
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


Lời giải.
c.
$x^3-3x^2+3x-1=0$
$\Leftrightarrow (x-1)^3=0$
$\Leftrightarrow x-1=0$
$\Leftrightarrow x=1$
Vậy pt có tập nghiệm $S=\left\{1\right\}$
d. ĐKXĐ: $x\neq \frac{-1}{3}; -3$
PT $\Leftrightarrow \frac{(3x-1)(x+3)+(x-3)(3x+1)}{(3x+1)(x+3)}=2$
$\Leftrightarrow \frac{6x^2-6}{3x^2+10x+3}=2$
$\Leftrightarrow 6x^2-6=2(3x^2+10x+3)$
$\Leftrightarrow 20x+12=0$
$\Leftrightarrow x=\frac{-3}{5}$ (tm)
Vậy tập nghiệm của pt là $S=\left\{\frac{-3}{5}\right\}$
Bài 2:
a.
\(\left\{\begin{matrix} 2x-3y=11\\ 5x-4y=3\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow \left\{\begin{matrix} 10x-15y=55\\ 10x-8y=6\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow (10x-8y)-(10x-15y)=6-55\)
\(\Leftrightarrow 7y=-49\Leftrightarrow y=-7\)
\(x=\frac{3y+11}{2}=\frac{3.(-7)+11}{2}=-5\)
Vậy hpt có nghiệm $(x,y)=(-5,-7)$
b. Không đủ cơ sở để tìm $x,y$
c.
\(\left\{\begin{matrix} 5x+3y=\lambda\\ -x+\lambda y=-8\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow \left\{\begin{matrix} 5x+3y=\lambda\\ -5x+5\lambda y=-40\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow (3+5\lambda)y=\lambda-40\)
Nếu $\lambda = \frac{-3}{5}$ thì $0.y=\frac{-203}{5}$ (vô lý) nên hpt vô nghiệm
Nếu $\lambda \neq \frac{-3}{5}$ thì:
$y=\frac{\lambda - 40}{3+5\lambda}$
$x=8+\lambda y=\frac{\lambda ^2+24}{5\lambda +3}$


b: \(\Leftrightarrow\left(2x-7\right)\left(3x+7\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{7}{2}\\x=-\dfrac{7}{3}\end{matrix}\right.\)

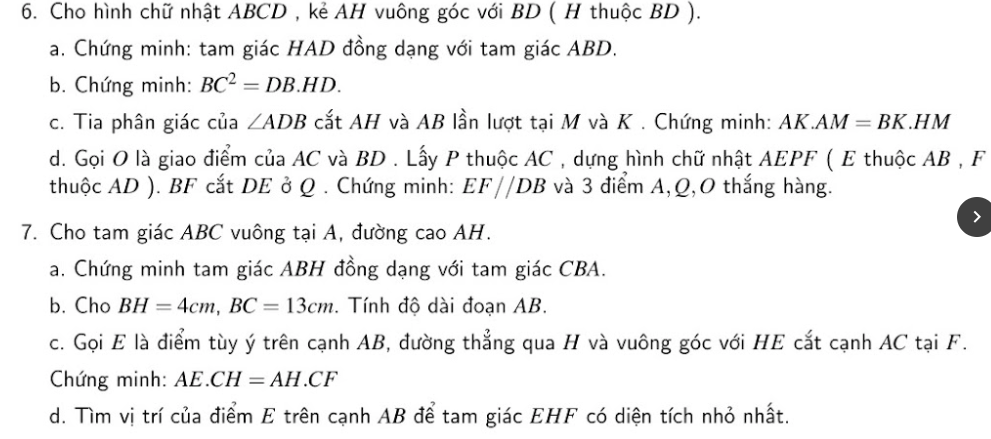
a: Xét tứ giác AEDF có
AE//DF
AF//DE
Do đó: AEDF là hình bình hành
mà \(\widehat{DAE}=90^0\)
nên AEDF là hình chữ nhật

Bài 2:
a: Xét ΔEHK và ΔGFI có
\(\widehat{EHK}=\widehat{GFI}\)
EH=GF
\(\widehat{E}=\stackrel\frown{G}\)
Do đó: ΔEHK=ΔGFI
Suy ra: EK=GI và KH=IF
Ta có: EK+KF=EF
GI+IH=GH
mà EF=GH
và EK=GI
nên KF=IH
Xét tứ giác FKHI có
FK=HI
HK=FI
Do đó: FKHI là hình bình hành

a)Đk:\(x\ne4\)
\(\dfrac{x^4}{4-x}+x^3+1=\dfrac{x^4+\left(x^3+1\right)\left(4-x\right)}{4-x}\)\(=\dfrac{x^4+\left(-x^4+4x^3+4-x\right)}{4-x}=\dfrac{4x^3-x+4}{4-x}\)
b) Đk: \(x\ne0;x\ne1\)
\(\dfrac{1}{x^2-x}+\dfrac{2x}{x-1}=\dfrac{1}{x\left(x-1\right)}+\dfrac{2x^2}{x\left(x-1\right)}=\dfrac{1+2x^2}{x\left(x-1\right)}\)


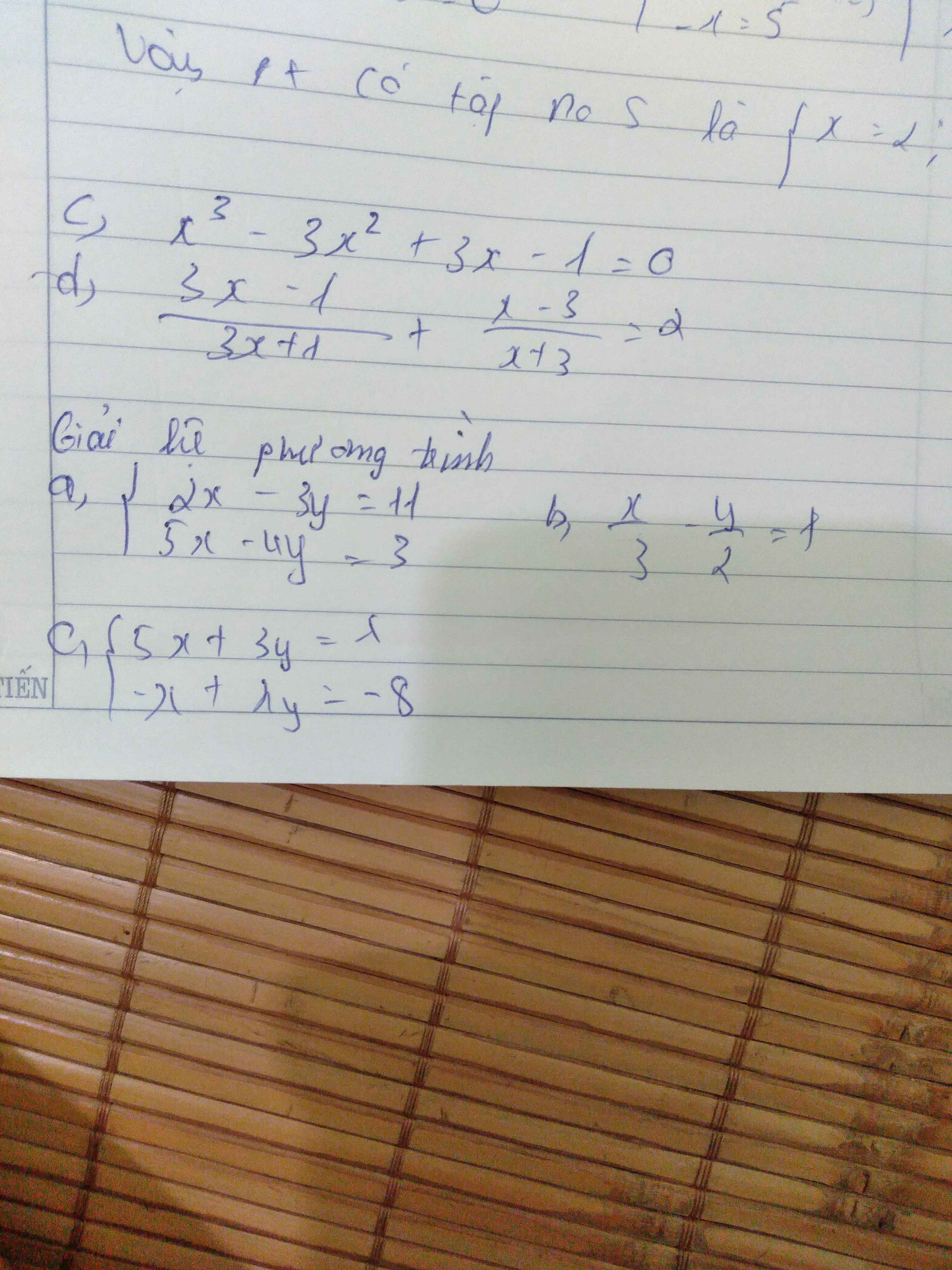



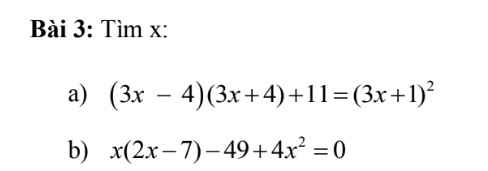











a) \(\dfrac{2x}{3}\)+\(\dfrac{2x-1}{6}\)=4 - \(\dfrac{x}{3}\)
<=>\(\dfrac{2x}{3}\)+\(\dfrac{2x-1}{6}\) - 4+\(\dfrac{x}{3}\)=0
<=>\(\dfrac{2x.2+2x-1-4.6+x.2}{6}\)=0
=>4x-2x-24+2x=0
<=>4x-24=0
<=>4x=24
<=>x=6
Vậy x=6
b)\(\dfrac{x-1}{2}\)+\(\dfrac{x-1}{4}\)=1 - \(\dfrac{2\left(x-1\right)}{3}\)
<=>\(\dfrac{x-1}{2}\)+\(\dfrac{x-1}{4}\)-1+\(\dfrac{2\left(x-1\right)}{3}\)=0
<=>\(\dfrac{6.\left(x-1\right)+3\left(x-1\right)-1.12+4.2\left(x-1\right)}{12}\)=0
=>6x-6+3x-3-12+4x-4+2x-2=0
<=>15x-27=0
<=>15x=27
<=>x=\(\dfrac{9}{5}\)
Vậy x=\(\dfrac{9}{5}\)