Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

Lời giải:
ĐKXĐ: $x\geq 5$
$2x^2-8x-6=2\sqrt{x-5}\leq (x-5)+1$ theo BĐT Cô-si
$\Leftrightarrow 2x^2-9x-2\leq 0$
$\Leftrightarrow 2x(x-5)+(x-2)\leq 0$
Điều này vô lý do $2x(x-5)\geq 0; x-2\geq 3>0$ với mọi $x\geq 5$
Vậy pt vô nghiệm nên không có đáp án nào đúng.

b. Tự đặt đk
\(x^{^2}+5\sqrt{x-3}=21\\\Leftrightarrow x^{^2}-9+5\sqrt{x-3}=12 \)
Đặt \(a=\sqrt{x-3}\) \(\left(a\ge0\right)\) Phương trình trở thành:
\(a^{^2}\left(a^{^2}+6\right)+5a=12\\ \Leftrightarrow a^{^4}+6a^{^2}+5a-12=0\\ \Leftrightarrow a^{^4}-a^{^3}+a^{^3}-a^{^2}+7a^{^2}-7a+12a-12=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(a-1\right)\left(a^{^3}+a^{^2}+7a+12\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow a=1\left(tmdk\right)\)
Ta có: vì \(a\ge0\) nên \(a^{^3}+a^{^2}+7a+12\ne0\)
Với a = 1 ta có x=4 (tmdk)

Ta có: \(\Delta=4m^2+4m-11\)
Để phương trình có 2 nghiệm phân biệt \(\Leftrightarrow4m^2+4m-11>0\)
Theo Vi-ét, ta có: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x_1+x_2=2m+3\\x_1x_2=2m+5\end{matrix}\right.\)
Để phương trình có 2 nghiệm dương phân biệt
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}4m^2+4m-11>0\\2m+3>0\\2m+5>0\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\left[{}\begin{matrix}m< \dfrac{-1-2\sqrt{3}}{2}\\m>\dfrac{-1+2\sqrt{3}}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\\m>-\dfrac{3}{2}\\m>-\dfrac{5}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Leftrightarrow m>\dfrac{-1+2\sqrt{3}}{2}\)
Mặt khác: \(\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{x_1}}+\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{x_2}}=\dfrac{4}{3}\)
\(\Rightarrow\dfrac{x_1+x_2+2\sqrt{x_1x_2}}{x_1x_2}=\dfrac{16}{9}\) \(\Rightarrow\dfrac{2m+3+2\sqrt{2m+5}}{2m+5}=\dfrac{16}{9}\)
\(\Rightarrow18m+27+18\sqrt{2m+5}=32m+80\)
\(\Leftrightarrow14m-53=18\sqrt{2m+5}\)
\(\Rightarrow\) ...

d. \(\sqrt{9x^2+12x+4}=4\)
<=> \(\sqrt{\left(3x+2\right)^2}=4\)
<=> \(|3x+2|=4\)
<=> \(\left[{}\begin{matrix}3x+2=4\\3x+2=-4\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}3x=2\\3x=-6\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{2}{3}\\x=-2\end{matrix}\right.\)
c: Ta có: \(\dfrac{5\sqrt{x}-2}{8\sqrt{x}+2.5}=\dfrac{2}{7}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow35\sqrt{x}-14=16\sqrt{x}+5\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=1\)

\(x^2=6+2\sqrt{2}+2\sqrt{\left[\left(3+\sqrt{2}\right)+\left(\sqrt{3}+\sqrt{6}\right)\right].\left[\left(3+\sqrt{2}\right)-\left(\sqrt{3}+\sqrt{6}\right)\right]}\)
\(=6+2\sqrt{2}+2\sqrt{11+6\sqrt{2}-\left(9+6\sqrt{2}\right)}=6+2\sqrt{2}+2\sqrt{2}=6+4\sqrt{2}=\left(\sqrt{2}+2\right)^2\)
\(\Rightarrow x=\sqrt{2}+2\)
...............................................................

`B=sqrtx/(sqrtx+3)+(2sqrtx)/(\sqrtx-3)-(3x+9)/(x-9)(x>0,x ne 9)`
`=(x-3sqrtx+2x+6sqrtx-3x-9)/(x-9)`
`=(3sqrtx-9)/(x-9)`
`=(3(sqrtx-3))/((sqrtx-3)(sqrtx+3))`
`=3/(sqrtx+3)`
`P=A.B=3/x`
`Px+3\sqrt{x-5}=x-2sqrtx+7(x>=5)`
`<=>3+3\sqrt{x-5}=x-2sqrtx+7`
`<=>x-2sqrtx+4-3\sqrt{x-5}=0`
`<=>2x-4sqrtx+8-6sqrt{x-5}=0`
`<=>x-4sqrtx+4+x-5-6sqrt{x-5}+9=0`
`<=>(sqrtx-2)^2+(\sqrt{x-5}-3)^2=0`
Dấu "=" xảy ra khi $\begin{cases}x=4\\x=14\\\end{cases}(l)$
Vậy khong có giá trị của x thể pt có nghiệm

c: Ta có: \(\sqrt{x-1}+\sqrt{9x-9}-\sqrt{4x-4}=4\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2\sqrt{x-1}=4\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x-1=4\)
hay x=5
e: Ta có: \(\sqrt{4x^2-28x+49}-5=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left|2x-7\right|=5\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}2x-7=5\\2x-7=-5\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=6\\x=1\end{matrix}\right.\)
a. ĐKXĐ: $x\in\mathbb{R}$
PT $\Leftrightarrow \sqrt{(x-2)^2}=2-x$
$\Leftrightarrow |x-2|=2-x$
$\Leftrightarrow 2-x\geq 0$
$\Leftrightarrow x\leq 2$
b. ĐKXĐ: $x\geq 2$
PT $\Leftrightarrow \sqrt{4}.\sqrt{x-2}-\frac{1}{5}\sqrt{25}.\sqrt{x-2}=3\sqrt{x-2}-1$
$\Leftrightarrow 2\sqrt{x-2}-\sqrt{x-2}=3\sqrt{x-2}-1$
$\Leftrightarrow 1=2\sqrt{x-2}$
$\Leftrightarrow \frac{1}{2}=\sqrt{x-2}$
$\Leftrightarrow \frac{1}{4}=x-2$
$\Leftrightarrow x=\frac{9}{4}$ (tm)

a) Ta có: \(A=\dfrac{\sqrt{x}+1}{\sqrt{x}-1}+\dfrac{\sqrt{x}-1}{\sqrt{x}+1}-\dfrac{3\sqrt{x}}{x-1}\)
\(=\dfrac{x+2\sqrt{x}+1+x-2\sqrt{x}+1-3\sqrt{x}}{\left(\sqrt{x}-1\right)\left(\sqrt{x}+1\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{2x-3\sqrt{x}+2}{\left(\sqrt{x}-1\right)\left(\sqrt{x}+1\right)}\)
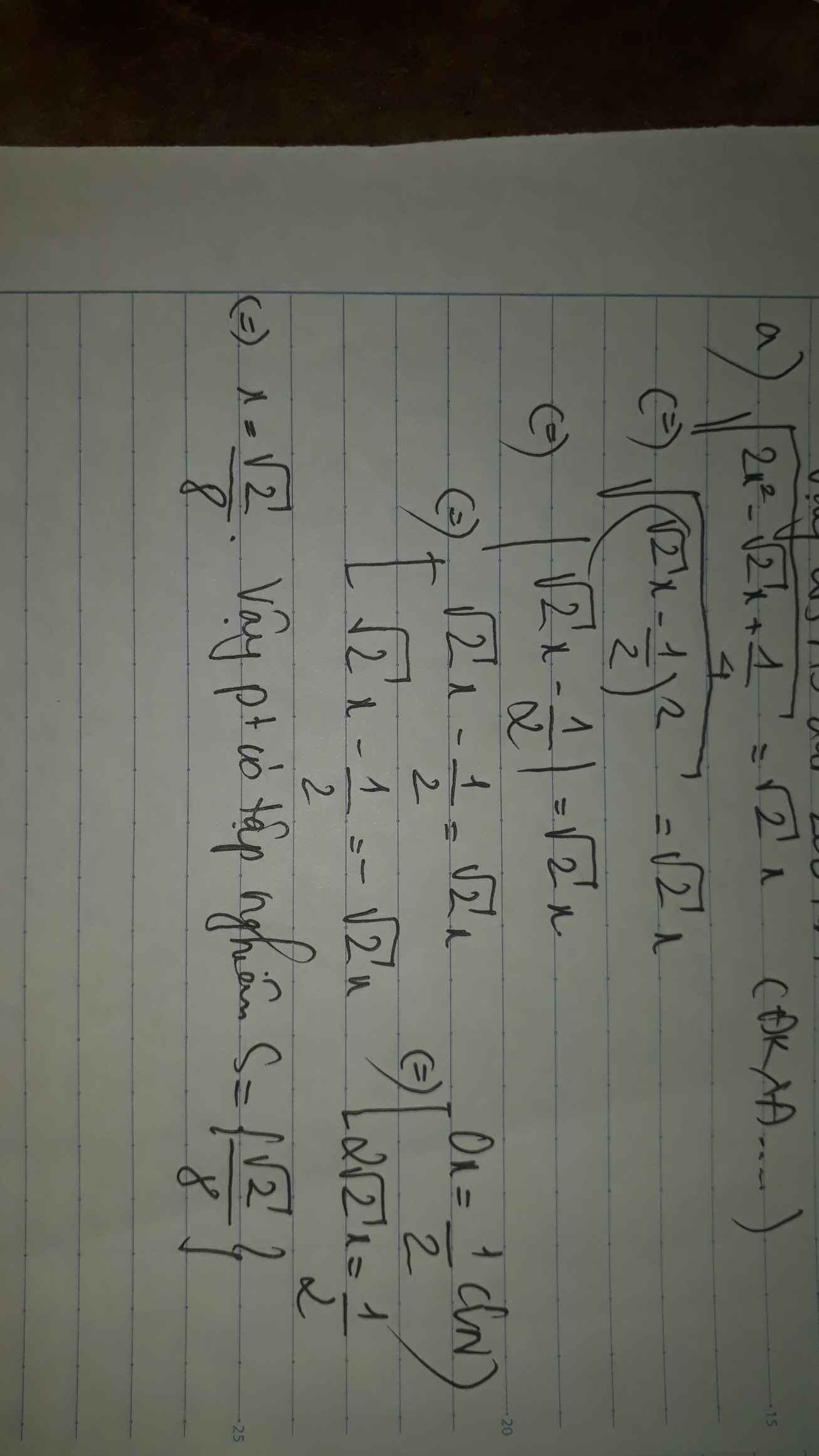

\(\sqrt{4x-8}-2\sqrt{\dfrac{x-2}{4}}=3\left(x\ge2\right)\\ \Leftrightarrow2\sqrt{x-2}-\sqrt{x-2}=3\\ \Leftrightarrow\sqrt{x-2}=3\Leftrightarrow x-2=9\\ \Leftrightarrow x=11\left(tm\right)\)
ĐKXĐ: \(x\ge2\)
\(pt\Leftrightarrow2\sqrt{x-2}-\sqrt{x-2}=3\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\sqrt{x-2}=3\Leftrightarrow x-2=9\Leftrightarrow x=11\left(tm\right)\)