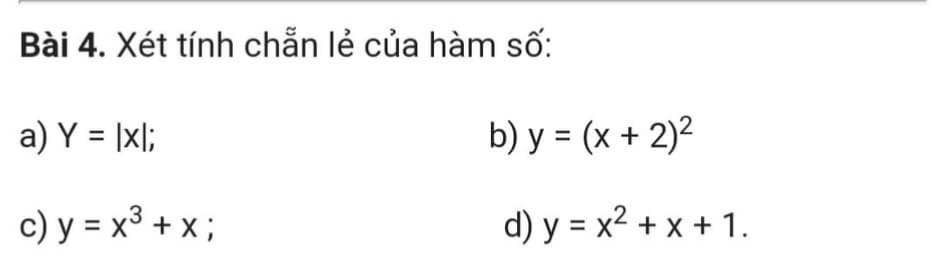Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


11c.
Từ đề bài ta có:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{16a-b^2}{4a}=\dfrac{9}{2}\\16a+4b+4=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}2b^2=-4a\\b=-4a-1\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow2b^2-b=1\Leftrightarrow2b^2-b-1=0\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}b=1\Rightarrow a=-\dfrac{1}{2}\\b=-\dfrac{1}{2}\Rightarrow a=-\dfrac{1}{8}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Có 2 parabol thỏa mãn: \(\left[{}\begin{matrix}y=-\dfrac{1}{2}x^2+x+4\\y=-\dfrac{1}{8}x^2-\dfrac{1}{2}x+4\end{matrix}\right.\)
4f.
Từ đề bài ta có:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}1+b+c=0\\\dfrac{4c-b^2}{4}=-1\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}c=-b-1\\c=\dfrac{b^2}{4}-1\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow\dfrac{b^2}{4}+b=0\)
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}b=0\Rightarrow c=-1\\b=-4\Rightarrow c=3\end{matrix}\right.\)
Có 2 parabol thỏa mãn: \(\left[{}\begin{matrix}y=x^2-1\\y=x^2-4x+3\end{matrix}\right.\)

2b.
\(Q=\dfrac{cosx}{sinx}+\dfrac{sinx}{1+cosx}=\dfrac{cosx\left(1+cosx\right)+sin^2x}{sinx\left(1+cosx\right)}=\dfrac{cosx+cos^2x+sin^2x}{sinx\left(1+cosx\right)}=\dfrac{cosx+1}{sinx\left(1+cosx\right)}=\dfrac{1}{sinx}\)
4b.
\(\Delta\) có 1 vtpt là (3;-4)
Gọi d là đường thẳng qua M và vuông góc \(\Delta\Rightarrow d\) nhận (4;3) là 1 vtpt
Phương trình d:
\(4\left(x-4\right)+3\left(y+2\right)=0\Leftrightarrow4x+3y-10=0\)
H là giao điểm d và \(\Delta\) nên tọa độ thỏa mãn:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}3x-4y+5=0\\4x+3y-10=0\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Rightarrow H\left(1;2\right)\)







Lời giải:
a. TXĐ: $\mathbb{R}$
Với $x\in\mathbb{R}$ thì $-x\in\mathbb{R}$
$f(x)=|x|=|-x|=f(-x)$
$\Rightarrow $ hàm chẵn
b. TXĐ: $\mathbb{R}$
Với $1\in\mathbb{R}$ thì $-1\in\mathbb{R}$
$f(1)=9; -f(1)=-9; f(-1)=1$
$\Rightarrow f(1)\neq f(-1); -f(1)\neq f(-1)$ nên hàm không chẵn không lẻ.
c.
TXĐ: $\mathbb{R}$
Với $x\in\mathbb{R}$ thì $-x\in\mathbb{R}$
$f(-x)=(-x)^3+(-x)=-(x^3+x)=-f(x)$ nên hàm lẻ
d.
TXĐ: $\mathbb{R}$
Với $1\in\mathbb{R}$ thì $-1\in\mathbb{R}$
$f(1)=3; f(-1)=1$
$\Rightarrow f(1)\neq f(-1); -f(1)\neq f(-1)$
Do đó hàm không chẵn không lẻ.