Cho x, y là các số thực dương thỏa mãn 2 ( x 2 + y 2 ) + x y = ( x + y ) ( x y + 2 ) Giá trị nhỏ nhất của biểu thức P = 4 ( x 3 y 3 + y 3 x 3 ) - 9 ( x 2 y 2 + y 2 x 2 )
A. - 25 4
B. 5
C. -13
D. - 23 4
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

Đáp án B.
Từ giả thiết, suy ra
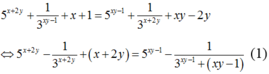
Xét hàm số f ( t ) = 5 t - 1 3 t + t trên ℝ .
Đạo hàm f ' ( t ) = 5 t . ln 5 - ln 3 3 t + 1 > 0 , ∀ t ∈ ℝ ⇒ hàm số f ( t ) luôn đồng biến trên ℝ .
Suy ra
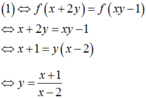
Do y > 0 nên x + 1 x - 2 > 0 ⇔ [ x > 2 x < - 1 . Mà x > 0 nên x > 2 .
Từ đó T = x + y = x + x + 1 x - 2 . Xét hàm số g ( x ) = x + x + 1 x - 2 trên 2 ; + ∞ .
Đạo hàm
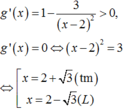
Lập bảng biến thiên của hàm số trên 2 ; + ∞ , ta thấy min g ( x ) = g ( 2 + 3 ) = 3 + 2 3 .
Vậy T m i n = 3 + 2 3 khi x = 2 + 3 và x = 1 + 3 .

Đáp án C.
Ta có:
G T ⇔ 5 x + 2 y + x + 2 y − 3 − x − 2 y = 5 x y − 1 − 3 1 − x y + x y − 1.
Xét hàm số
f t = 5 t + t − 3 − t ⇒ f t = 5 t ln 5 + 1 + 3 − t ln 3 > 0 ∀ t ∈ ℝ
Do đó hàm số đồng biến trên ℝ suy ra f x + 2 y = f x y − 1 ⇔ x + 2 y = x y − 1
⇔ x = 2 y + 1 y − 1 ⇒ T = 2 y + 1 y − 1 + y . Do x > 0 ⇒ y > 1
Ta có: T = 2 + y + 3 y − 1 = 3 + y − 1 + 3 y − 1 ≥ 3 + 2 3 .

Đáp án C.
Ta có: GT
<=> 5x+2y + x + 2y – 3–x–2y = 5xy–1 – 31–xy + xy – 1.
X é t h à m s ố f t = 5 t + t - 3 - t
⇒ f t = 5 t ln 5 + 1 + 3 - t ln 3 > 0 ∀ t ∈ ℝ
Do đó hàm số đồng biến trên ℝ suy ra
f(x+2y) = f(xy – 1) <=> x+ 2y = xy – 1
⇔ x = 2 y + 1 y - 1 ⇒ T = 2 y + 1 y - 1 + y .
Do x > 0 => y > 1.
Ta có:
T = 2 + y + 3 y - 1 = 3 + y - 1 + 3 y - 1 ≥ 3 + 2 3 .

\(P=\dfrac{x^2+y^2+6}{x+y}=\dfrac{x^2+y^2+2xy+4}{x+y}=\dfrac{\left(x+y\right)^2+4}{x+y}=x+y+\dfrac{4}{x+y}\)
\(P\ge2\sqrt{\left(x+y\right).\dfrac{4}{x+y}}=4\)
\(P_{min}=4\) khi \(x=y=1\)

\(T\ge\dfrac{\left(x+y+z\right)^2}{x+y+z+\sqrt{xy}+\sqrt{yz}+\sqrt{zx}}\ge\dfrac{\left(x+y+z\right)^2}{x+y+z+x+y+z}=\dfrac{x+y+z}{2}\ge\dfrac{2019}{2}\)
áp dụng BĐT:\(\dfrac{a^2}{x}+\dfrac{b^2}{y}+\dfrac{c^2}{z}\) với a,b,c,x,y,z là số dương
ta có BĐT Bunhiacopxki cho 3 bộ số:\(\left(\dfrac{a}{\sqrt{x}};\sqrt{x}\right);\left(\dfrac{b}{\sqrt{y}};\sqrt{y}\right);\left(\dfrac{c}{\sqrt{z}};\sqrt{z}\right)\)
ta có :
\(\dfrac{a^2}{x}+\dfrac{b^2}{y}+\dfrac{c^2}{z}\left(x+y+z\right)\)\(=\left[\left(\dfrac{a}{\sqrt{x}}\right)^2+\left(\dfrac{b}{\sqrt{y}}\right)^2+\left(\dfrac{c}{\sqrt{z}}\right)^2\right]\).\(\left[\left(\sqrt{x}\right)^2+\left(\sqrt{y}\right)^2+\left(\sqrt{z}\right)^2\right]\)\(\ge\left(\dfrac{a}{\sqrt{x}}.\sqrt{x}+\dfrac{b}{\sqrt{y}}.\sqrt{y}+\dfrac{c}{\sqrt{z}}.\sqrt{z}\right)^2=\left(a+b+c\right)^2\)
lúc đó ta có :\(\dfrac{a^2}{x}+\dfrac{b^2}{y}+\dfrac{c^2}{z}\ge\dfrac{\left(a+b+c\right)^2}{x+y+z}\)
ta có \(T=\dfrac{x^2}{x+\sqrt{yz}}+\dfrac{y^2}{y+\sqrt{zx}}+\dfrac{z^2}{z+\sqrt{xy}}\)\(\ge\dfrac{\left(x+y+z\right)^2}{x+\sqrt{yz}+y+\sqrt{zx}+z+\sqrt{xy}}\) mà ta có :
\(\sqrt{yz}+\sqrt{zx}+\sqrt{xy}\)\(\le\dfrac{x+y}{2}+\dfrac{x+z}{2}+\dfrac{z+y}{2}\)\(\Rightarrow\sqrt{yz}+\sqrt{zx}+\sqrt{xy}\le x+y+z\)
\(\Rightarrow T=\dfrac{2019}{2}\Leftrightarrow x=y=z=673\)
vậy \(\text{MinT}=\dfrac{2019}{2}\) khi và chỉ khi x=y=z=673

Đáp án B.
Từ giả thiết, suy ra 5 x + 2 y + 1 3 x y - 1 + x + 1 = 5 x y - 1 + 1 3 x + 2 y + x y - 2 y
⇔ 5 x + 2 y - 1 3 x + 2 y + x + 2 y = 5 x y - 1 - 1 3 x y - 1 + ( x y - 1 ) (1)
Xét hàm số f ( t ) = 5 t - 1 3 t + t trên ℝ .
Đạo hàm f ' ( t ) = 5 t . ln 5 + ln 3 3 t + 1 > 0 , ∀ t ∈ ℝ ⇒ hàm số f (t) luôn đồng biến trên ℝ .
Suy ra 1 ⇔ f ( x + 2 y ) = f ( x y - 1 ) ⇔ x + 2 y = x y - 1 ⇔ x + 1 = y ( x - 2 )
y = x + 1 x - 2
Do y > 0 nên x + 1 x - 2 > 0 ⇔ x > 2 x < - 1 . Mà x > 0 nên x > 2.
Từ đó T = x + y = x + x + 1 x - 2 . Xét hàm số g ( x ) = x + x + 1 x - 2 trên 2 ; + ∞ .
Đạo hàm g ' ( x ) = 1 - 3 x - 2 2 > 0 , g ' ( x ) = 0 ⇔ ( x - 2 ) 2 = 3
⇔ x = 2 + 3 ( t m ) x = 2 - 3 ( L ) . Lập bảng biến thiên của hàm số trên 2 ; + ∞ , ta thấy m i n g ( x ) = g ( 2 + 3 ) = 3 + 2 3 .
Vậy T m i n = 3 + 2 3 khi x = 2 + 3 và y = 1 + 3 .
Đáp án D
Cho x,y > 0 thỏa mãn 2 ( x 2 + y 2 ) + x y = ( x + y ) ( 2 + x y ) ⇔ 2 ( x + y ) 2 - ( 2 + x y ) ( x + y ) - 3 x y = 0 (*)
Đặt x + y = u x y = v ta đc PT bậc II: 2 u 2 - ( v + 2 ) u - 3 = 0 gải ra ta được u = v + 2 + v 2 + 28 v + 4 4
Ta có P = 4 ( x 3 y 3 + y 3 x 3 ) - 9 ( x 2 y 2 + y 2 x 2 ) = 4 ( x y + y x ) 3 - 9 ( x y + y x ) 2 - 12 ( x y + y x ) + 18 , đặt t = ( x y + y x ) , ( t ≥ 2 ) ⇒ P = 4 t 3 - 9 t 2 - 12 t + 18 ; P ' = 6 ( 2 t 2 - 3 t + 2 ) ≥ 0 với ∀ t ≥ 2 ⇒ M i n P = P ( t 0 ) trong đó t 0 = m i n t = m i n ( x y + y x ) với x,y thỏa mãn điều kiện (*).
Ta có :
t = ( x y + y x ) = ( x + y ) 2 x y - 2 = u 2 v - 2 = ( v + 2 + v 2 + 28 v + 4 ) 2 16 v - 2 = 1 16 ( v + 2 v + v + 4 v + 28 ) 2 - 2 ≥ 1 16 ( 2 2 + 32 ) 2 - 2 = 5 2
Vậy m i n P = P ( 5 2 ) = 4 . ( 5 2 ) 2 - 9 ( 5 2 ) 2 - 12 . 5 2 + 18 = - 23 4