 Cần gấp mng oi
Cần gấp mng oi
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


g: \(=\dfrac{x^2+2x-x^2-4x-2x+4}{x\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)}=\dfrac{-4x+4}{x\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)}\)
h: \(=\dfrac{2x^2+1-x^2+1-x^2+x-1}{\left(x+1\right)\left(x^2-x+1\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{x+1}{\left(x+1\right)\left(x^2-x+1\right)}=\dfrac{1}{x^2-x+1}\)
\(e,=\dfrac{1}{x-1}-\dfrac{2x}{\left(x^2+1\right)\left(x-1\right)}=\dfrac{x^2-2x+1}{\left(x^2+1\right)\left(x-1\right)}=\dfrac{\left(x-1\right)^2}{\left(x^2+1\right)\left(x-1\right)}=\dfrac{x-1}{x^2+1}\\ f,=\dfrac{3x-1}{2\left(3x+1\right)}+\dfrac{3x+1}{2\left(3x-1\right)}-\dfrac{6x}{\left(3x-1\right)\left(3x+1\right)}\\ =\dfrac{9x^2-6x+1+9x^2+6x+1-12x}{2\left(3x-1\right)\left(3x+1\right)}=\dfrac{2\left(3x-1\right)^2}{2\left(3x-1\right)\left(3x+1\right)}=\dfrac{3x-1}{3x+1}\)
\(g,=\dfrac{x}{x\left(x-2\right)}-\dfrac{x^2+4x}{x\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)}-\dfrac{2}{x\left(x+2\right)}\\ =\dfrac{x^2+2x-x^2-4x-2x+4}{x\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)}=\dfrac{-4x+4}{x\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)}\\ h,=\dfrac{2x^2+1-x^2+1-x^2+x-1}{\left(x+1\right)\left(x^2-x+1\right)}=\dfrac{x+1}{\left(x+1\right)\left(x^2-x+1\right)}=\dfrac{1}{x^2-x+1}\)

2:
a: Xét tứ giác DIHK có
\(\widehat{DIH}=\widehat{DKH}=\widehat{IDK}=90^0\)
Do đó: DIHK là hình chữ nhật
Suy ra: DH=KI(1)
Xét ΔDEF vuông tại D có DH là đường cao ứng với cạnh huyền EF
nên \(DH^2=HE\cdot HF\left(2\right)\)
Từ (1) và (2) suy ra \(IK^2=HE\cdot HF\)


a.\(A=\dfrac{1}{x-1}-\dfrac{x^2+x}{x^2+1}.\left(\dfrac{1}{x-1}-\dfrac{1}{x+1}\right)\);\(ĐK:x\ne\pm1\)
\(A=\dfrac{1}{x-1}-\dfrac{x\left(x+1\right)}{x^2+1}.\left(\dfrac{x+1-x+1}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)}\right)\)
\(A=\dfrac{1}{\left(x-1\right)}-\dfrac{2x\left(x+1\right)}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)\left(x^2+1\right)}\)
\(A=\dfrac{1}{x-1}-\dfrac{2x}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x^2+1\right)}\)
\(A=\dfrac{x^2+1-2x}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x^2+1\right)}\)
\(A=\dfrac{\left(x-1\right)^2}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x^2+1\right)}\)
\(A=\dfrac{x-1}{x^2+1}\)
b.\(A=0,2=\dfrac{1}{5}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{x-1}{x^2+1}=\dfrac{1}{5}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2+1=5x-5\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-5x+6=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=3\\x=2\end{matrix}\right.\)
c.\(A< 0\) mà \(x^2+1\ge1>0\)
--> A<0 khi \(x-1< 0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x< 1\)
a. -ĐKXĐ:\(x\ne\pm1\)
\(A=\dfrac{1}{x-1}-\dfrac{x^2+x}{x^2+1}.\left(\dfrac{1}{x-1}-\dfrac{1}{x+1}\right)\)
\(=\dfrac{1}{x-1}-\dfrac{x\left(x+1\right)}{x^2+1}.\left(\dfrac{x+1}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)}-\dfrac{x-1}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)}\right)\)
\(=\dfrac{1}{x-1}-\dfrac{x\left(x+1\right)}{x^2+1}.\dfrac{x+1-x+1}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{1}{x-1}-\dfrac{x\left(x+1\right)}{x^2+1}.\dfrac{2}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{1}{x-1}-\dfrac{2x}{\left(x^2+1\right)\left(x-1\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{x^2+1}{\left(x^2+1\right)\left(x-1\right)}-\dfrac{2x}{\left(x^2+1\right)\left(x-1\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{\left(x-1\right)^2}{\left(x^2+1\right)\left(x-1\right)}=\dfrac{x-1}{x^2+1}\)
b. \(A=\dfrac{x-1}{x^2+1}=0,2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{x-1}{x^2+1}=\dfrac{1}{5}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{5\left(x-1\right)}{5\left(x^2+1\right)}=\dfrac{x^2+1}{5\left(x^2+1\right)}\)
\(\Rightarrow5x-5=x^2+1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-5x+1+5=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-5x+6=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-2x-3x+6=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\left(x-2\right)-3\left(x-2\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-2\right)\left(x-3\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=2\left(nhận\right)\\x=3\left(nhận\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
c. \(A=\dfrac{x-1}{x^2+1}< 0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x-1< 0\) (vì \(x^2+1>0\forall x\))
\(\Leftrightarrow x< 1\)

a) \(\Rightarrow\left|\dfrac{3}{4}+x\right|=0\Rightarrow\dfrac{3}{4}+x=0\Rightarrow x=-\dfrac{3}{4}\)
b) \(\Rightarrow x+0,4=\dfrac{4}{9}:\dfrac{2}{3}=\dfrac{2}{3}\Rightarrow x=\dfrac{2}{3}-0,4=\dfrac{4}{15}\)


\(\dfrac{5}{2\cdot4}+\dfrac{5}{4\cdot6}+...+\dfrac{5}{48\cdot50}\\ =\dfrac{5}{2}\left(\dfrac{2}{2\cdot4}+\dfrac{2}{4\cdot6}+...+\dfrac{2}{48\cdot50}\right)\\ =\dfrac{5}{2}\left(\dfrac{1}{2}-\dfrac{1}{4}+\dfrac{1}{4}-\dfrac{1}{6}+...+\dfrac{1}{48}-\dfrac{1}{50}\right)\\ =\dfrac{5}{2}\left(\dfrac{1}{2}-\dfrac{1}{50}\right)=\dfrac{5}{2}\cdot\dfrac{12}{25}=\dfrac{6}{5}\)
Ta có: \(\dfrac{5}{2\cdot4}+\dfrac{5}{4\cdot6}+...+\dfrac{5}{48\cdot50}\)
\(=\dfrac{5}{2}\cdot\left(\dfrac{2}{2\cdot4}+\dfrac{2}{4\cdot6}+...+\dfrac{2}{48\cdot50}\right)\)
\(=\dfrac{5}{2}\left(\dfrac{1}{2}-\dfrac{1}{4}+\dfrac{1}{4}-\dfrac{1}{6}+...+\dfrac{1}{48}-\dfrac{1}{50}\right)\)
\(=\dfrac{5}{2}\left(\dfrac{1}{2}-\dfrac{1}{50}\right)\)
\(=\dfrac{5}{2}\cdot\dfrac{12}{25}\)
\(=\dfrac{60}{50}=\dfrac{6}{5}\)

Bài 5:
d: Áp dụng tính chất của dãy tỉ số bằng nhau, ta được:
\(\dfrac{x}{2}=\dfrac{y}{3}=\dfrac{z}{4}=\dfrac{x+y-z}{2+3-4}=\dfrac{-20}{1}=-20\)
Do đó: x=-40; y=-60; z=-80

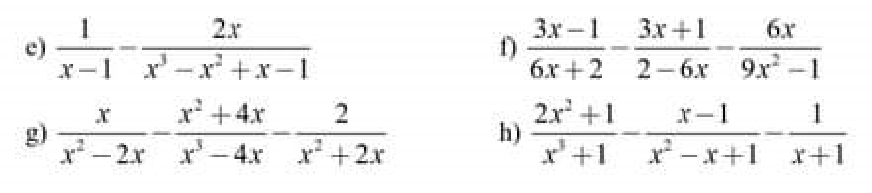


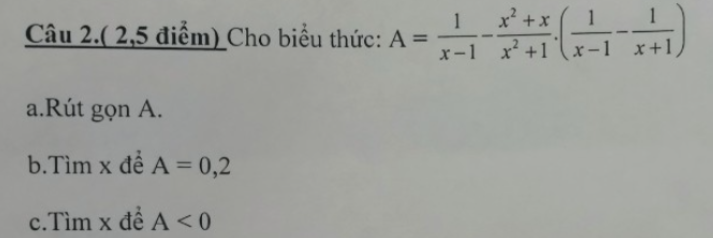

 mng giúp mik bài 1 vs bài 3 vs, mik cần gấp lắm, cảm ơn mng.
mng giúp mik bài 1 vs bài 3 vs, mik cần gấp lắm, cảm ơn mng.
 mng ơi giúp em với ạ! e đag cần gấp! e cảm ơn mng nhiều lắmm <33
mng ơi giúp em với ạ! e đag cần gấp! e cảm ơn mng nhiều lắmm <33 
Bài 128:
a: Tổng số hàng khi thêm vào kho A 7 tấn hàng nữa là:
203+7=210(tấn)
Số hàng của kho A ban đầu là:
\(210\times\dfrac{2}{5}-7=77\left(tấn\right)\)
b: Tổng số hàng của hai kho B và C là:
203-77=126(tấn)
Tổng số hàng ở hai kho B và C sau khi lấy đi ở kho B 9 tấn hàng là:
126-9=117(tấn)
3/2 số hàng ở kho B là:
117-6=111(tấn)
Số hàng ở kho B ban đầu là:
111:1,5+9=83(tấn)
Số hàng ở kho C ban đầu là:
117-83=34(tấn)