
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


a) x(4x + 2) = 4x2 - 14
⇔ 4x2 + 2x = 4x2 - 14
⇔ 4x2 - 4x2 + 2x = -14
⇔ 2x = -14
⇔ x = -7
Vậy tập nghiệm S = ......
b) (x2 - 9)(2x - 1) = 0
⇔ x2 - 9 = 0 hoặc 2x - 1 = 0
⇔ x2 = 9 hoặc 2x = 1
⇔ x = 3 hoặc -3 hoặc x = \(\dfrac{1}{2}\)
Vậy .......
c) \(\dfrac{3}{x-2}\) + \(\dfrac{4}{x+2}\) = \(\dfrac{x-12}{x^2-4}\)
⇔ \(\dfrac{3}{x-2}\) + \(\dfrac{4}{x+2}\) = \(\dfrac{x-12}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)}\)
ĐKXĐ: x - 2 ≠ 0 và x + 2 ≠ 0
⇔ x ≠ 2 và x ≠ -2MSC (mẫu số chung): (x - 2)(x + 2)Quy đồng mẫu hai vế và khử mẫu ta được:3x + 6 + 4x - 8 = x - 12⇔ 3x + 4x - x = 8 - 6 - 12⇔ 6x = -10⇔ x = \(-\dfrac{5}{3}\) (nhận)Vậy ........
a: Ta có: \(\left(x-3\right)^2-x\left(x+5\right)=9\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-6x+9-x^2-5x=9\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=0\)
b: Ta có: \(\left(x+2\right)\left(x^2-2x+4\right)-x\left(x^2+2\right)=15\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^3+8-x^3-2x=15\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x=-7\)
hay \(x=-\dfrac{7}{2}\)

a. 6x2 - (2x + 5)(3x - 2) = 7
<=> 6x2 - 6x2 + 4x - 15x + 10 = 7
<=> -11x = -3
<=> \(x=\dfrac{3}{11}\)
b. (5 - x)(25 + 5x + x2) + x(x2 - 7) = 25
<=> 125 - x3 + x3 - 7x = 25
<=> -7x = 25 - 125
<=> -7x = -100
<=> \(x=\dfrac{100}{7}\)
c. (7 - 2x)2 + (3 + 2x)(3 - 2x) = 30
<=> 49 - 28x + 4x2 + 9 - 4x2 = 30
<=> 4x2 - 4x2 - 28x = 30 - 49 - 9
<=> -28x = -28
<=> x = 1

c,\(\dfrac{5-x}{2}-\dfrac{3x+4}{3}=\dfrac{1}{4}\)
⇔\(\dfrac{5-x}{2}+\dfrac{-3x-4}{3}=\dfrac{1}{4}\)
⇔\(\dfrac{6\left(5-x\right)}{12}+\dfrac{4\left(-3x-4\right)}{12}=\dfrac{3}{12}\)
⇔6(5-x)+4(-3x-4)=3
⇔ 30-6x-12x-16=3
⇔ 30-16-3=12x+6x
⇔ 11=18x
⇔ x=\(\dfrac{11}{18}\)
Vậy S=\(\left\{\dfrac{11}{18}\right\}\)
d)x2-5x=9(x-5)
⇔x(x-5)=9(x-5)
⇔x(x-5)-9(x-5)=0
⇔(x-9)(x-5)=0
⇔\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x-9=0\Leftrightarrow x=9\\x-5=0\Leftrightarrow x=5\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy S=\(\left\{5;9\right\}\)

pt: \(\left(1-2x\right)\left(x+3\right)\left(x^2+2\right)=0\)\(\Leftrightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}1-2x=0\\x+3=0\\x^2+2=0\end{cases}}\)\(\Leftrightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}x=\frac{1}{2}\\x=-3\\x^2=-2\left(loại\right)\end{cases}}\)
vậy: \(x=\frac{1}{2}\),\(x=-3\)

\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-6x+9-x^2+4=1\)
=>-6x=-12
hay x=2

pt <=> (x^2+2x).(x^2+2x+2)+1 = 0
<=> (x^2+2x+1)^2 - 1 + 1 = 0
<=> (x^2+2x+1)^2 = 0
<=> (x+1)^4 = 0
<=> x+1 = 0
<=> x = -1
Vậy pt có tập nghiệm S = {-1}
Tk mk nha
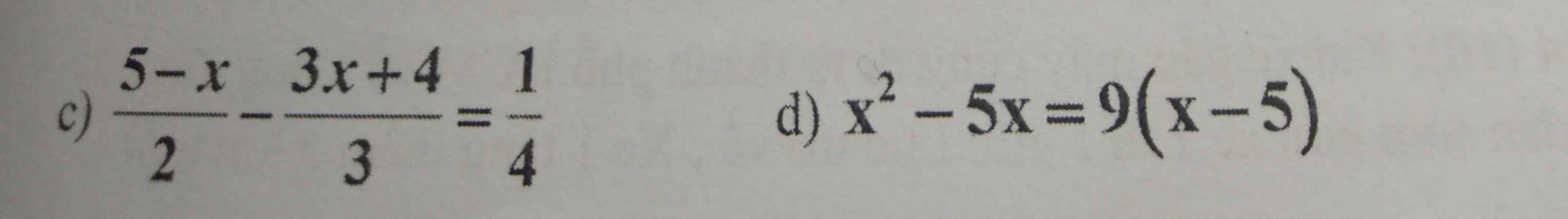
\(\left(x-\sqrt{2}\right)+3.\left(x^2-2\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-\sqrt{2}\right)+3.\left(x^2-\sqrt{2}^2\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-\sqrt{2}\right)+3.\left(x-\sqrt{2}\right).\left(x+\sqrt{2}\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-\sqrt{2}\right).\left[1+3.\left(x+\sqrt{2}\right)\right]=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x-\sqrt{2}=0\\1+3.\left(x+\sqrt{2}\right)=0\end{cases}\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=\sqrt{2}\\x+\sqrt{2}=-\frac{1}{3}\end{cases}\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=\sqrt{2}\\x=-\frac{1}{3}-\sqrt{2}\end{cases}}}}\)
Vậy ...