Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

b) Phương trình hoành độ giao điểm là:
\(2x+6=-x+3\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x+x=3-6\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3x=-3\)
hay x=-1
Thay x=-1 vào (d), ta được:
\(y=2\cdot\left(-1\right)+6=-2+6=4\)
Vậy: A(-1;4)

a:
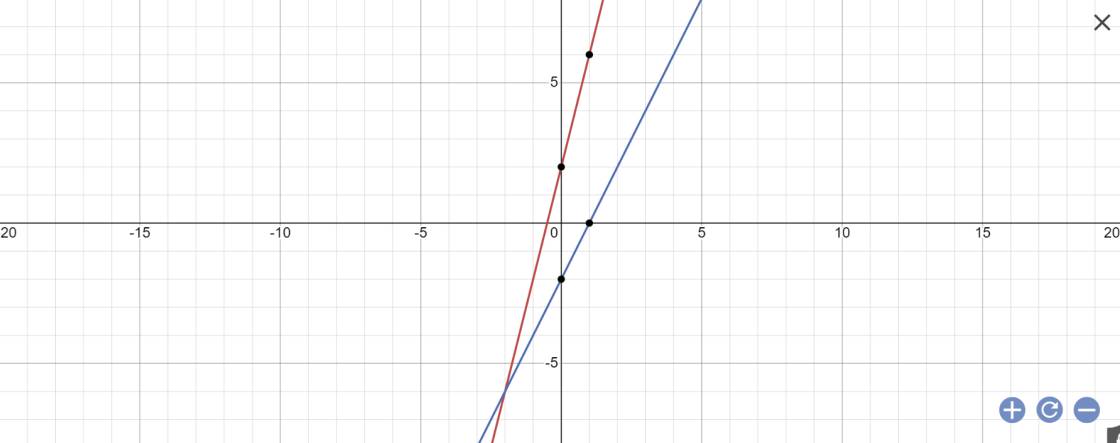
b: phương trình hoành độ giao điểm là:
4x+2=2x-2
=>4x-2x=-2-2
=>2x=-4
=>x=-2
Thay x=-2 vào y=4x+2, ta được:
\(y=4\cdot\left(-2\right)+2=-8+2=-6\)
Vậy: M(-2;-6)
c: Tọa độ A là:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=0\\4x+2=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=0\\4x=-2\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=0\\x=-\dfrac{1}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Tọa độ B là:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=0\\2x-2=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=0\\2x=2\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=0\\x=1\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy: B(1;0); A(-1/2;0)
d: M(-2;-6); B(1;0); A(-1/2;0)
\(MA=\sqrt{\left(-\dfrac{1}{2}+2\right)^2+\left(0-6\right)^2}=\dfrac{3\sqrt{17}}{2}\)
\(MB=\sqrt{\left(1+2\right)^2+\left(0+6\right)^2}=3\sqrt{5}\)
\(AB=\sqrt{\left(-\dfrac{1}{2}-1\right)^2+\left(0-0\right)^2}=\dfrac{3}{2}\)
Chu vi tam giác MAB là:
\(C_{MAB}=MA+MB+AB=\dfrac{3}{2}+3\sqrt{5}+\dfrac{3\sqrt{17}}{2}\)
Xét ΔMAB có \(cosAMB=\dfrac{MA^2+MB^2-AB^2}{2\cdot MA\cdot MB}=\dfrac{9}{\sqrt{85}}\)
=>\(sinAMB=\sqrt{1-\left(\dfrac{9}{\sqrt{85}}\right)^2}=\dfrac{2}{\sqrt{85}}\)
Diện tích tam giác MAB là:
\(S_{AMB}=\dfrac{1}{2}\cdot MA\cdot MB\cdot sinAMB=\dfrac{1}{2}\cdot\dfrac{3\sqrt{17}}{2}\cdot3\sqrt{5}\cdot\dfrac{2}{\sqrt{85}}\)
\(=\dfrac{9}{2}\)

a: 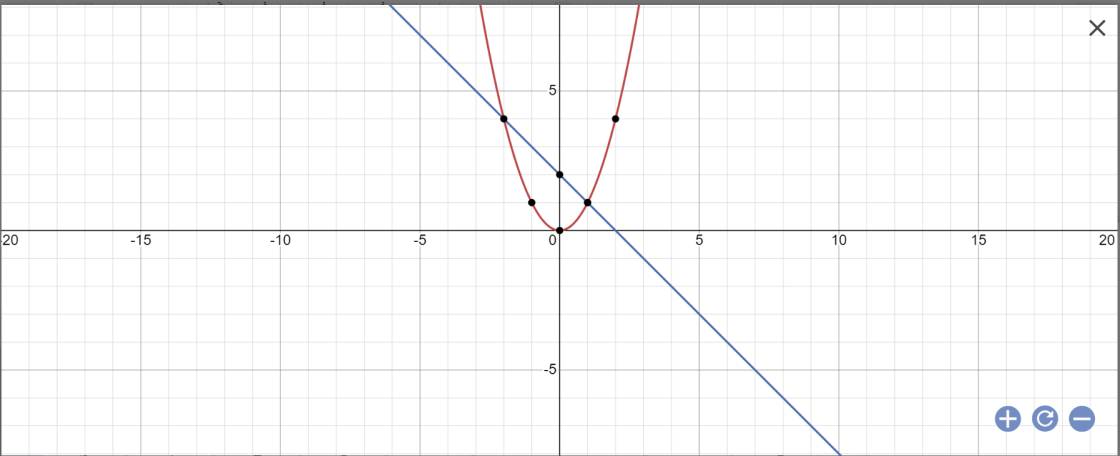
b: PTHĐGĐ là:
x^2+x-2=0
=>(x+2)(x-1)=0
=>x=-2 hoặc x=1
=>y=4 hoặc y=1

cảm ơn bà nha, nhưng mà tui cop sai đề nên giờ phải làm lại từ đầu

b: Tọa độ giao điểm là:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}2x+2=x\\y=x\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow x=y=-2\)
a: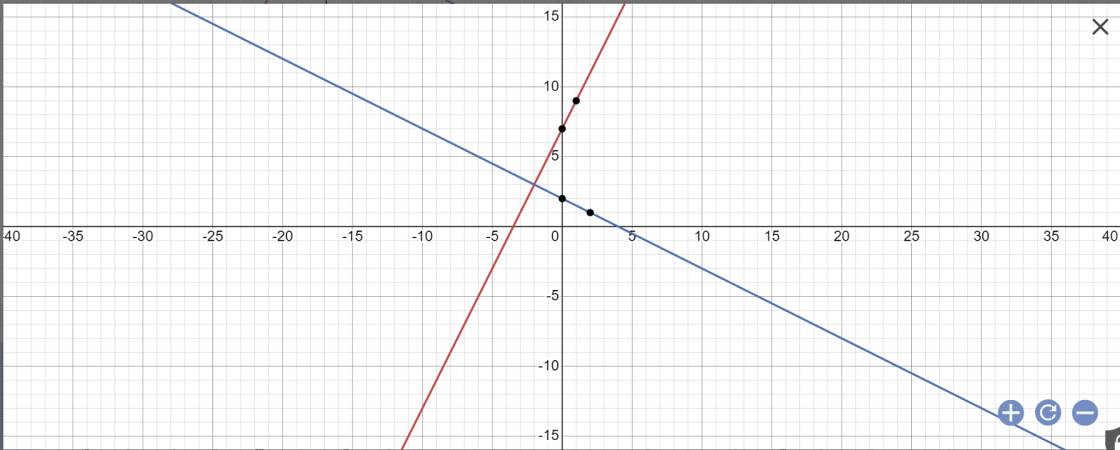
b: Phương trình hoành độ giao điểm là:
\(2x+7=-\dfrac{1}{2}x+2\)
=>\(2x+\dfrac{1}{2}x=2-7=-5\)
=>2,5x=-5
=>x=-2
Thay x=-2 vào y=2x+7, ta được:
\(y=2\cdot\left(-2\right)+7=7-4=3\)
Vậy: A(-2;3)
c: Tọa độ B là:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=0\\2x+7=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=0\\2x=-7\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=0\\x=-3,5\end{matrix}\right.\)
Tọa độ C là:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=0\\-\dfrac{1}{2}x+2=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=0\\-\dfrac{1}{2}x=-2\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=0\\x=4\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy: C(4;0)
A(-2;3); B(-3,5;0); C(4;0)
\(AB=\sqrt{\left(-3,5+2\right)^2+\left(0-3\right)^2}=\dfrac{3\sqrt{5}}{2}\)
\(AC=\sqrt{\left(4+2\right)^2+\left(0-3\right)^2}=3\sqrt{5}\)
\(BC=\sqrt{\left(4+3,5\right)^2+\left(0-0\right)^2}=7,5\)
Vì \(AB^2+AC^2=BC^2\)
nên ΔABC vuông tại A
=>\(\widehat{BAC}=90^0\)
Xét ΔABC vuông tại A có \(sinABC=\dfrac{AC}{BC}=\dfrac{3\sqrt{5}}{7,5}\)
=>\(\widehat{ABC}\simeq63^0\)
ΔABC vuông tại A
=>\(\widehat{ABC}+\widehat{ACB}=90^0\)
=>\(\widehat{ACB}=90^0-63^0=27^0\)
d: Chu vi tam giác ABC là:
\(C_{ABC}=AB+AC+BC=\dfrac{3\sqrt{5}}{2}+3\sqrt{5}+7,5=\dfrac{9\sqrt{5}+15}{2}\)
Diện tích tam giác ABC là:
\(S_{ABC}=\dfrac{1}{2}\cdot AB\cdot AC=\dfrac{1}{2}\cdot\dfrac{3\sqrt{5}}{2}\cdot3\sqrt{5}=\dfrac{45}{4}\)