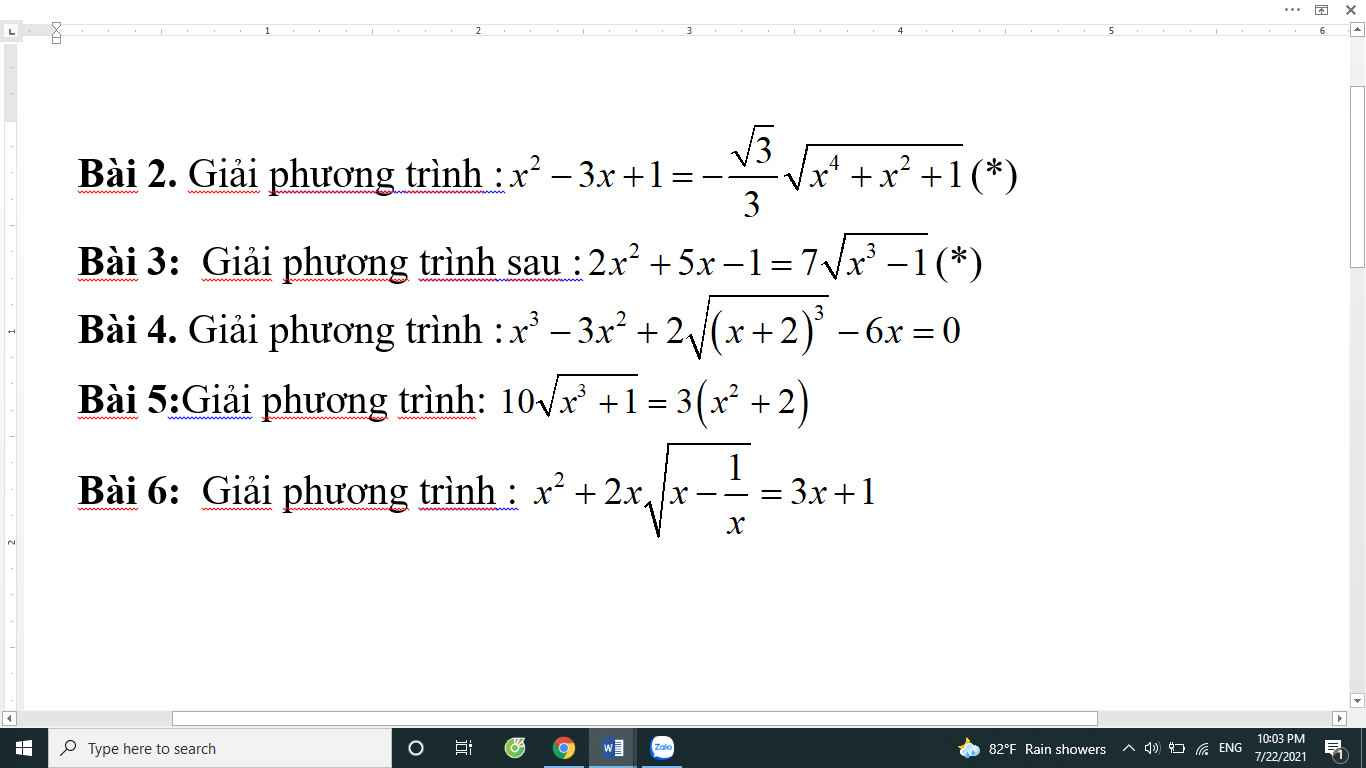
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


Đặt \(\sqrt{x^2-x+1}=a>0;\sqrt{x^2+x+1}=b>0\).
\(PT\Leftrightarrow2a^2-b^2=-\dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{3}ab\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(a+\dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{2}b\right)\left(2a-\dfrac{2\sqrt{3}}{3}b\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2a-\dfrac{2\sqrt{3}}{3}b=0\) (Do a, b > 0)
\(\Leftrightarrow2\sqrt{x^2-x+1}=\dfrac{2\sqrt{3}}{3}\sqrt{x^2+x+1}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-x+1=\dfrac{1}{3}\left(x^2+x+1\right)\Leftrightarrow2x^2-4x+2=0\Leftrightarrow x=1\).
Vậy x = 1

b: Xét tứ giác ACOD có
I là trung điểm của CD
I là trung điểm của OA
Do đó: ACOD là hình bình hành
mà OC=OD
nên ACOD là hình thoi
Xét ΔCMO có
CA là đường trung tuyến
CA=MO/2
Do đó: ΔCMO vuông tại C
hay CM là tiếp tuyến của (O)

\(b,B=\dfrac{\sqrt{x}+2}{\sqrt{x}-3}+\dfrac{\sqrt{x}-8}{x-5\sqrt{x}+6}\left(x\ge0;x\ne4;x\ne9\right)\\ B=\dfrac{\left(\sqrt{x}+2\right)\left(\sqrt{x}-2\right)+\sqrt{x}-8}{\left(\sqrt{x}-2\right)\left(\sqrt{x}-3\right)}\\ B=\dfrac{x-4+\sqrt{x}-8}{\left(\sqrt{x}-2\right)\left(\sqrt{x}-3\right)}=\dfrac{\left(\sqrt{x}-3\right)\left(\sqrt{x}-4\right)}{\left(\sqrt{x}-2\right)\left(\sqrt{x}-3\right)}=\dfrac{\sqrt{x}-4}{\sqrt{x}-2}\)
\(c,B< A\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{\sqrt{x}-4}{\sqrt{x}-2}< \dfrac{\sqrt{x}+1}{\sqrt{x}-2}\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{\sqrt{x}-4}{\sqrt{x}-2}-\dfrac{\sqrt{x}+1}{\sqrt{x}-2}< 0\\ \Leftrightarrow\dfrac{-5}{\sqrt{x}-2}< 0\Leftrightarrow\sqrt{x}-2>0\left(-5< 0\right)\\ \Leftrightarrow x>4\\ d,P=\dfrac{B}{A}=\dfrac{\sqrt{x}-4}{\sqrt{x}-2}:\dfrac{\sqrt{x}+1}{\sqrt{x}-2}=\dfrac{\sqrt{x}-4}{\sqrt{x}+1}=1-\dfrac{5}{\sqrt{x}+1}\in Z\\ \Leftrightarrow5⋮\sqrt{x}+1\Leftrightarrow\sqrt{x}+1\inƯ\left(5\right)=\left\{-5;-1;1;5\right\}\\ \Leftrightarrow\sqrt{x}\in\left\{-6;-2;0;4\right\}\\ \Leftrightarrow x\in\left\{0;16\right\}\left(\sqrt{x}\ge0\right)\)
\(e,P=1-\dfrac{5}{\sqrt{x}+1}\)
Ta có \(\sqrt{x}+1\ge1,\forall x\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{5}{\sqrt{x}+1}\ge5\Leftrightarrow1-\dfrac{5}{\sqrt{x}+1}\le-4\)
\(P_{max}=-4\Leftrightarrow x=0\)


`4x^2 = 13`.
`=> x^2 = 13/4`.
`=> x = (sqrt 13)/(sqrt 4)`
`=> x = (+-sqrt 13)/2`.
Vậy `S = (+-sqrt 13)/2`.

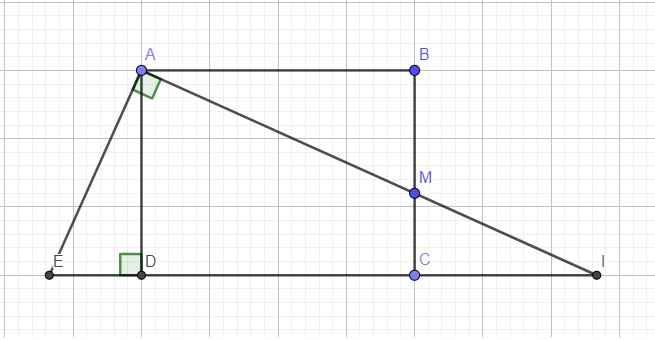
Qua A kẻ đường thẳng vuông góc AI cắt CD kéo dài tại E
Ta có \(\widehat{EAD}=\widehat{MAB}\) (cùng phụ \(\widehat{DAM}\))
\(\Rightarrow\Delta_vADE\sim\Delta_vABM\Rightarrow\dfrac{AE}{AM}=\dfrac{AD}{AB}=\dfrac{3}{4}\)
\(\Rightarrow\dfrac{1}{AE}=\dfrac{4}{3AM}\)
Áp dụng hệ thức lượng trong tam giác vuông AEI:
\(\dfrac{1}{AD^2}=\dfrac{1}{AE^2}+\dfrac{1}{AI^2}\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{1}{\left(\dfrac{3}{4}AB\right)^2}=\left(\dfrac{4}{3AM}\right)^2+\dfrac{1}{AI^2}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{1}{AB^2}=\dfrac{1}{AM^2}+\dfrac{9}{16AI^2}\)

\(x^2-3x=1\Leftrightarrow x^2-3x-1=0\)
Theo Vi - ét, ta có :
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x_1+x_2=-\dfrac{b}{a}=1\\x_1x_2=\dfrac{c}{a}=-1\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(A=\left(x_1-x_2\right)^2=\left(x_1+x_2\right)^2-4x_1x_2\)
\(=1^2-4.\left(-1\right)\)
\(=5\)
\(B=\dfrac{x_1}{x_2}+\dfrac{x_2}{x_1}=\dfrac{x_1^2+x_2^2}{x_1x_2}=\dfrac{\left(x_1+x_2\right)^2-2x_1x_2}{x_1x_2}=\dfrac{1^2-2.\left(-1\right)}{\left(-1\right)}=-4\)

5:
Gọi số học sinh giỏi, khá ở trường HK1 lần lượt là a,b
Theo đề, ta có hệ:
a+b=500 và 1,04a+1,02b=513
=>a=150 và b=350