Cho hai số thực dương x, y thỏa mãn log 3 x = log 6 y = log 2 x + y . Biểu thức P = 1 x 2 + 1 y 2 có giá trị bằng
A. 27
B. 36
C. 18
D. 45
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

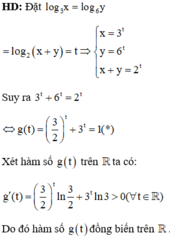
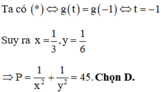

Đáp án B
Ta có log(x + 2y) = log x + log y
<=> log 2 (x+2y) = log 2xy
<=> 2 (x+2y) = 2xy (*).
Đ ặ t a = x > 0 b = 2 y > 0 , khi đó
* ⇔ 2 a + b = a b
và P = a 2 1 + b + b 2 1 + a ≥ a + b 2 a + b + 2
Lại có a b ≤ a + b 2 4 ⇒ 2 a + b ≤ a + b 2 4 ⇔ a + b ≥ 8 .
Đặt t = a + b, do đó
P ≥ f t = t 2 t + 2 .
X é t h à m s ố f t = t 2 t + 2 t r ê n [ 8 ; + ∞ )
c ó f ' t = t 2 + 2 t t + 2 2 > 0 ; ∀ ≥ 8
Suy ra f(t) là hàm số đồng biến trên [ 8 ; + ∞ )
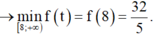
Vậy gía trị nhỏ nhất của biểu thức P là 32 5 .

Nếu một trong các số \(x+y-z;y+z-x;z+x-y\) bằng 0 thì cả 3 số đều bằng 0 và dẫn đến \(x=y=z=0\), mâu thuẫn
Từ giả thiết ta có : \(\begin{cases}x\log y\left(y+z-x\right)=y\log x\left(z+x-y\right)\\y\log z\left(z+x-y\right)=z\log y\left(x+y-z\right)\\z\log x\left(x+y-z\right)=x\log z\left(y+z-x\right)\end{cases}\)
Xét đẳng thức thứ nhất ta có :
\(x\log y\left(y+z-x\right)=y\log x\left(z+x-y\right)\Leftrightarrow x\log y=y\log x.\frac{z+x-y}{y+z-x}\) \(\Leftrightarrow x\log y+y\log x=y\log x\left(\frac{z+x-y}{y+z-x}+1\right)\Leftrightarrow x\log y+z\log x=y\log x\frac{2z}{y+z-x}\)
Biến đổi tương tự với đẳng thức thứ hai ta có :
\(y\log z+z\log y=z\log y\frac{2z}{z+z-y}\)
Ta thấy rằng : \(x^y.y^x=y^z.z^y\Leftrightarrow x\log y+y\log x=y\log z+z\log y\)
Do đó ta cần có :
\(y\log x\frac{2z}{y+z-x}=z\log y\frac{2z}{z+x-y}\Leftrightarrow y\log x\left(z+x-y\right)=x\log y\left(y+z-x\right)\), đúng
Do đó ta được : \(x^yy^x=y^z.z^y\)
Chứng minh tương tự ta có : \(y^zz^y=z^x.x^z\)
=> Điều phải chứng minh

\(log_xy=log_yx=\frac{1}{log_xy}\Rightarrow\left(log_xy\right)^2=1\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}log_xy=1\\log_xy=-1\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=y\\x=\frac{1}{y}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Do \(log_x\left(x-y\right)\) tồn tại \(\Rightarrow x-y\ne0\Rightarrow x\ne y\Rightarrow x=\frac{1}{y}\)
\(log_x\left(x-y\right)=log_y\left(x+1\right)\Leftrightarrow log_x\left(x-\frac{1}{x}\right)=-log_x\left(x+1\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow log_x\left[\left(x-\frac{1}{x}\right)\left(x+1\right)\right]=0\Leftrightarrow\left(x-\frac{1}{x}\right)\left(x+1\right)=1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x^2-1\right)\left(x+1\right)=x\Leftrightarrow x^3+x^2-2x-1=0\)
Pt này nghiệm xấu, đề bài có vấn đề

ĐKXĐ: \(x\ne y\)
\(log_xy=\frac{1}{log_xy}\Leftrightarrow log_x^2y=1\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}log_xy=1\\log_xy=-1\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=y\left(l\right)\\x=\frac{1}{y}\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(log_x\left(x-\frac{1}{x}\right)=log_{x^{-1}}\left(x+\frac{1}{x}\right)\Leftrightarrow log_x\left(x-\frac{1}{x}\right)=-log_x\left(x+\frac{1}{x}\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow log_x\left(x-\frac{1}{x}\right)\left(x+\frac{1}{x}\right)=0\Leftrightarrow\left(x-\frac{1}{x}\right)\left(x+\frac{1}{x}\right)=1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-\frac{1}{x^2}=1\Leftrightarrow x^4-x^2-1=0\Rightarrow x^2=\frac{1+\sqrt{5}}{2}\Rightarrow y^2=\frac{1}{x^2}=\frac{-1+\sqrt{5}}{2}\)
\(\Rightarrow x^2+xy+y^2=\frac{1+\sqrt{5}}{2}+1+\frac{-1+\sqrt{5}}{2}=\sqrt{5}+1\)