
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


\(\left|2x-\dfrac{1}{2}\right|+\dfrac{3}{7}=5\dfrac{3}{7}\)
<=> \(\left|2x-\dfrac{1}{2}\right|=5\)
<=> \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}2x-\dfrac{1}{2}=5\\2x-\dfrac{1}{2}=-5\end{matrix}\right.\)
<=> \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}2x=\dfrac{11}{2}\\2x=-\dfrac{9}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
<=> \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{11}{4}\\x=-\dfrac{9}{4}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Do x < 0 => x = \(-\dfrac{9}{4}\)
Giải:
\(\left|2x-\dfrac{1}{2}\right|+\dfrac{3}{7}=5\dfrac{3}{7}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left|2x-\dfrac{1}{2}\right|=5\dfrac{3}{7}-\dfrac{3}{7}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left|2x-\dfrac{1}{2}\right|=4\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}2x-\dfrac{1}{2}=4\\2x-\dfrac{1}{2}=-4\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}2x=\dfrac{9}{2}\\2x=-\dfrac{7}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{9}{4}\\x=-\dfrac{7}{4}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Mà x < 0
Nên \(x=-\dfrac{7}{4}\)
Vậy \(x=-\dfrac{7}{4}\).
Chúc bạn học tốt!

a: =>1/2x=7/2-2/3=21/6-4/6=17/6
=>x=17/3
b: =>2/3:x=-7-1/3=-22/3
=>x=2/3:(-22/3)=-1/11
c: =>1/3x+2/5x-2/5=0
=>11/15x=2/5
hay x=6/11
d: =>2x-3=0 hoặc 6-2x=0
=>x=3/2 hoặc x=3

a: (x+1/2)(2/3-2x)=0
=>x+1/2=0 hoặc 2/3-2x=0
=>x=-1/2 hoặc x=1/3
b: 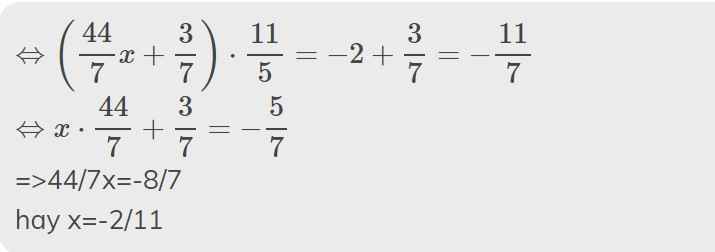
c: \(\Leftrightarrow x\cdot\left(\dfrac{13}{4}-\dfrac{7}{6}\right)=\dfrac{5}{12}+\dfrac{5}{3}=\dfrac{5}{12}+\dfrac{20}{12}=\dfrac{25}{12}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{25}{12}:\dfrac{39-14}{12}=\dfrac{25}{25}=1\)

a: =>x-3/4=1/6-1/2=1/6-3/6=-2/6=-1/3
=>x=-1/3+3/4=-4/12+9/12=5/12
b: =>x(1/2-5/6)=7/2
=>-1/3x=7/2
hay x=-21/2
c: (4-x)(3x+5)=0
=>4-x=0 hoặc 3x+5=0
=>x=4 hoặc x=-5/3
d: x/16=50/32
=>x/16=25/16
hay x=25
e: =>2x-3=-1/4-3/2=-1/4-6/4=-7/4
=>2x=-7/4+3=5/4
hay x=5/8

a) \(\dfrac{x+3}{x-5}=\dfrac{x-5+8}{x-5}=\dfrac{x-5}{x-5}+\dfrac{8}{x-5}=1+\dfrac{8}{x-5}\)
Để \(\dfrac{x+3}{x-5}\) có giá trị âm thì \(8⋮x-5\) và \(x-5< 0\)
\(\Rightarrow x-5\inƯ\left(8\right)=\left\{\pm1;\pm2;\pm4;\pm8\right\}\)
Để \(x-5< 0\Rightarrow x< 5\)
Nên \(x\in\left\{\pm1;\pm2;\pm4;-8\right\}\)
~ Học tốt ~
1) Tìm x
a) B(32) = { 0 , 32 , 64 , 96 , 128 ; 160 ; 192 ; ... }
b) \(\dfrac{11}{12}\) - ( \(\dfrac{2}{5}\) +x ) = \(\dfrac{2}{3}\)
\(\dfrac{2}{5}\) + x = \(\dfrac{11}{12}\) - \(\dfrac{2}{3}\)
\(\dfrac{2}{5}\) +x = \(\dfrac{1}{4}\)
x = \(\dfrac{1}{4}\) - \(\dfrac{2}{5}\)
x = \(\dfrac{-3}{20}\)
B(41 ) = { 0 , 41 , 82 , 123 , 164 , 205 , .... }
c ) 2.( 2x-\(\dfrac{1}{7}\) ) = 0
=> \(2\text{x}-\dfrac{1}{7}\) = 0
=> 2x = \(\dfrac{1}{7}\)
=> x = \(\dfrac{1}{14}\)
d) ( 3 - 2x ) (7x - \(\dfrac{1}{8}\) ) = 0
=> 3-2x = 0 hoặc 7x - \(\dfrac{1}{8}\) =0
* Nếu 3 - 2x = 0
=> 2x = 3
=> x = \(\dfrac{3}{2}\)
*Nếu 7x - \(\dfrac{1}{8}\) = 0
=> 7x = \(\dfrac{1}{8}\)
=> x = \(\dfrac{1}{56}\)
Vậy x = \(\dfrac{3}{2}\) hoặc x = \(\dfrac{1}{56}\)
2) Xác định giá trị của x để :
a) \(\dfrac{x+3}{x-5}\) có giá trị âm
=> x+3 phải là số nguyên dương
=> x-5 phải là số nguyên âm
b) Để ( \(x+\dfrac{2}{3}\) ) . ( x - 2 ) > 0
=> ( \(x+\dfrac{2}{3}\) ) và ( x-2 ) \(\in\) N*

\(\dfrac{6}{7}+\dfrac{5}{8}:5-\dfrac{3}{16}.\left(-2\right)^2=\dfrac{6}{7}+\dfrac{5}{8}:5-\dfrac{3}{16}.4=\dfrac{6}{7}+\dfrac{1}{8}-\dfrac{3}{4}=\dfrac{5}{56}\)
\(\dfrac{2}{3}+\dfrac{1}{3}.\left(-\dfrac{4}{9}+\dfrac{5}{6}\right):\dfrac{7}{12}=\dfrac{2}{3}+\dfrac{1}{3}.\dfrac{7}{18}:\dfrac{7}{12}=\dfrac{2}{3}+\dfrac{2}{9}=\dfrac{8}{9}\)

a: =>2x-1=-2
=>2x=-1
hay x=-1/2
b: \(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}3x+2=0\\-\dfrac{2}{5}x-7=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow x\in\left\{-\dfrac{2}{3};-\dfrac{35}{2}\right\}\)
c: x/8=9/4
nên x/8=18/8
hay x=18
d: \(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-3\right)^2=36\)
=>x-3=6 hoặc x-3=-6
=>x=9 hoặc x=-3
e: =>-1,7x=6,12
hay x=-3,6
h: =>x-3,4=27,6
hay x=31
a) \(\dfrac{1}{3}\div\left(2x-1\right)=\dfrac{-1}{6}\)
\(\left(2x-1\right).\dfrac{1}{3}\div\left(2x-1\right)=\left(2x-1\right)\left(-\dfrac{1}{6}\right)\)
\(\dfrac{1}{3}=\left(2x-1\right)\left(-\dfrac{1}{6}\right)\)
\(\dfrac{1}{3}=-1\left(2x-1\right)\div6\)
\(\dfrac{1}{3}=-2x+1\div6\)
\(x=-\dfrac{1}{2}\)
b) \(\left(3x+2\right)\left(\dfrac{-2}{5}x-7\right)=0\)
\(TH1:3x+2=0\)
\(3x=0-2\)
\(3x=-2\)
\(x=\dfrac{-2}{3}\)
\(TH2:\left(-\dfrac{2}{5}x-7\right)=0\)
\(\left(\dfrac{-2}{5}x-7\right)=0\)
\(\left(\dfrac{-2x}{5}+\dfrac{5\left(-7\right)}{5}\right)=0\)
\(\left(\dfrac{-2x-35}{5}\right)=0\)
\(-2x-35=0\)
\(-2x=0+35\)
\(x=-\dfrac{35}{2}\)
c) \(\dfrac{x}{8}=\dfrac{9}{4}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{9.8}{4}=\dfrac{72}{4}=18\)
\(x=18\)
d) \(\dfrac{x-3}{2}=\dfrac{18}{x-3}\)
\(x-3=18+2\)
\(x=20-3\)
\(x=17\)
e) \(4,5x-6,2x=6,12\)
\(\dfrac{9x}{2}-6,2.x=6,12\)
\(\dfrac{9x}{2}+\dfrac{-31x}{5}=6,12\)
\(\dfrac{5.9x}{10}+\dfrac{2\left(-31\right)x}{10}=6.12\)
\(\dfrac{45x-62x}{10}=6.12\)
\(=-17x\div10=6.12\)
\(-17x=10.6.12\)
\(x=-3,6\)
h) \(11,4-\left(x-3,4\right)=-16,2\)
\(x-3,4=-16,2+11,4\)
\(x-3,4=-4,8\)
\(x=-1,4\)
\(\left|2x-\frac{1}{2}\right|+\frac{3}{7}=5\frac{3}{7}\)
\(\left|2x-\frac{1}{2}\right|=\frac{38}{7}-\frac{3}{7}\)
\(\left|2x-\frac{1}{2}\right|=5\)
Ta xét hai trường hợp:
TH1: \(2x-\frac{1}{2}=5\)
2x = 5 + 1/2
2x = 11/2
x = 11/2 : 2
x = 11/4 (loại vì x < 0)
TH2: 2x - 1/2 = -5
2x = -5 + 1/2
2x = -9/2
x = -9/2:2
x = -9/4 (chọn)
Vậy x = -9/4
\(\left|2x-\frac{1}{2}\right|+\frac{3}{7}=5\frac{3}{7}\)
\(\left|2x-\frac{1}{2}\right|=5\frac{3}{7}-\frac{3}{7}=5\)
\(\Rightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}2x-\frac{1}{2}=5\\2x-\frac{1}{2}=-5\end{cases}}\Rightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}2x=\frac{11}{2}\\2x=\frac{-9}{2}\end{cases}\Rightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=11\\x=-9\end{cases}}}\)
\(x=-9\)