Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

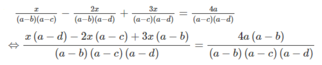
⇔ x(a − d) − 2x(a − c) + 3x(a − b) = 4a(a − b)
⇔ x(a − d − 2a + 2c + 3a − 3b) = 4a(a − b)
⇔ x(2a − 3b + 2c − d) = 4a(a − b)
Theo giả thiết, b + d = 2c nên 2a – 3b + 2c – d = 2a – 2b = 2 (a – b ).
Do đó phương trình đã cho tương đương với phương trình 2(a − b)x = 4a(a − b)
Để ý rằng a – b ≠ 0, ta thấy ngay phương trình cuối có nghiệm duy nhất x = 2a.
Vậy phương trình đã cho cũng có nghiệm duy nhất x = 2a.

Điều kiện đã cho có thể được viết lại thành \(\dfrac{a}{a+b}+\dfrac{b}{b+c}+\dfrac{c}{c+d}+\dfrac{d}{d+a}=2\)
hay \(1-\dfrac{a}{a+b}-\dfrac{b}{b+c}+1-\dfrac{c}{c+d}-\dfrac{d}{d+a}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{b}{a+b}-\dfrac{b}{b+c}+\dfrac{d}{c+d}-\dfrac{d}{d+a}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{b^2+bc-ab-b^2}{\left(a+b\right)\left(b+c\right)}+\dfrac{d^2+da-cd-d^2}{\left(c+d\right)\left(d+a\right)}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{b\left(c-a\right)}{\left(a+b\right)\left(b+c\right)}+\dfrac{d\left(a-c\right)}{\left(c+d\right)\left(d+a\right)}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(c-a\right)\left[\dfrac{b}{\left(a+b\right)\left(b+c\right)}-\dfrac{d}{\left(c+d\right)\left(d+a\right)}\right]=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{b}{\left(a+b\right)\left(b+c\right)}=\dfrac{d}{\left(c+d\right)\left(d+a\right)}\) (do \(c\ne a\))
\(\Leftrightarrow b\left(cd+ca+d^2+da\right)=d\left(ab+ac+b^2+bc\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow bcd+abc+bd^2+abd=abd+acd+b^2d+bcd\)
\(\Leftrightarrow abc+bd^2-acd-b^2d=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow ac\left(b-d\right)-bd\left(b-d\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(b-d\right)\left(ac-bd\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow ac=bd\) (do \(b\ne d\))
Do đó \(A=abcd=ac.ac=\left(ac\right)^2\), mà \(a,c\inℕ^∗\) nên A là SCP (đpcm)
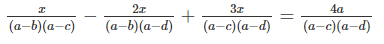
\(\frac{x}{\left(a-b\right)\left(a-c\right)}-\frac{2x}{\left(a-b\right)\left(a-d\right)}+\frac{3x}{\left(a-c\right)\left(a-d\right)}=\frac{4a}{\left(a-c\right)\left(a-d\right)}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\frac{x\left(a-d\right)-2x\left(a-c\right)+3x\left(a-b\right)}{\left(a-b\right)\left(a-c\right)\left(a-d\right)}=\frac{4a\left(a-b\right)}{\left(a-b\right)\left(a-c\right)\left(a-d\right)}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\left(a-d-2a+2c+3a-3b\right)=4a\left(a-b\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\left(2a-3b+2c-d\right)=4a\left(a-b\right)\)
Theo giả thiết ,b + d = 2c nên 2a - 3b + 2c - d = 2a - 2b = 2(a-b) .Do đó phương trình đã cho tương đương với phương trình2(a-b) x = 4a(a-b)
Để ý rằng a - b \(\ne\)0,ta thấy ngay phương trình cuối có nghiệm duy nhất x = 2a
Vậy phương trình đã cho có nghiệm duy nhất x = 2a
b+d=2c mà đề bài cho là c+d=2b mà bạn