Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

\(Q-\left(5x^2-xyz\right)=xy+2x^2-3xyz+5\)
\(\Leftrightarrow Q=xy+2x^2-3xyz+5+5x^2-xyz\)
\(\Leftrightarrow Q=7x^2+xy-4xyz+5\)

a: A = -2xy + 3/2xy^2 + 1/2xy^2 + xy = -2xy + 2xy^2 + xy = 2xy^2 - xy
b: B = xy^2z + 2xy^2z - xyz - 3xy^2z + xy^2z = 3xy^2z - xyz
c: C = 4x^2y^3 + x^4 - 2x^2 + 6x^4 - x^2y^3 = 7x^4 + 3x^2y^3 - 2x^2
d: D = 3/4xy^2 - 2xy - 1/2xy^2 + 3xy = 5/4xy^2 + xy
e: E = 2x^2 - 3y^3 - z^4 - 4x^2 + 2y^3 + 3z^4 = -2x^2 - y^3 + 2z^4
f: F = 3xy^2z + xy^2z - xyz + 2xy^2z - 3xyz = 6xy^2z - 2xyz
a: A=-2xy+3/2xy^2+1/2xy^2+xy
=-2xy+xy+3/2xy^2+1/2xy^2
=2xy^2-xy
b: \(B=xy^2z+2xy^2z-xyz-3xy^2z+xy^2z\)
\(=xy^2z\left(1+2-3+1\right)-xyz=xy^2z-xyz\)
c: \(=4x^2y^3-x^2y^3+x^4+6x^4-2x^2\)
\(=7x^4-x^2+3x^2y^3\)
d: \(=\dfrac{3}{4}xy^2-\dfrac{1}{2}xy^2+3xy-2xy\)
=1/4xy^2+xy
e: \(=2x^2-4x^2-3y^3+2y^3+3z^4-z^4\)
\(=-2x^2-y^3+2z^4\)
f: \(=xy^2z+3xy^2z+2xy^2z-xyz-3xyz\)
\(=6xy^2z-4xyz\)

\(\begin{array}{l}M - 5{x^2} + xyz = xy + 2{x^2} - 3xyz + 5\\ \Rightarrow M = xy + 2{x^2} - 3xyz + 5 + 5{x^2} - xyz\\ = \left( { - 3xyz - xyz} \right) + \left( {2{x^2} + 5{x^2}} \right) + xy + 5\\ = - 4xyz + 7{x^2} + xy + 5\end{array}\)

Để \(M=\dfrac{x^2+2x-13}{x-3}\in Z\) thì \(x^2+2x-13⋮x-3\)
\(\Rightarrow\left(x^2-3x\right)+5x-13⋮x-3\)
\(\Rightarrow x\left(x-3\right)+5x-13⋮x-3\)
\(\Rightarrow5x-13⋮x-3\)
\(\Rightarrow\left(5x-15\right)+2⋮x-3\)
\(\Rightarrow5\left(x-3\right)+2⋮x-3\)
\(\Rightarrow2⋮x-3\)
\(\Rightarrow x-3\in U\left(2\right)=\left\{-1;1;-2;2\right\}\)
\(\Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x-3=-1\Rightarrow x=2\\x-3=1\Rightarrow x=4\\x-3=-2\Rightarrow x=1\\x-3=2\Rightarrow x=5\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy \(x\in\left\{2;4;1;5\right\}\) thì \(M\in Z\)
a) \(x^2-9x\)
\(=x\left(x-9\right)\)
b) \(3x^2-3xy-5x+5y\)
\(=\left(3x^2-3xy\right)-\left(5x-5y\right)\)
\(=3x\left(x-y\right)-5\left(x-y\right)\)
\(=\left(x-y\right)\left(3x-5\right)\)
c) \(x^3+5x^2-6x\)
\(=x\left(x^2+5x-6\right)\)
\(=x\left(x^2-x+6x-6\right)\)
\(=x\left[\left(x^2-x\right)+\left(6x-6\right)\right]\)
\(=x\left[x\left(x-1\right)+6\left(x-1\right)\right]\)
\(=x\left(x-1\right)\left(x+6\right)\)

Lời giải
Ta có
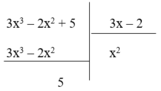
Vì phần dư R = 5 ≠ 0 nên phép chia đa thức 3 x 3 – 2 x 2 + 5 cho đa thức 3x – 2 là phép chia có dư. Do đó (I) sai
Lại có
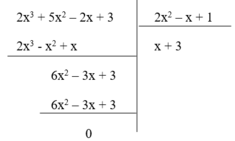
Nhận thấy phần dư R = 0 nên phép chia đa thức ( 2 x 3 + 5 x 2 – 2x + 3) cho đa thức (2 x 2 – x + 1) là phép chia hết. Do đó (II) đúng
Đáp án cần chọn là: D

Bài 13:
1: \(A=-x^2+4x+3\)
\(=-\left(x^2-4x-3\right)=-\left(x^2-4x+4-7\right)\)
\(=-\left(x-2\right)^2+7\le7\)
Dấu '=' xảy ra khi x=2
2: \(B=-\left(x^2-6x+11\right)\)
\(=-\left(x-3\right)^2-2\le-2\)
Dấu '=' xảy ra khi x=3

\(\dfrac{A}{B}=\dfrac{8x^3+2x^2-8x-2-3}{4x+1}\)
\(=2x^2-2-\dfrac{3}{4x+1}\)
\(M+N=3xyz-2x^2+5xy+5x^2+xyz-5y+3-2y=3x^2+4xyz+5xy-7y+3\)
\(N-M=5x^2+xyz-5y+3-2y-3xyz+2x^2-5xy=7x^2-2xyz-5xy-7y+3\)