Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

1:
a: Khi m=1 thì (1) sẽ là x^2+2x-5=0
=>\(x=-1\pm\sqrt{6}\)
b: Δ=(2m)^2-4(-2m-3)
=4m^2+8m+12
=4m^2+8m+4+8=(2m+2)^2+8>=8>0
=>Phương trình luôn có hai nghiệm phân biệt
2:
Thay x=-1 và y=2 vào (P), ta được:
a*(-1)^2=2
=>a=2

a: Thay x=25/16 vào A, ta được:
\(A=\left(\dfrac{5}{4}+1\right):\left(\dfrac{5}{4}-3\right)=\dfrac{9}{4}:\dfrac{-7}{4}=\dfrac{-9}{7}\)
b: \(B=\dfrac{2x-6\sqrt{x}+x+3\sqrt{x}-3x-3}{x-9}\)
\(=\dfrac{-3\sqrt{x}-3}{x-9}\)

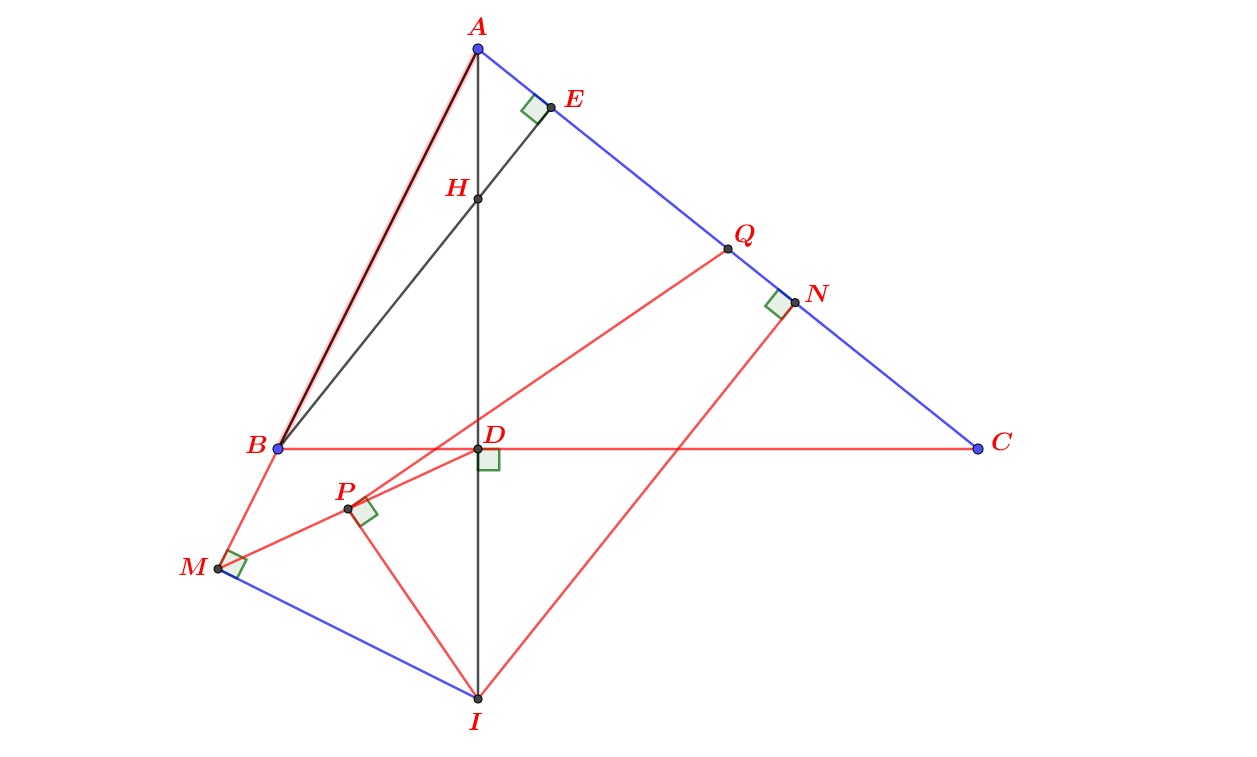
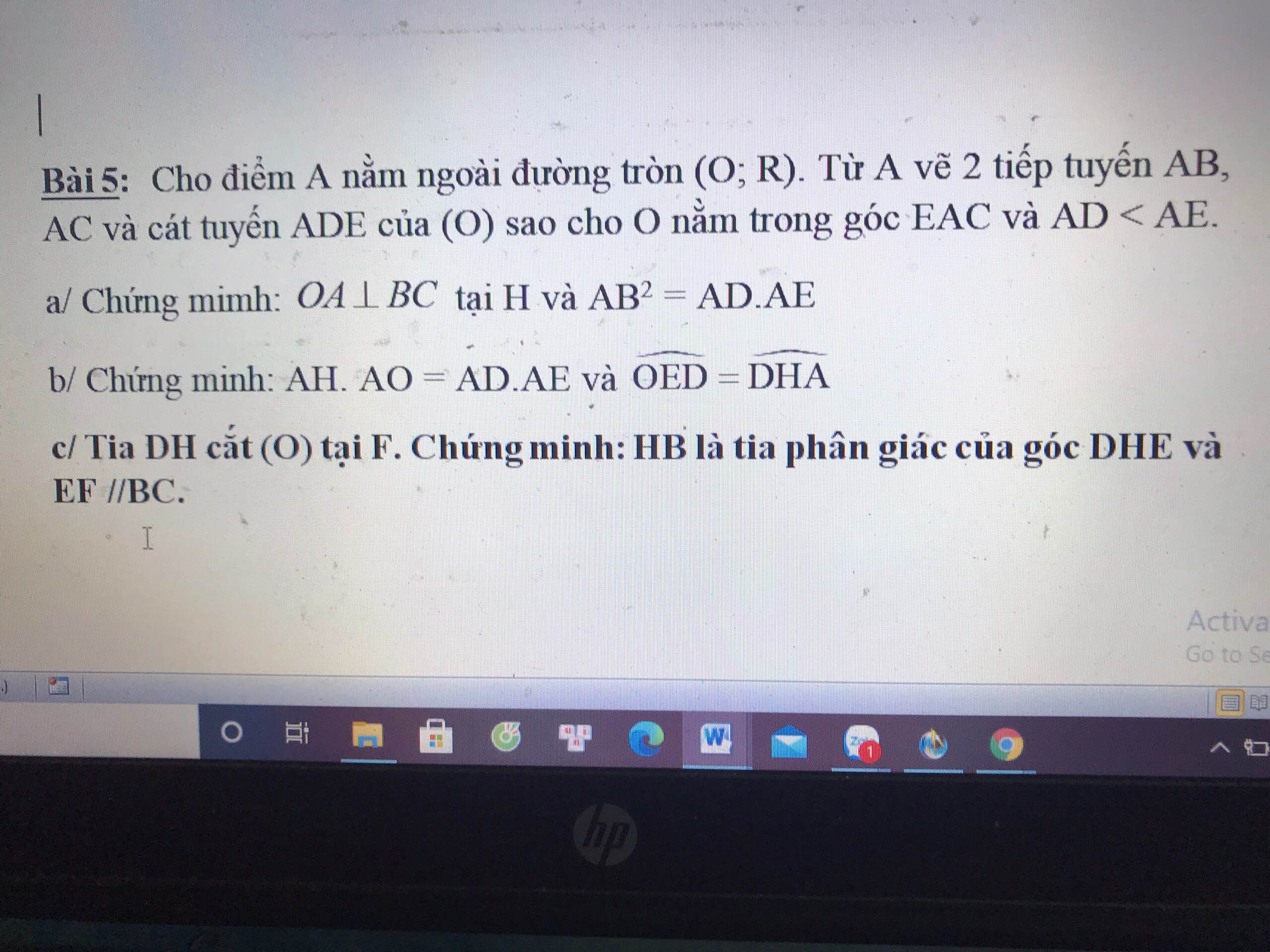
AB là tiếp tuyến nên \(AB\perp OB\) hay tam giác OAB vuông tại B
Áp dụng hệ thức lượng trong tam giác OAB với đường cao BH:
\(AB^2=AH.AO\)
Mà theo câu a. ta có \(AB^2=AD.AE\)
\(\Rightarrow AH.AO=AD.AE\)
//Từ đó ta cũng suy ra \(\dfrac{AH}{AD}=\dfrac{AE}{AO}\)
Xét hai tam giác AHE và ADO có: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{AH}{AD}=\dfrac{AE}{AO}\\\widehat{OAE}-chung\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow\Delta AHE\sim\Delta ADO\left(c.g.c\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow\widehat{DOA}=\widehat{HEA}\)
\(\Rightarrow\) Tứ giác OHDE nội tiếp (2 góc cùng chắn DH bằng nhau)
\(\Rightarrow\widehat{OED}+\widehat{OHD}=180^0\)
Mà \(\widehat{OHD}+\widehat{DHA}=180^0\)
\(\Rightarrow\widehat{OED}=\widehat{DHA}\)

b) \(\dfrac{x^2+2\sqrt{2}x+2}{x^2-2}=\dfrac{\left(x+\sqrt{2}\right)^2}{\left(x-\sqrt{2}\right)\left(x+\sqrt{2}\right)}=\dfrac{x+\sqrt{2}}{x-\sqrt{2}}\)



\(3x^4+4x^3-3x^2-2x+1=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3x^4+x^3-x^2+3x^3+x^2-x-3x^2-x+1=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2\left(3x^2+x-1\right)+x\left(3x^2+x-1\right)-\left(3x^2+x-1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x^2+x-1\right)\left(3x^2+x-1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x^2+x-1=0\left(1\right)\\3x^2+x-1=0\left(2\right)\end{cases}}\)
- \(\Delta_{\left(1\right)}=1^2-\left(-4\left(1.1\right)\right)=5\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x_{1,2}=\frac{-1\pm\sqrt{5}}{2}\left(tm\right)\)
- \(\Delta_{\left(2\right)}=1^2-\left(-4\left(3.1\right)\right)=13\)
\(x_{1,2}=\frac{-1\pm\sqrt{13}}{6}\left(tm\right)\)

Bài 4:
b: Xét ΔAHB vuông tại H có HM là đường cao
nên \(AM\cdot AB=AH^2\left(1\right)\)
Xét ΔAHC vuông tại H có HN là đường cao
nên \(AN\cdot AC=AH^2\left(2\right)\)
Từ (1) và (2) suy ra \(AM\cdot AB=AN\cdot AC\)
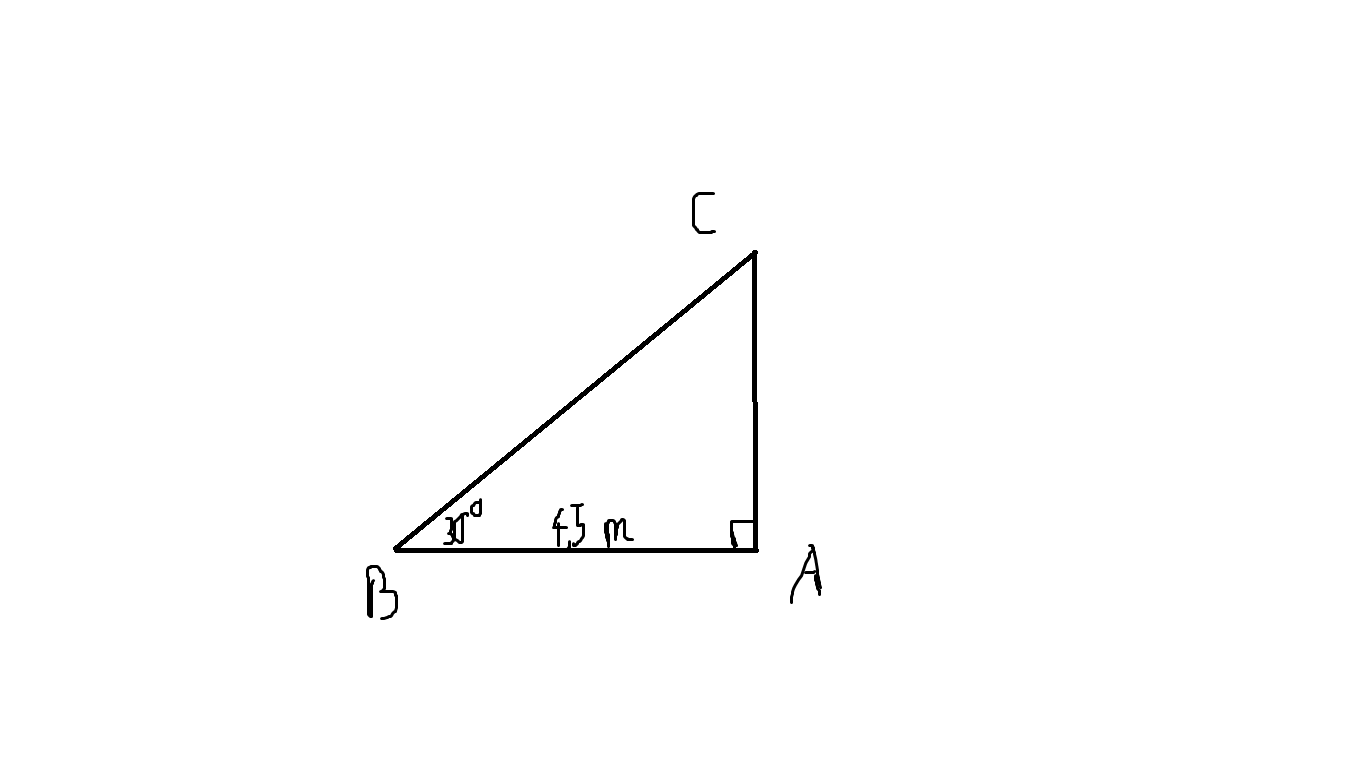
\(TanB=\dfrac{AC}{AB}\Rightarrow Tan30^o=\dfrac{AC}{4,5}\Rightarrow AC=Tan30^o.4,5=\dfrac{3\sqrt{3}}{2}\left(m\right)\)
\(CosB=\dfrac{AB}{BC}\Rightarrow Cos30^o=\dfrac{4,5}{BC}\Rightarrow BC=Cos30^o.4,5=\dfrac{9\sqrt{3}}{4}\)
Chiều cao ban đầu của cây tre là: \(\dfrac{3\sqrt{3}}{2}+\dfrac{9\sqrt{3}}{4}=\dfrac{15\sqrt{3}}{4}\approx6,5\left(m\right)\)




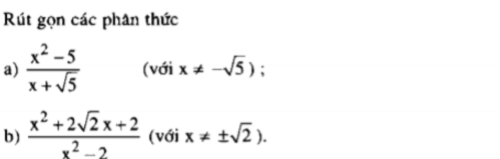

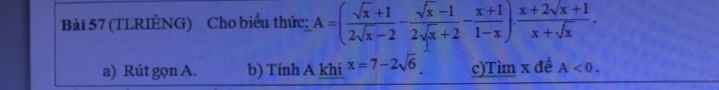

nhỏ quá bn !