Điều kiện xác định của biểu thức 1/4 x mũ 2 trừ 1 là
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


a) ĐKXĐ: \(x\notin\left\{1;-1\right\}\)
b) Ta có: \(P=\dfrac{2}{x^4-1}-\dfrac{1}{1-x^2}\)
\(=\dfrac{2}{\left(x^2-1\right)\left(x^2+1\right)}+\dfrac{1}{x^2-1}\)
\(=\dfrac{2+x^2-1}{\left(x^2-1\right)\left(x^2+1\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{x^2+1}{\left(x^2-1\right)\left(x^2+1\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{1}{x^2-1}\)

ĐKXĐ: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x\ge\dfrac{1}{2}\\x\ne1\end{matrix}\right.\)

a: ĐKXĐ: \(x\notin\left\{-2;-5\right\}\)
b: ĐKXĐ: \(x\notin\left\{2;-2\right\}\)

Lời giải:
ĐKXĐ: \(\left\{\begin{matrix}
x^2-2x+1\neq 0\\
\frac{1}{x^2-2x+1}\geq 0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow x^2-2x+1>0\)
$\Leftrightarrow (x-1)^2>0$
$\Leftrightarrow x-1\neq 0$
$\Leftrightarrow x\neq 1$

\(P=\dfrac{\dfrac{x}{x-2}-\dfrac{x-2}{x+2}}{\dfrac{1}{x^2-4}}\)
a)
Để giá trị của biểu thức P được xác định, thì :
\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-2\ne0\\x+2\ne0\\x^2-4\ne0\end{matrix}\right.\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x\ne2\\x\ne-2\\x\ne-2;2\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy ĐKXĐ của biểu thức P là : \(x\ne\left\{2;-2\right\}\)
b)
\(P=\dfrac{\dfrac{x}{x-2}-\dfrac{x-2}{x+2}}{\dfrac{1}{x^2-4}}=\left(\dfrac{x}{x-2}-\dfrac{x-2}{x+2}\right):\dfrac{1}{x^2-4}=\left(\dfrac{x\left(x+2\right)-\left(x-2\right)\left(x-2\right)}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)}\right).\dfrac{x^2-4}{1}\)
\(=\dfrac{x^2+2x-x^2+2x-4}{x^2-4}.\dfrac{x^2-4}{1}=\dfrac{4x-4}{x^2-4}.\dfrac{x^2-4}{1}=4x-4\)
c)
Để :
\(P=0\Rightarrow4x-4=0\)
\(\Rightarrow4\left(x-1\right)=0\)
\(\Rightarrow x-1=0\)
\(\Rightarrow x=1\)
Vậy.....

Câu 6:
ĐKXĐ: \(x\ne-\dfrac{1}{3}\)
Để \(\dfrac{9x+4}{3x+1}\in Z\) thì \(9x+4⋮3x+1\)
=>\(9x+3+1⋮3x+1\)
=>\(1⋮3x+1\)
=>\(3x+1\in\left\{1;-1\right\}\)
=>\(3x\in\left\{0;-2\right\}\)
=>\(x\in\left\{0;-\dfrac{2}{3}\right\}\)
mà x nguyên
nên x=0
Câu 2:
a: ĐKXĐ: \(x\notin\left\{2;-2;0\right\}\)
b: \(A=\left(\dfrac{1}{x+2}-\dfrac{2x}{4-x^2}+\dfrac{1}{x-2}\right)\cdot\dfrac{x^2-4x+4}{4x}\)
\(=\left(\dfrac{1}{x+2}+\dfrac{2x}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)}+\dfrac{1}{x-2}\right)\cdot\dfrac{\left(x-2\right)^2}{4x}\)
\(=\dfrac{x-2+2x+x+2}{\left(x+2\right)\left(x-2\right)}\cdot\dfrac{\left(x-2\right)^2}{4x}\)
\(=\dfrac{4x\left(x-2\right)}{4x\left(x+2\right)}=\dfrac{x-2}{x+2}\)

\(\dfrac{x+1}{\sqrt{x+2}-1}=3\left(đk:x\ge-2;x\ne-1\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{\left(x+1\right)\left(\sqrt{x+2}+1\right)}{\left(\sqrt{x+2}\right)^2-1}=3\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{\left(x+1\right)\left(\sqrt{x+2}+1\right)}{x+1}=3\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\sqrt{x+2}+1=3\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x+2=4\) \(\Leftrightarrow x=2\) (tm)
Vậy x=2
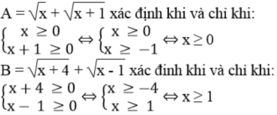
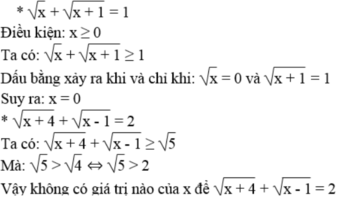
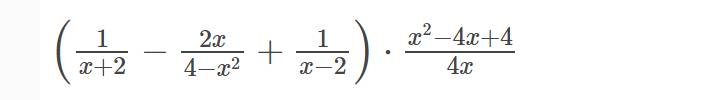
ĐKXĐ: \(4x^2-1\ne0\)
=>\(x^2\ne\dfrac{1}{4}\)
=>\(x\notin\left\{\dfrac{1}{2};-\dfrac{1}{2}\right\}\)