vậy để hàm số liên tục tại x = 0 thì a + 2 = 1 ⇔ a = -1.

a)
ĐK: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}2x-4>0\\x-1>0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow x>1\)
\(\log_5\left(2x-4\right)+\log_{\dfrac{1}{5}}\left(x-1\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\log_5\left(2x-4\right)-\log_5\left(x-1\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\log_5\left(\dfrac{2x-4}{x-1}\right)=\log_51\\ \Leftrightarrow\dfrac{2x-4}{x-1}=1\\ \Leftrightarrow2x-4=x-1\\ \Leftrightarrow x=3\left(tm\right)\)
Vậy x = 3.
b) ĐK: x > 0
\(\log_2x+\log_4x=3\\ \Leftrightarrow\log_2x+\dfrac{1}{2}\log_2x=3\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(1+\dfrac{1}{2}\right)\log_2x=3\\ \Leftrightarrow\dfrac{3}{2}\log_2x=3\\ \Leftrightarrow\log_2x=2\\ \Leftrightarrow x=4\left(tm\right)\)
Vậy x= 4

a) \({3^{{x^2} - 4x + 5}} = 9 \Leftrightarrow {x^2} - 4x + 5 = 2 \Leftrightarrow {x^2} - 4x + 3 = 0 \Leftrightarrow \left( {x - 3} \right)\left( {x - 1} \right) = 0\)
\( \Leftrightarrow \left[ \begin{array}{l}x = 3\\x = 1\end{array} \right.\)
Vậy phương trình có nghiệm là \(x \in \left\{ {1;3} \right\}\)
b) \(0,{5^{2x - 4}} = 4 \Leftrightarrow 2x - 4 = {\log _{0,5}}4 \Leftrightarrow 2x = 2 \Leftrightarrow x = 1\)
Vậy phương trình có nghiệm là x = 1
c) \({\log _3}(2x - 1) = 3\) ĐK: \(2x - 1 > 0 \Leftrightarrow x > \frac{1}{2}\)
\( \Leftrightarrow 2x - 1 = 27 \Leftrightarrow x = 14\) (TMĐK)
Vậy phương trình có nghiệm là x = 14
d) \(\log x + \log (x - 3) = 1\) ĐK: \(x - 3 > 0 \Leftrightarrow x > 3\)
\(\begin{array}{l} \Leftrightarrow \log \left( {x.\left( {x - 3} \right)} \right) = 1\\ \Leftrightarrow {x^2} - 3x = 10\\ \Leftrightarrow {x^2} - 3x - 10 = 0\\ \Leftrightarrow \left( {x + 2} \right)\left( {x - 5} \right) = 0\\ \Leftrightarrow \left[ \begin{array}{l}x = - 2 (loại) \,\,\,\\x = 5 (TMĐK) \,\,\,\,\,\,\,\end{array} \right.\end{array}\)
Vậy phương trình có nghiệm x = 5

tham khảo:
a)\(y'\left(x\right)=5\left(\dfrac{2x-1}{x+2}\right)^4.\dfrac{\left(x+2\right)\left(2\right)-\left(2x-1\right).1}{\left(x+2\right)^2}\)
\(=\dfrac{10\left(2x-1\right)\left(x+2\right)^3}{\left(x+2\right)^4}=\dfrac{20x-50}{\left(x+2\right)^4}\)
b)\(y'\left(x\right)=\dfrac{2\left(x^2+1\right)-2x\left(2x\right)}{\left(x^2+1\right)^2}\)\(=\dfrac{2\left(1-x^2\right)}{\left(x^2+1\right)^2}\)
c)\(y'\left(x\right)=e^x.2sinxcosx+e^xsin^2x.2cosx\)
\(=2e^xsinx\left(cosx+sinxcosx\right)\)
\(=2e^xsinxcos^2x\)
d)\(y'\left(x\right)=\dfrac{1}{x\sqrt{x}}.\left(+\dfrac{1}{2\sqrt{x}}\right)\)
\(=\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{x}\left(2\sqrt{x}+\sqrt{x}+2\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{x}\left(3\sqrt{x}+2\right)}\)

Đáp án B
Ta có log(x + 2y) = log x + log y
<=> log 2 (x+2y) = log 2xy
<=> 2 (x+2y) = 2xy (*).
Đ ặ t a = x > 0 b = 2 y > 0 , khi đó
* ⇔ 2 a + b = a b
và P = a 2 1 + b + b 2 1 + a ≥ a + b 2 a + b + 2
Lại có a b ≤ a + b 2 4 ⇒ 2 a + b ≤ a + b 2 4 ⇔ a + b ≥ 8 .
Đặt t = a + b, do đó
P ≥ f t = t 2 t + 2 .
X é t h à m s ố f t = t 2 t + 2 t r ê n [ 8 ; + ∞ )
c ó f ' t = t 2 + 2 t t + 2 2 > 0 ; ∀ ≥ 8
Suy ra f(t) là hàm số đồng biến trên [ 8 ; + ∞ )
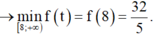
Vậy gía trị nhỏ nhất của biểu thức P là 32 5 .
Đáp án C