Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


Gọi M là trung điểm BC, theo tính chất trọng tâm:
\(\overrightarrow{AG}=\dfrac{2}{3}\overrightarrow{AM}\)
Mà I là trung điểm AG \(\Rightarrow\overrightarrow{IG}=\dfrac{1}{2}\overrightarrow{AG}=\dfrac{1}{3}\overrightarrow{AM}\Rightarrow\overrightarrow{GI}=-\dfrac{1}{3}\overrightarrow{AM}\)
Lại có: M là trung điểm BC \(\Rightarrow\overrightarrow{MB}+\overrightarrow{MC}=\overrightarrow{0}\)
Nên ta có:
\(\overrightarrow{AB}+\overrightarrow{AC}+6\overrightarrow{GI}=\overrightarrow{AM}+\overrightarrow{MB}+\overrightarrow{AM}+\overrightarrow{MC}+6.\left(-\dfrac{1}{3}\right)\overrightarrow{AM}\)
\(=2\overrightarrow{AM}-2\overrightarrow{AM}=\overrightarrow{0}\) (đpcm)

H đối xứng G qua B \(\Rightarrow\) B là trung điểm của HG
\(\Rightarrow\overrightarrow{AG}+\overrightarrow{AH}=2\overrightarrow{AB}\Rightarrow\overrightarrow{AB}=\frac{1}{2}\overrightarrow{AG}+\frac{1}{2}\overrightarrow{AH}\)
Lại có: \(\overrightarrow{AB}+\overrightarrow{AC}=3\overrightarrow{AG}\Rightarrow\overrightarrow{AC}=3\overrightarrow{AG}-\overrightarrow{AB}\)
\(\Rightarrow\overrightarrow{AC}=3\overrightarrow{AG}-\left(\frac{1}{2}\overrightarrow{AG}+\frac{1}{2}\overrightarrow{AH}\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow\overrightarrow{AC}=\frac{5}{2}\overrightarrow{AG}-\frac{1}{2}\overrightarrow{AH}\)

Cách 1:
Gọi O là giao điểm của AC và BD.

Ta có:
\(\begin{array}{l}\overrightarrow {AG} = \overrightarrow {AB} + \overrightarrow {BG} = \overrightarrow a + \overrightarrow {BG} ;\\\overrightarrow {CG} = \overrightarrow {CB} + \overrightarrow {BG} = \overrightarrow {DA} + \overrightarrow {BG} = - \overrightarrow b + \overrightarrow {BG} ;\end{array}\)(*)
Lại có: \(\overrightarrow {BD} =\overrightarrow {BA} + \overrightarrow {AD} = - \overrightarrow a + \overrightarrow b \).
\(\overrightarrow {BG} ,\overrightarrow {BD} \) cùng phương và \(\left| {\overrightarrow {BG} } \right| = \frac{2}{3}BO = \frac{1}{3}\left| {\overrightarrow {BD} } \right|\)
\( \Rightarrow \overrightarrow {BG} = \frac{1}{3}\overrightarrow {BD} = \frac{1}{3}\left( { - \overrightarrow a + \overrightarrow b } \right)\)
Do đó (*) \( \Leftrightarrow \left\{ \begin{array}{l}\overrightarrow {AG} = \overrightarrow a + \overrightarrow {BG} = \overrightarrow a + \frac{1}{3}\left( { - \overrightarrow a + \overrightarrow b } \right) = \frac{2}{3}\overrightarrow a + \frac{1}{3}\overrightarrow b ;\\\overrightarrow {CG} = -\overrightarrow b + \overrightarrow {BG} = -\overrightarrow b + \frac{1}{3}\left( { - \overrightarrow a + \overrightarrow b } \right) = - \frac{1}{3}\overrightarrow a - \frac{2}{3}\overrightarrow b ;\end{array} \right.\)
Vậy \(\overrightarrow {AG} = \frac{2}{3}\overrightarrow a + \frac{1}{3}\overrightarrow b ;\;\overrightarrow {CG} = - \frac{1}{3}\overrightarrow a - \frac{2}{3}\overrightarrow b .\)
Cách 2:
Gọi AE, CF là các trung tuyến trong tam giác ABC.
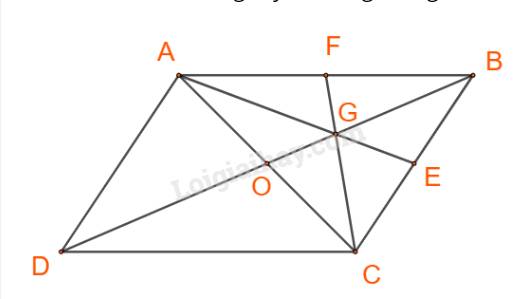
Ta có:
\(\overrightarrow {AG} = \frac{2}{3}\overrightarrow {AE} = \frac{2}{3}.\frac{1}{2}\left( {\overrightarrow {AB} + \overrightarrow {AC} } \right) = \frac{2}{3}.\frac{1}{2}\left[ {\overrightarrow {AB} + \left( {\overrightarrow {AB} + \overrightarrow {AD} } \right)} \right] \\= \frac{1}{3}\left( {2\overrightarrow a + \overrightarrow b } \right) = \frac{2}{3}\overrightarrow a + \frac{1}{3}\overrightarrow b \)
\(\overrightarrow {CG} = \frac{2}{3}\overrightarrow {CF} = \frac{2}{3}.\frac{1}{2}\left( {\overrightarrow {CA} + \overrightarrow {CB} } \right) = \frac{2}{3}.\frac{1}{2}\left[ {\left( {\overrightarrow {CB} + \overrightarrow {CD} } \right) + \overrightarrow {CB} } \right] = \frac{1}{3}\left( {2\overrightarrow {CB} + \overrightarrow {CD} } \right) = \frac{1}{3}\left( { - 2\overrightarrow {AD} - \overrightarrow {AB} } \right) = - \frac{1}{3}\overrightarrow a - \frac{2}{3}\overrightarrow b \)
Vậy \(\overrightarrow {AG} = \frac{2}{3}\overrightarrow a + \frac{1}{3}\overrightarrow b ;\;\overrightarrow {CG} = - \frac{1}{3}\overrightarrow a - \frac{2}{3}\overrightarrow b .\)

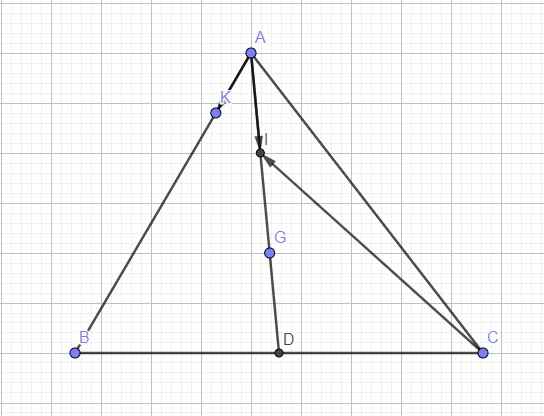
Do G là trọng tâm tam giác
\(\Rightarrow\overrightarrow{AG}=\dfrac{2}{3}\overrightarrow{AD}=\dfrac{2}{3}\left(\dfrac{1}{2}\overrightarrow{AB}+\dfrac{1}{2}\overrightarrow{AC}\right)=\dfrac{1}{3}\overrightarrow{AB}+\dfrac{1}{3}\overrightarrow{AC}=\dfrac{1}{3}\overrightarrow{AC}+\dfrac{1}{3}\overrightarrow{CB}+\dfrac{1}{3}\overrightarrow{AC}\)
\(=\dfrac{2}{3}\overrightarrow{AC}+\dfrac{1}{3}\overrightarrow{CB}=-\dfrac{2}{3}\overrightarrow{CA}+\dfrac{1}{3}\overrightarrow{CB}\)
Do I là trung điểm AG
\(\Rightarrow\overrightarrow{AI}=\dfrac{1}{2}\overrightarrow{AG}=\dfrac{1}{2}\left(-\dfrac{2}{3}\overrightarrow{CA}+\dfrac{1}{3}\overrightarrow{CB}\right)=-\dfrac{1}{3}\overrightarrow{CA}+\dfrac{1}{6}\overrightarrow{CB}\)
\(\overrightarrow{AK}=\dfrac{1}{5}\overrightarrow{AB}=\dfrac{1}{5}\left(\overrightarrow{AC}+\overrightarrow{CB}\right)=-\dfrac{1}{5}\overrightarrow{CA}+\dfrac{1}{5}\overrightarrow{CB}\)
\(\overrightarrow{CI}=\overrightarrow{CA}+\overrightarrow{AI}=\overrightarrow{CA}-\dfrac{1}{3}\overrightarrow{CA}+\dfrac{1}{6}\overrightarrow{CB}=\dfrac{2}{3}\overrightarrow{CA}+\dfrac{1}{6}\overrightarrow{CB}\)
\(\overrightarrow{CK}=\overrightarrow{CA}+\overrightarrow{AK}=\overrightarrow{CA}-\dfrac{1}{5}\overrightarrow{CA}+\dfrac{1}{5}\overrightarrow{CB}=\dfrac{4}{5}\overrightarrow{CA}+\dfrac{1}{5}\overrightarrow{CB}\)

1.
Gọi M là trung điểm BC thì theo tính chất trọng tâm: \(\overrightarrow{AG}=\dfrac{2}{3}\overrightarrow{AM}=\dfrac{2}{3}\left(\dfrac{1}{2}\overrightarrow{AB}+\dfrac{1}{2}\overrightarrow{AC}\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow\overrightarrow{AG}=\dfrac{1}{3}\overrightarrow{AB}+\dfrac{1}{3}\overrightarrow{AC}\Rightarrow x+y=\dfrac{2}{3}\)
2.
\(CH=\dfrac{1}{2}BC=\dfrac{a}{2}\)
\(T=\left|\text{ }\overrightarrow{CA}-\overrightarrow{HC}\right|=\left|\overrightarrow{CA}+\overrightarrow{CH}\right|\)
\(\Rightarrow T^2=CA^2+CH^2+2\overrightarrow{CA}.\overrightarrow{CH}=a^2+\left(\dfrac{a}{2}\right)^2+2.a.\dfrac{a}{2}.cos60^0=\dfrac{7a^2}{4}\)
\(\Rightarrow T=\dfrac{a\sqrt{7}}{2}\)
3.
\(10< x< 100\Rightarrow10< 3k< 100\)
\(\Rightarrow\dfrac{10}{3}< k< \dfrac{100}{3}\Rightarrow4\le k\le33\)
\(\Rightarrow\sum x=3\left(4+5+...+33\right)=1665\)

Ta có \(\overrightarrow{IB}=\overrightarrow{BA}\Rightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}I\in AB\\\overrightarrow{AI}=2\overrightarrow{AB}\end{cases}}\). Tương tự \(\hept{\begin{cases}J\in\left[AC\right]\\\overrightarrow{AJ}=\frac{AJ}{AC}\overrightarrow{AC}=\frac{2}{5}\overrightarrow{AC}\end{cases}}\)
Do đó \(\overrightarrow{IJ}=\overrightarrow{AJ}-\overrightarrow{AI}=\frac{2}{5}\overrightarrow{AC}-2\overrightarrow{AB}\)(đpcm).
giải giúp t câu này nha : tính vecto IG theo vecto AB và vecto AC (các b vẽ hình ra hộ t nhé)
Cho tam giác ABC có trung tuyến BM và trọng tâm G . Phân tích vecto BG theo hai vecto BA và vecto BC

\(\overrightarrow{BG}=\dfrac{2}{3}\overrightarrow{BM}=\dfrac{2}{3}\overrightarrow{BA}+\dfrac{2}{3}\overrightarrow{BC}\)