3/2 + 9/2:x = 1/5
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


a: =91/105+60/105-101/105
=50/105=10/21
c: \(\dfrac{3}{4}\cdot\dfrac{5}{2}\cdot\dfrac{7}{6}=\dfrac{3}{6}\cdot\dfrac{7}{2}\cdot\dfrac{5}{4}=\dfrac{1}{2}\cdot\dfrac{7}{2}\cdot\dfrac{5}{4}=\dfrac{35}{16}\)
d: =2-2/9
=18/9-2/9
=16/9
e: =24/36-9/36+8/36
=23/36
g: =5/2+1/2
=3


`@` `\text {Ans}`
`\downarrow`
`1)`
\(x+\dfrac{1}{2}=\dfrac{5}{3}\)
`\Rightarrow` \(x=\dfrac{5}{3}-\dfrac{1}{2}\)
`\Rightarrow`\(x=\dfrac{7}{6}\)
Vậy, `x =`\(\dfrac{7}{6}\)
`2)`
\(\dfrac{3}{5}-x=\dfrac{1}{3}\)
`\Rightarrow`\(x=\dfrac{3}{5}-\dfrac{1}{3}\)
`\Rightarrow`\(x=\dfrac{4}{15}\)
Vậy, `x =`\(\dfrac{4}{15}\)
`3)`
\(\dfrac{3}{4}+x=\dfrac{7}{2}\)
`\Rightarrow`\(x=\dfrac{7}{2}-\dfrac{3}{4}\)
`\Rightarrow`\(x=\dfrac{11}{4}\)
Vậy, \(x=\dfrac{11}{4}\)
`4)`
\(x-\dfrac{4}{3}=\dfrac{7}{9}\)
`\Rightarrow`\(x=\dfrac{7}{9}+\dfrac{4}{3}\)
`\Rightarrow`\(x=\dfrac{19}{9}\)
Vậy, `x=`\(\dfrac{19}{9}\)
`5)`
\(x-\dfrac{5}{6}=\dfrac{7}{3}\)
`\Rightarrow`\(x=\dfrac{7}{3}+\dfrac{5}{6}\)
`\Rightarrow x =`\(\dfrac{19}{6}\)
Vậy, `x=`\(\dfrac{19}{6}\)
`6)`
\(x-\dfrac{1}{5}=\dfrac{9}{10}\)
`\Rightarrow x=`\(\dfrac{9}{10}+\dfrac{1}{5}\)
`\Rightarrow x=`\(\dfrac{11}{10}\)
Vậy, `x=`\(\dfrac{11}{10}\)

\(1,\\ x+\dfrac{1}{2}=-\dfrac{5}{3}\\ x=-\dfrac{5}{3}-\dfrac{1}{2}\\ x=-\dfrac{13}{6}\\ Vậyx=-\dfrac{13}{6}\)
\(2,\\ \dfrac{1}{3}-x=\dfrac{3}{5}\\ x=\dfrac{1}{3}-\dfrac{3}{5}\\ x=-\dfrac{4}{15}\\ Vậyx=-\dfrac{4}{15}\)
\(3,\\ 3-4+x=\dfrac{7}{2}\\ -1+x=\dfrac{7}{2}\\ x=\dfrac{7}{2}+1\\ x=\dfrac{9}{2}\\ Vậyx=\dfrac{9}{2}\)
\(4,\\ x-\dfrac{4}{3}=-\dfrac{7}{9}\\ x=-\dfrac{7}{9}+\dfrac{4}{3}\\ x=\dfrac{15}{27}\\ Vậyx=\dfrac{15}{27}\)
\(5,\\ x-\left(-\dfrac{7}{3}\right)=\dfrac{5}{6}\\ x=\dfrac{5}{6}-\dfrac{7}{3}\\ x=-\dfrac{27}{18}\\ Vậyx=-\dfrac{27}{18}\)
\(6,\\ x-\dfrac{1}{5}=\dfrac{9}{10}\\ x=\dfrac{9}{10}+\dfrac{1}{5}\\ x=\dfrac{11}{10}\\ Vậyx=\dfrac{11}{10}\)
\(7,\\ x+\dfrac{5}{12}=\dfrac{3}{8}\\ x=\dfrac{3}{8}-\dfrac{5}{12}\\ x=-\dfrac{1}{24}\\ Vậyx=-\dfrac{1}{24}\)
\(8,\\ x+\dfrac{5}{4}=\dfrac{7}{6}\\ x=\dfrac{7}{6}-\dfrac{5}{4}\\ x=-\dfrac{9}{24}\\ Vậyx=-\dfrac{9}{24}\)
\(9,\\ x-\dfrac{2}{7}=\dfrac{1}{35}\\ x=\dfrac{1}{35}+\dfrac{2}{7}\\ x=\dfrac{11}{35}\\ Vậyx=\dfrac{11}{35}\\ 10,\\ x-\dfrac{1}{5}=-\dfrac{7}{10}\\ x=-\dfrac{7}{10}+\dfrac{1}{5}\\ x=-\dfrac{1}{2}\\ Vậyx=-\dfrac{1}{2}\)
ahiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiiii hãy ấn a

Let's solve each equation step by step:
√(x^2 - 6x + 9) = 3 - xSquaring both sides of the equation, we get:
x^2 - 6x + 9 = (3 - x)^2
x^2 - 6x + 9 = 9 - 6x + x^2
The x^2 terms cancel out, and we are left with:
-6x = -6x
This equation is true for any value of x. Therefore, there are infinitely many solutions.
x^2 - (1/2)x + 1/16 = x + 3/2Moving all terms to one side of the equation, we get:
x^2 - (1/2)x - x + 3/2 - 1/16 = 0
x^2 - (3/2)x + 29/16 = 0
To solve this quadratic equation, we can use the quadratic formula:
x = (-b ± √(b^2 - 4ac)) / (2a)
In this case, a = 1, b = -3/2, and c = 29/16. Plugging in these values, we get:
x = (3/2 ± √((-3/2)^2 - 4(1)(29/16))) / (2(1))
x = (3/2 ± √(9/4 - 29/4)) / 2
x = (3/2 ± √(-20/4)) / 2
x = (3/2 ± √(-5)) / 2
Since the square root of a negative number is not a real number, this equation has no real solutions.
√(x - 2)√(x - 1) = √(x - 1) - 1Squaring both sides of the equation, we get:
(x - 2)(x - 1) = (x - 1) - 2√(x - 1) + 1
x^2 - 3x + 2 = x - 1 - 2√(x - 1) + 1
x^2 - 4x + 2 = -2√(x - 1)
Squaring both sides again, we get:
(x^2 - 4x + 2)^2 = (-2√(x - 1))^2
x^4 - 8x^3 + 20x^2 - 16x + 4 = 4(x - 1)
x^4 - 8x^3 + 20x^2 - 16x + 4 = 4x - 4
Rearranging terms, we have:
x^4 - 8x^3 + 20x^2 - 20x + 8 = 0
This equation does not have a simple solution and requires further calculations or approximation methods to find the solutions.
√9 - 4√5 - √5 = -2Simplifying the left side of the equation, we get:
3 - 4√5 - √5 = -2
-√5 - 5 = -2
-√5 = 3
This equation is not true since the square root of a number cannot be negative.
Therefore, the given equations either have infinitely many solutions or no real solutions.

a: x*3/4=1/5
=>x=1/5:3/4=1/5*4/3=4/15
b: x*3/7=2/5
=>x=2/5:3/7=2/5*7/3=14/15
c: 1/3+2/9=2/12x
=>1/6x=3/9+2/9=5/9
=>x=5/9*6=30/9=10/3
d: 4/15*x-2/3=1/5
=>4/15*x=2/3+1/5=10/15+3/15=13/15
=>4x=13
=>x=13/4
e: x:1/7=2/3
=>x=2/3*1/7=2/21
f: 1/9:x=7/3
=>x=1/9:7/3=1/9*3/7=3/63=1/21
j: 1/4+5/12=8/3:x
=>8/3:x=3/12+5/12=8/12=2/3
=>x=4
h: =>7/4:x=1/5+1/2=7/10
=>x=7/4:7/10=10/4=5/2
thankkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkk

a) x - 3/2 = 4/3
x = 4/3 + 3/2
x = 8/6 + 9/6 = 17/6
b) 2/5 * x = 1/3
x = 1/3 : 2/5
x = 1/3 x 5/2 = 5/6
c) x - 4/9 = 3/7 : 9/14
x - 4/9 = 2/3
x = 2/3 + 4/9
x = 6/9 + 4/9 = 10/9
d) 3/5 * x - 1/2 = 1/5
3/5 * x = 1/5 + 1/2 = 7/10
x = 7/10 : 3/5
x = 7/10 * 5/3 = 7/6
a/\(x-\dfrac{3}{2}=\dfrac{4}{3}\)
\(x=\dfrac{4}{3}+\dfrac{3}{2}\)
\(x=\dfrac{17}{6}\)
b/\(\dfrac{2}{5}\times x=\dfrac{1}{3}\)
\(x=\dfrac{1}{3}:\dfrac{2}{5}\)
\(x=\dfrac{5}{6}\)
c/\(x-\dfrac{4}{9}=\dfrac{3}{7}:\dfrac{9}{14}\)
\(x-\dfrac{4}{9}=\dfrac{2}{3}\)
\(x=\dfrac{2}{3}+\dfrac{4}{9}\)
\(x=\dfrac{10}{9}\)
d/\(\dfrac{3}{5}\times x-\dfrac{1}{2}=\dfrac{1}{5}\)
\(\dfrac{3}{5}\times x=\dfrac{1}{5}+\dfrac{1}{2}\)
\(\dfrac{3}{5}\times x=\dfrac{7}{10}\)
\(x=\dfrac{7}{10}:\dfrac{3}{5}\)
\(x=\dfrac{7}{6}\)

\(a,\frac{1}{2}+\frac{3}{4}x=\frac{1}{4}\)
\(\Rightarrow\frac{3}{4}x=\frac{1}{4}-\frac{1}{2}=-\frac{1}{4}\)
\(\Rightarrow x=-\frac{1}{3}\)
Bạn Hồng có một tờ bìa hình chữ nhật có chiều rộng 1/5 m và chiều dài 1/4 m . bạn Hồng muốn cắt từ tấm bìa đó thành một hình chữ nhật có diện tích bằng một nửa diện tích tấm bìa và độ dài một cạnh là 1/4 m để làm hộp đồ chơi.
a) tính diện tích hình chữ nhật bạn Hồng đã cắt
b) bạn Hồng có thể cắt như thế nào ? Vẽ hình minh họa

1) ĐKXĐ: \(x\notin\left\{1;-1\right\}\)
Ta có: \(\dfrac{x+1}{x-1}-\dfrac{x-1}{x+1}=\dfrac{4}{x^2-1}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{\left(x+1\right)^2}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)}-\dfrac{\left(x-1\right)^2}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)}=\dfrac{4}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)}\)
Suy ra: \(x^2+2x+1-\left(x^2-2x+1\right)=4\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2+2x+1-x^2+2x-1=4\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4x=4\)
hay x=1(loại)
Vậy: \(S=\varnothing\)
2) ĐKXĐ: \(x\notin\left\{2;-2\right\}\)
Ta có: \(\dfrac{x+2}{x-2}+\dfrac{x}{x+2}=2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{\left(x+2\right)^2}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)}+\dfrac{x\left(x-2\right)}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)}=\dfrac{2\left(x^2-4\right)}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)}\)
Suy ra: \(x^2+4x+4+x^2-2x=2x^2-8\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x^2+2x+4-2x^2-8=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x-4=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x=4\)
hay x=2(loại)
Vậy: \(S=\varnothing\)

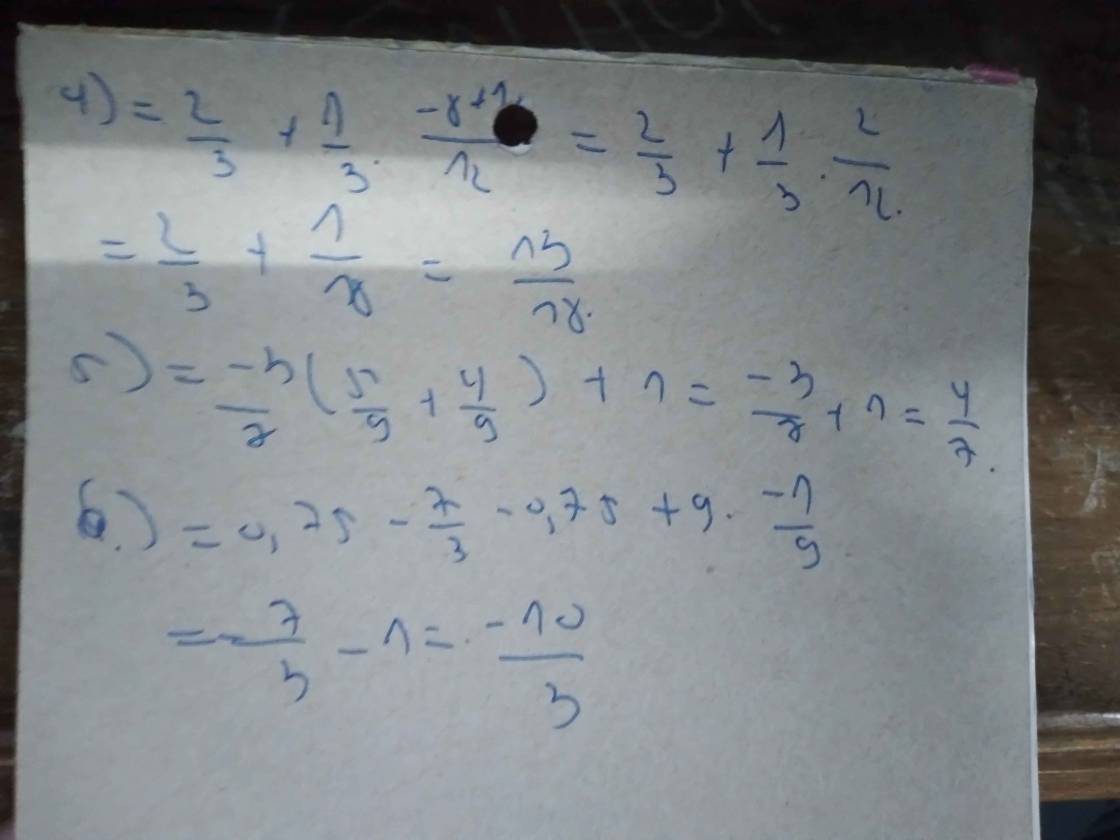
\(\dfrac{3}{2}+\dfrac{9}{2}:x=\dfrac{1}{5}\)
\(\dfrac{9}{2}:x=\dfrac{1}{5}-\dfrac{3}{2}\)
\(\dfrac{9}{2}:x=-\dfrac{13}{10}\)
\(x=\dfrac{9}{2}:\dfrac{-13}{10}\)
\(x=\dfrac{45}{-13}\)