
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


ĐKXĐ: \(x\notin\left\{0;-9\right\}\)
Ta có: \(\dfrac{1}{x+9}-\dfrac{1}{x}=\dfrac{1}{5}+\dfrac{1}{4}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{20x}{20x\left(x+9\right)}-\dfrac{20\left(x+9\right)}{20x\left(x+9\right)}=\dfrac{4x\left(x+9\right)+5x\left(x+9\right)}{20x\left(x+9\right)}\)
Suy ra: \(4x^2+36x+5x^2+45x=20x-20x-180\)
\(\Leftrightarrow9x^2+81x+180=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2+9x+20=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2+4x+5x+20=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\left(x+4\right)+5\left(x+4\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+4\right)\left(x+5\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x+4=0\\x+5=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-4\left(nhận\right)\\x=-5\left(nhận\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy: S={-4;-5}

Hướng làm:
Thấy cả tử mẫu cộng lại đều bằng 2021 → Cộng thêm 1 rồi quy đồng với mỗi phân thức
\(\dfrac{x+2}{2019}+1+\dfrac{x+3}{2018}+1=\dfrac{x+4}{2017}+1+\dfrac{x}{2021}+1\\ \Leftrightarrow\dfrac{x+2021}{2019}+\dfrac{x+2021}{2018}-\dfrac{x+2021}{2017}-\dfrac{x+2021}{2021}=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(x+2021\right)\left(\dfrac{1}{2019}+\dfrac{1}{2018}-\dfrac{1}{2017}-\dfrac{1}{2021}\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow x+2021=0\Leftrightarrow x=-2021\)
\(< =>\dfrac{x+2}{2019}+1+\dfrac{x+3}{2018}+1=\dfrac{x+4}{2017}+1+\dfrac{x}{2021}+1\)
\(< =>\dfrac{x+2+2019}{2019}+\dfrac{x+3+2018}{2018}=\dfrac{x+4+2017}{2017}+\dfrac{x+2021}{2021}\)
\(< =>\dfrac{x+2021}{2019}+\dfrac{x+2021}{2018}-\dfrac{x+2021}{2017}-\dfrac{x+2021}{2021}=0\)
\(< =>\left(x+2021\right)\left(\dfrac{1}{2019}+\dfrac{1}{2018}-\dfrac{1}{2017}-\dfrac{1}{2021}=\right)=0\)
\(< =>x+2021=0< =>x=-2021\)
Vậy....

\(\frac{x+2}{2019}+\frac{x+3}{2018}=\frac{x+4}{2017}+\frac{x}{2021}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\frac{x+2}{2019}+1+\frac{x+3}{2018}+1=\frac{x+4}{2017}+1+\frac{x}{2021}+1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\frac{x+2021}{2019}+\frac{x+2021}{2018}=\frac{x+2021}{2017}+\frac{x+2021}{2021}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x+2021=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=-2021\)

a: \(A=\dfrac{x}{x+3}-1=\dfrac{x-x-3}{x+3}=\dfrac{-3}{x+3}\)
\(B=\dfrac{9-x^2+x^2-9-x^2+4x-4}{\left(x+3\right)\left(x-2\right)}=\dfrac{-\left(x-2\right)^2}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x+3\right)}=\dfrac{-x+2}{x+3}\)
b: B nguyên
=>-x-3+5 chia hết cho x+3
=>x+3 thuộc {1;-1;5;-5}
=>x thuộc {-2;-4;-8}
c: P=A:B
=(-3/x+3):(-x+2)/(x+3)
=3/(x-2)

\(1,7x-8=4x+7\)
\(\Leftrightarrow7x-8-4x=7\)
\(\Leftrightarrow7x-4x=7+8\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3x=15\)
\(\Rightarrow x=5\)
\(2,3-2x=3\left(x+1\right)-x-2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3-2x=2x+1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-2x+3=2x+1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-2x-2x=1-3\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-4x=-2\)
\(\Rightarrow x=\dfrac{1}{2}\)
\(3,5\left(3x+2\right)=4x+1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow5.3x+5.2=4x+1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow15x+10=4x+1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow15x-4x=1-10\)
\(\Leftrightarrow11x=-9\)
\(\Rightarrow x=\dfrac{-9}{11}\)



\(a,=x^2+x+4x+4=\left(x+1\right)\left(x+4\right)\\ b,=x^2+2x-3x-6=\left(x-3\right)\left(x+2\right)\\ c,=x^2-2x-3x+6=\left(x-2\right)\left(x-3\right)\\ d,=3\left(x^2-2x+5x-10\right)=3\left(x-2\right)\left(x+5\right)\\ e,=-3x^2+6x-x+2=\left(x-2\right)\left(1-3x\right)\\ f,=x^2-x-6x+6=\left(x-1\right)\left(x-6\right)\\ h,=4\left(x^2-3x-6x+18\right)=4\left(x-3\right)\left(x-6\right)\\ i,=3\left(3x^2-3x-8x+5\right)=3\left(x-1\right)\left(3x-8\right)\\ k,=-\left(2x^2+x+4x+2\right)=-\left(2x+1\right)\left(x+2\right)\\ l,=x^2-2xy-5xy+10y^2=\left(x-2y\right)\left(x-5y\right)\\ m,=x^2-xy-2xy+2y^2=\left(x-y\right)\left(x-2y\right)\\ n,=x^2+xy-3xy-3y^2=\left(x+y\right)\left(x-3y\right)\)

a: Xét ΔBAC có
D là trung điểm của AB
M là trung điểm của AC
Do đó: DM là đường trung bình của ΔABC
Suy ra: DM//BC và \(DM=\dfrac{BC}{2}=3.5\left(cm\right)\)

a: Xét tứ giác MIPC có
K là trung điểm của MP
K là trung điểm của IC
Do đó: MIPC là hình bình hành
mà MI=PI
nên MIPC là hình thoi


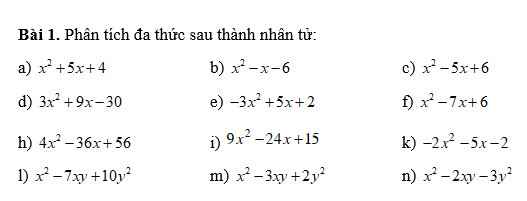

Ta có
\(\frac{1}{a^2}+\frac{1}{b^2}+\frac{1}{c^2}=\frac{b^2c^2+a^2c^2+a^2b^2}{a^2b^2c^2}=\frac{2}{3}.\)
\(\Rightarrow b^2c^2+a^2c^2+a^2b^2=\frac{2.a^2b^2c^2}{3}\)
Ta có
\(\frac{bc}{a}+\frac{ac}{b}+\frac{ab}{c}=\frac{b^2c^2+a^2c^2+a^2b^2}{abc}=\)
\(=\frac{2.a^2b^2c^2}{3.abc}=\frac{2.a.b.c}{3}=\frac{2.9}{3}=6\)