
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


Câu 6:
ĐKXĐ: \(x\ne-\dfrac{1}{3}\)
Để \(\dfrac{9x+4}{3x+1}\in Z\) thì \(9x+4⋮3x+1\)
=>\(9x+3+1⋮3x+1\)
=>\(1⋮3x+1\)
=>\(3x+1\in\left\{1;-1\right\}\)
=>\(3x\in\left\{0;-2\right\}\)
=>\(x\in\left\{0;-\dfrac{2}{3}\right\}\)
mà x nguyên
nên x=0
Câu 2:
a: ĐKXĐ: \(x\notin\left\{2;-2;0\right\}\)
b: \(A=\left(\dfrac{1}{x+2}-\dfrac{2x}{4-x^2}+\dfrac{1}{x-2}\right)\cdot\dfrac{x^2-4x+4}{4x}\)
\(=\left(\dfrac{1}{x+2}+\dfrac{2x}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)}+\dfrac{1}{x-2}\right)\cdot\dfrac{\left(x-2\right)^2}{4x}\)
\(=\dfrac{x-2+2x+x+2}{\left(x+2\right)\left(x-2\right)}\cdot\dfrac{\left(x-2\right)^2}{4x}\)
\(=\dfrac{4x\left(x-2\right)}{4x\left(x+2\right)}=\dfrac{x-2}{x+2}\)

a) Điều kiện : 3x2 – 12x ≠ 0; 3x3 – 12x = 3x(x2 – 4) = 3x(x – 2)(x + 2).
Vậy: x ≠ 0; x ≠ 2 và x ≠ -2.

\(a,đk\left(B\right):x\ne\pm3\\ B=\dfrac{3}{x-3}-\dfrac{6x}{9-x^2}+\dfrac{x}{x+3}\\ =\dfrac{3}{x-3}+\dfrac{6x}{x^2-9}+\dfrac{x}{x+3}\\ =\dfrac{3\left(x+3\right)+6x+x\left(x-3\right)}{x^2-9}\\ =\dfrac{3x+9+6x+x^2-3x}{x^2-9}\\ =\dfrac{x^2+6x+9}{x^2-9}\\ =\dfrac{\left(x+3\right)^2}{x^2-9}\\ =\dfrac{x+3}{x-3}\)
\(b,P=A.B\\ =\dfrac{x+1}{x+3}\times\dfrac{x+3}{x-3}\\ =\dfrac{x+1}{x-3}\)
\(c,\) Để P nguyên
\(\dfrac{x+1}{x-3}=1+\dfrac{4}{x-3}\)
=> \(x-3\inƯ\left(4\right)\)
\(Ư\left(4\right)=\left\{-1;1;2;-2;4;-4\right\}\)
\(=>x=\left\{2;4;5;1;7;-1\right\}\)

a) Để giá trị của \(\dfrac{2x^2+7}{3x+21}\) được xác định thì 3x + 21 \(\ne\) 0
=> 3(x+7) \(\ne\) 0
=> x+7 \(\ne\) 0
=> x \(\ne\) -7
Vậy để giá trị của biểu thức \(\dfrac{2x^2 +7}{3x+21}\) được xác định thì x \(\ne\) -7
b) Để giá trị của \(\dfrac{x+5}{-12+6}\) được xác định thì x \(\in\) R ( vì -12+6 \(\ne\) 0)

a) Ta có: x - 1 ≠ 0 ⇒ x ≠ 1
x2 - 1 = (x + 1)(x - 1) ≠ 0 ⇔ x ≠ -1 và x ≠ 1
x2 - 2x + 1 = (x - 1)2 ≠ 0 ⇔ x - 1 ≠ 0 ⇔ x ≠ 1
ĐKXĐ: x ≠ -1 và x ≠ 1

![]()
![]()
![]()
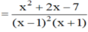

a) Vì mỗi đơn thức là một đa thức nên ta có thể viết bất kỳ đơn thức nào ở câu này.
Ví dụ: P(x) = xy2 (Vì đơn thức cũng là một đa thức)
b) Có vô số đa thức không phải là đơn thức.
Ví dụ: 2x + 3y; x2 + 2y

\(a,ĐK:x\ne\pm1\\ b,B=\dfrac{x^2+x-x^2-1}{2\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)}=\dfrac{x-1}{2\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)}=\dfrac{1}{2\left(x+1\right)}\\ c,B=-\dfrac{1}{2}\Leftrightarrow2\left(x+1\right)=-2\Leftrightarrow x+1=-1\Leftrightarrow x=-2\left(tm\right)\)

a) ĐKXĐ: \(x\ne-3,x\ne2\)
b) \(A=\dfrac{\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)-5-\left(x+3\right)}{\left(x+3\right)\left(x-2\right)}=\dfrac{x^2-x-12}{\left(x+3\right)\left(x-2\right)}=\dfrac{\left(x+3\right)\left(x-4\right)}{\left(x+3\right)\left(x-2\right)}=\dfrac{x-4}{x-2}\)
c) \(A=\dfrac{x-4}{x-2}=\dfrac{3-4}{3-2}=-1\)

a) ĐKXĐ: 3x + 6 khác 0
x khác -2
b) A = (x² + 4x + 4)/(3x + 6)
= (x + 2)²/[3(x + 2)]
= (x + 2)/3
c) Khi x = 1/4, ta có:
A = (1/4 + 2)/3
= (9/4)/3
= 3/4
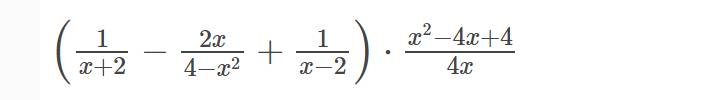
ĐKXĐ la B>=0 bn nhé