x2-2(m-1)x-m+1=0
a)Giải phương trình khi m=-2
b)Tìm m để phương trình có 2 nghiệm x1,x2 thỏa mãn x12+x22+7x1x2=9
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

Sửa đề: \(x_1^2+x_2^2+2\left(x_1\cdot x_2\right)^2=7x_1x_2\)
Ta có: \(\Delta=2^2-4\cdot1\cdot\left(m-3\right)=4-4m+12=-4m+16\)
Để phương trình có hai nghiệm phân biệt thì \(\Delta>0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-4m+16>0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-4m>-16\)
hay m<4
Khi m<4, Áp dụng hệ thức Vi-et, ta có:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x_1+x_2=-2\\x_1\cdot x_2=m-3\end{matrix}\right.\)
Ta có: \(x_1^2+x_2^2+2\left(x_1\cdot x_2\right)^2=7x_1x_2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x_1+x_2\right)^2-2\cdot x_1\cdot x_2+2\left(x_1\cdot x_2\right)^2=7\cdot x_1\cdot x_2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(-2\right)^2-2\cdot\left(m-3\right)+2\cdot\left(m-3\right)^2=7\left(m-3\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4-2m+6+2\left(m^2-6m+9\right)=7m-21\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-2m+10+2m^2-12m+18-7m+21=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2m^2-21m+49=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2m^2-14m-7m+49=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2m\left(m-7\right)-7\left(m-7\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(m-7\right)\left(2m-7\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}m-7=0\\2m-7=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}m=7\left(loại\right)\\2m=7\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow m=\dfrac{7}{2}\left(nhận\right)\)
Vậy: Để phương trình có hai nghiệm phân biệt thỏa mãn \(x_1^2+x_2^2+2\left(x_1\cdot x_2\right)^2=7x_1x_2\) thì \(m=\dfrac{7}{2}\)
Ta có: x2 + 2x + m - 3 = 0
Theo hệ thực Vi-ét ta có:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x_1+x_2=-2\\x_1x_2=m-3\end{matrix}\right.\) (I)
Ta có: x12 + x22 + 2(x1x2)2 = 7x1x2
\(\Leftrightarrow\) (x1 + x2)2 - 2x1x2 + 2(x1x2)2 = 7x1x2 (*)
Thay (I) vào (*) ta được:
(-2)2 - 2(m - 3) + 2(m - 3)2 = 7(m - 3)
\(\Leftrightarrow\) 4 - 9m + 27 + 2(m2 - 6m + 9) = 0
\(\Leftrightarrow\) 31 - 9m + 2m2 - 12m + 18 = 0
\(\Leftrightarrow\) 2m2 - 21m + 49 = 0
\(\Leftrightarrow\) \(\left[{}\begin{matrix}m=7\\m=3,5\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy ...
Chúc bn học tốt!

Lời giải:
Để PT có 2 nghiệm $x_1,x_2$ thì:
$\Delta'=(m+1)^2-(m^2-1)>0\Leftrightarrow 2m+2>0\Leftrightarrow m>-1$
Áp dụng định lý Viet:
$x_1+x_2=2(m+1)$ và $x_1x_2=m^2-1$
Khi đó, để $x_1^2+x_2^2=x_1x_2+8$
$\Leftrightarrow (x_1+x_2)^2-2x_1x_2=x_1x_2+8$
$\Leftrightarrow (x_1+x_2)^2=3x_1x_2+8$
$\Leftrightarrow 4(m+1)^2=3(m^2-1)+8$
$\Leftrightarrow m^2+8m-1=0$
$\Leftrightarrow m=-4\pm \sqrt{17}$. Vì $m>-1$ nên $m=-4+\sqrt{17}$

a) Với m= 2, ta có phương trình: x 2 + 2 x − 3 = 0
Ta có: a + b + c = 1 + 2 − 3 = 0
Theo định lý Viet, phương trình có 2 nghiệm:
x 1 = 1 ; x 2 = − 3 ⇒ S = 1 ; − 3 .
b) Chứng minh rằng phương trình luôn có nghiệm ∀ m .
Ta có: Δ ' = m − 1 2 − 1 + 2 m = m 2 ≥ 0 ; ∀ m
Vậy phương trình luôn có nghiệm ∀ m .
c) Theo định lý Viet, ta có: x 1 + x 2 = − 2 m + 2 x 1 . x 2 = 1 − 2 m
Ta có:
x 1 2 . x 2 + x 1 . x 2 2 = 2 x 1 . x 2 + 3 ⇔ x 1 . x 2 x 1 + x 2 − 2 = 6 ⇒ 1 − 2 m − 2 m + 2 − 2 = 6 ⇔ 2 m 2 − m − 3 = 0
Ta có: a − b + c = 2 + 1 − 3 = 0 ⇒ m 1 = − 1 ; m 2 = 3 2
Vậy m= -1 hoặc m= 3/2

a. Em tự giải
b.
\(\Delta'=\left(m-1\right)^2-\left(m^2-6\right)=-2m+7\)
Pt đã cho có 2 nghiệm khi: \(-2m+7\ge0\Rightarrow m\le\dfrac{7}{2}\)
Khi đó theo hệ thức Viet: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x_1+x_2=2\left(m-1\right)\\x_1x_2=m^2-6\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(x_1^2+x_2^2=16\Leftrightarrow\left(x_1+x_2\right)^2-2x_1x_2=16\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4\left(m-1\right)^2-2\left(m^2-6\right)=16\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2m^2-8m=0\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}m=0\\m=4>\dfrac{7}{2}\left(loại\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy \(m=0\)

Δ=(m+1)^2-4(2m-8)
=m^2+2m+1-8m+32
=m^2-6m+33
=(m-3)^2+24>=24
=>Phương trình luôn có hai nghiệm pb
x1^2+x2^2+(x1-2)(x2-2)=11
=>(x1+x2)^2-2x1x2+x1x2-2(x1+x2)+4=11
=>(m+1)^2-(2m-8)-2(m+1)+4=11
=>m^2+2m+1-2m+8-2m-2-7=0
=>m^2-2m-8=0
=>(m-4)(m+2)=0
=>m=4 hoặc m=-2

b) Gọi x 1 ; x 2 lần lượt là 2 nghiệm của phương trình đã cho
Theo hệ thức Vi-et ta có:
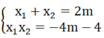
x 1 2 + x 2 2 - x 1 x 2 = x 1 + x 2 2 - 3x1 x2 = 4 m 2 + 3(4m + 4)
Theo bài ra: x 1 2 + x 2 2 - x 1 x 2 =13
⇒ 4m2 + 3(4m + 4) = 13 ⇔ 4m2 + 12m - 1 = 0
∆ m = 122 -4.4.(-1) = 160 ⇒ ∆ m = 4 10
Phương trình có 2 nghiệm phân biệt
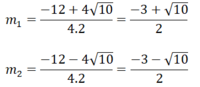
Vậy với 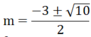 thì phương trình có 2 nghiệm
x
1
;
x
2
thỏa mãn điều kiện
x
1
2
+
x
2
2
-
x
1
x
2
= 13
thì phương trình có 2 nghiệm
x
1
;
x
2
thỏa mãn điều kiện
x
1
2
+
x
2
2
-
x
1
x
2
= 13

b, Để phương trình có 2 nghiệm \(\Delta\ge0\)
hay \(\left(2m+8\right)^2-4.m^2=4m^2+32m+64-4m^2=32m+64\ge0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow32m\ge64\Leftrightarrow m\ge2\)
Theo Vi et ta có : \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x_1+x_2=-\dfrac{b}{a}=2m+8\\x_1x_2=\dfrac{c}{a}=m^2\end{matrix}\right.\)
mà \(\left(x_1+x_2\right)^2=4m^2+32m+64\Rightarrow x_1^2+x_2^2=4m^2+32m+64-2x_1x_2\)
\(=4m^2+32m+64-2m^2=2m^2+32m+64\)
Lại có : \(x_1^2+x_2^2=-2\)hay \(2m^2+32m+66=0\Leftrightarrow m=-8+\sqrt{31}\left(ktm\right);m=-8-\sqrt{31}\left(ktm\right)\)
a) Thay m=8 vào phương trình, ta được:
\(x^2-2\cdot\left(8+4\right)x+8^2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-24x+64=0\)
\(\text{Δ}=\left(-24\right)^2-4\cdot1\cdot64=576-256=320\)
Vì Δ>0 nên phương trình có hai nghiệm phân biệt là:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x_1=\dfrac{24+8\sqrt{5}}{2}=12+4\sqrt{5}\\x_2=\dfrac{24-8\sqrt{5}}{2}=12-4\sqrt{5}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy: Khi m=8 thì phương trình có hai nghiệm phân biệt là \(x_1=12+4\sqrt{5};x_2=12-4\sqrt{5}\)
a, Thay m = -2 ta được :
x^2 + 6x + 3 = 0
\(\Leftrightarrow x=-3+\sqrt{6};x=-3-\sqrt{6}\)
b, Để pt có 2 nghiệm
\(\Delta'=\left(m-1\right)^2-\left(-m+1\right)=m^2-2m+1+m-1=m^2-m\)> 0
Theo Viet : \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x_1+x_2=2m-2\\x_1x_2=-m+1\end{matrix}\right.\)
Ta có : \(\left(x_1+x_2\right)^2+5x_1x_2=9\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4\left(m-1\right)^2+5\left(-m+1\right)=9\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4m^2-8m+4-5m+5=9\Leftrightarrow4m^2-13m=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow m\left(4m-13\right)=0\Leftrightarrow m=0\left(ktm\right);m=\dfrac{13}{4}\)(tm)
a, Thay m=-2 vào pt ta có:
\(x^2-2\left(m-1\right)x-m+1=0\\ \Leftrightarrow x^2-2\left(-2-1\right)x-\left(-2\right)+1=0\\ \Leftrightarrow x^2+6x+3=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(x^2+6x+9\right)-6=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(x+3\right)^2-\sqrt{6^2}=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(x+3-\sqrt{6}\right)\left(x+3+\sqrt{6}\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-3+\sqrt{6}\\x=-3-\sqrt{6}\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(b,\Delta'=\left[-\left(m-1\right)\right]^2-\left(-m+1\right)\\ =m^2-2m+1+m-1\\ =m^2-m\)
Để pt có 2 nghiệm thì \(\) \(\Delta'\ge0\Leftrightarrow m^2-m\ge0\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}m\ge1\\m\le0\end{matrix}\right.\)
Theo Vi-ét:\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x_1+x_2=2m-2\\x_1x_2=-m+1\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(x_1^2+x_2^2+7x_1x_2=9\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(x_1+x_2\right)^2+5x_1x_2=9\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(2m-2\right)^2+5\left(-m+1\right)=9\\ \Leftrightarrow4m^2-8m+4-5m+5-9=0\\ \Leftrightarrow4m^2-13m=0\\ \Leftrightarrow m\left(4m-13\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}m=0\left(tm\right)\\m=\dfrac{13}{4}\left(tm\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)