Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

1) ĐKXĐ: \(x\ge\dfrac{5}{2}\)
\(\sqrt{x^2}=2x-5\\ \Rightarrow\left|x\right|=2x-5\\ \Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=2x-5\\x=5-2x\end{matrix}\right.\\ \Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=5\left(tm\right)\\x=\dfrac{5}{3}\left(ktm\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
2) ĐKXĐ: \(x\ge3\)
\(\sqrt{25x^2-10x+1}=2x-6\\ \Rightarrow\left|5x-1\right|=2x-6\\ \Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}5x-1=2x-6\\5x-1=6-2x\end{matrix}\right.\\ \Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-\dfrac{5}{3}\left(ktm\right)\\x=1\left(tm\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
3) ĐKXĐ: \(x\ge\dfrac{5}{2}\)
\(\sqrt{25-10x+x^2}=2x-5\\ \Rightarrow\left|x-5\right|=2x-5\\ \Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-5=2x-5\\x-5=5-2x\end{matrix}\right.\\ \Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\left(ktm\right)\\x=\dfrac{10}{3}\left(tm\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
4) ĐKXĐ: \(x\ge\dfrac{1}{2}\)
\(\sqrt{1-2x+x^2}=2x-1\\ \Rightarrow\left|x-1\right|=2x-1\\ \Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-1=2x-1\\x-1=1-2x\end{matrix}\right.\\ \Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\left(ktm\right)\\x=\dfrac{2}{3}\left(tm\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)

a, ĐKXĐ : \(x\ge\dfrac{1}{2}\)
PT <=> 2x - 1 = 5
<=> x = 3 ( TM )
Vậy ...
b, ĐKXĐ : \(x\ge5\)
PT <=> x - 5 = 9
<=> x = 14 ( TM )
Vậy ...
c, PT <=> \(\left|2x+1\right|=6\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}2x+1=6\\2x+1=-6\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{5}{2}\\x=-\dfrac{7}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy ...
d, PT<=> \(\left|x-3\right|=3-x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-3=x-3\\x-3=3-x\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy phương trình có vô số nghiệm với mọi x \(x\le3\)
e, ĐKXĐ : \(-\dfrac{5}{2}\le x\le1\)
PT <=> 2x + 5 = 1 - x
<=> 3x = -4
<=> \(x=-\dfrac{4}{3}\left(TM\right)\)
Vậy ...
f ĐKXĐ : \(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x\le0\\1\le x\le3\end{matrix}\right.\)
PT <=> \(x^2-x=3-x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=\pm\sqrt{3}\) ( TM )
Vậy ...
a) \(\sqrt{2x-1}=\sqrt{5}\) (x \(\ge\dfrac{1}{2}\))
<=> 2x - 1 = 5
<=> x = 3 (tmđk)
Vậy S = \(\left\{3\right\}\)
b) \(\sqrt{x-5}=3\) (x\(\ge5\))
<=> x - 5 = 9
<=> x = 4 (ko tmđk)
Vậy x \(\in\varnothing\)
c) \(\sqrt{4x^2+4x+1}=6\) (x \(\in R\))
<=> \(\sqrt{\left(2x+1\right)^2}=6\)
<=> |2x + 1| = 6
<=> \(\left[{}\begin{matrix}\text{2x + 1=6}\\\text{2x + 1}=-6\end{matrix}\right.< =>\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{5}{2}\\x=\dfrac{-7}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)(tmđk)
Vậy S = \(\left\{\dfrac{5}{2};\dfrac{-7}{2}\right\}\)

a
ĐK:
\(3-x\ge0\\ \Leftrightarrow x\le3\)
\(\sqrt{x^2-3x+2}=3-x\\ \Leftrightarrow x^2-3x+2=\left(3-x\right)^2=9-6x+x^2\\ \Leftrightarrow x^2-3x+2-9+6x-x^2=0\\ \Leftrightarrow3x=7\\ \Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{7}{3}\left(nhận\right)\)
Thử lại: \(\sqrt{\left(\dfrac{7}{3}\right)^2-3.\dfrac{7}{3}+2}=\dfrac{2}{3}>0\)
Vậy phương trình có nghiệm duy nhất \(x=\dfrac{7}{3}\)
b
\(\sqrt{4x^2-20x+25}=\sqrt{\left(2x\right)^2-2.2x.5+5^2}=\sqrt{\left(2x-5\right)^2}=\left|2x-5\right|\)
Phương trình trở thành:
\(\left|2x-5\right|+2x=5\) (1)
Với \(x< \dfrac{5}{2}\) thì (1) \(\Leftrightarrow5-2x+2x=5\Leftrightarrow5=5\)
=> Với \(x< \dfrac{5}{2}\) thì phương trình có nghiệm với mọi x \(< \dfrac{5}{2}\) (I)
Với \(x\ge\dfrac{5}{2}\) thì (1)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x-5+2x=5\\ \Leftrightarrow2x-5+2x-5=0\\ \Leftrightarrow4x=10\\ \Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{10}{4}=\dfrac{5}{2}\left(nhận\right)\left(II\right)\)
Từ (I), (II) kết luận phương trình có nghiệm với mọi \(x\le\dfrac{5}{2}\)
c
\(\Leftrightarrow\left|3-2x\right|=4\) (1)
Nếu \(x\le\dfrac{3}{2}\) thì (1)
\(\Leftrightarrow3-2x=4\\ \Leftrightarrow2x=-1\\ \Leftrightarrow x=-\dfrac{1}{2}\left(nhận\right)\)
Nếu \(x>\dfrac{3}{2}\) thì (1)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x-3=4\\ \Leftrightarrow2x=7\\ \Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{7}{2}\left(nhận\right)\)
Vậy phương trình có 2 nghiệm \(S=\left\{-\dfrac{1}{2};\dfrac{7}{2}\right\}\)
a: =>x^2-3x+2=x^2-6x+9 và x<=3
=>3x=7 và x<=3
=>x=7/3(loại)
b: =>|2x-5|=5-2x
=>2x-5<=0
=>x<=5/2
c: =>|2x-3|=4
=>2x-3=4 hoặc 2x-3=-4
=>x=-1/2 hoặc x=7/2

1) \(ĐK:x\in R\)
2) \(ĐK:x< 0\)
3) \(ĐK:x\in\varnothing\)
4) \(=\sqrt{\left(x+1\right)^2+2}\)
\(ĐK:x\in R\)
5) \(=\sqrt{-\left(a-4\right)^2}\)
\(ĐK:x\in\varnothing\)

1) \(\sqrt{5-2x}=6\left(đk:x\le\dfrac{5}{2}\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow5-2x=36\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x=-31\Leftrightarrow x=-\dfrac{31}{2}\left(tm\right)\)
2) \(\sqrt{2-x}=\sqrt{x+1}\left(đk:2\ge x\ge-1\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2-x=x+1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x=1\Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{1}{2}\left(tm\right)\)
3) \(\Leftrightarrow\sqrt{\left(2x+1\right)^2}=6\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left|2x+1\right|=6\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}2x+1=6\\2x+1=-6\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{5}{2}\\x=-\dfrac{7}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
4) \(\sqrt{x^2-10x+25}=x-2\left(đk:x\ge2\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\sqrt{\left(x-5\right)^2}=x-2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left|x-5\right|=x-2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-5=x-2\left(x\ge5\right)\\x-5=2-x\left(2\le x< 5\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}5=2\left(VLý\right)\\x=\dfrac{7}{2}\left(tm\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)

a: Ta có: \(\sqrt{\left(x-3\right)^2}=3-x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left|x-3\right|=3-x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x-3\le0\)
hay \(x\le3\)
b: Ta có: \(\sqrt{4x^2-20x+25}+2x=5\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left|2x-5\right|=5-2x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x-5\le0\)
hay \(x\le\dfrac{5}{2}\)

a,\(Đkxđ:x\ge3\)
Ta có:
\(\sqrt{\left(x-3\right)^2}=3-x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow|x-3|=3-x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x-3=\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-3\\3-x\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(TH1:x-3=x-3\Leftrightarrow0x=0\)
\(\Rightarrow\)\(x\in R\) và \(x\ge3\)
\(TH2:x-3=3-x\Leftrightarrow2x=6\Leftrightarrow x=3\)( ko thỏa mãn điều kiện)
vậy \(\left\{x\in R/x\ge3\right\}\)
b, \(Đkxđ:x\le\dfrac{5}{2}\)
Ta có:
\(\sqrt{25-20x+4x^2}+2x=5\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\sqrt{\left(5-2x\right)^2}+2x=5\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left|5-2x\right|=5-2x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}5-2x=5-2x\\5-2x=2x-5\end{matrix}\right.\)\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}0x=0\\4x=10\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x\in R\\x=\dfrac{5}{2}\left(tmđk\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy \(\left\{x\in R/x\le\dfrac{5}{2}\right\}\)

√(x² + x + 1) = 1
⇔ x² + x + 1 = 1
⇔ x² + x = 0
⇔ x(x + 1) = 0
⇔ x = 0 hoặc x + 1 = 0
*) x + 1 = 0
⇔ x = -1
Vậy x = 0; x = -1
--------------------
√(x² + 1) = -3
Do x² ≥ 0 với mọi x
⇒ x² + 1 > 0 với mọi x
⇒ x² + 1 = -3 là vô lý
Vậy không tìm được x thỏa mãn yêu cầu
--------------------
√(x² - 10x + 25) = 7 - 2x
⇔ √(x - 5)² = 7 - 2x
⇔ |x - 5| = 7 - 2x (1)
*) Với x ≥ 5, ta có
(1) ⇔ x - 5 = 7 - 2x
⇔ x + 2x = 7 + 5
⇔ 3x = 12
⇔ x = 4 (loại)
*) Với x < 5, ta có:
(1) ⇔ 5 - x = 7 - 2x
⇔ -x + 2x = 7 - 5
⇔ x = 2 (nhận)
Vậy x = 2
--------------------
√(2x + 5) = 5
⇔ 2x + 5 = 25
⇔ 2x = 20
⇔ x = 20 : 2
⇔ x = 10
Vậy x = 10
-------------------
√(x² - 4x + 4) - 2x +5 = 0
⇔ √(x - 2)² - 2x + 5 = 0
⇔ |x - 2| - 2x + 5 = 0 (2)
*) Với x ≥ 2, ta có:
(2) ⇔ x - 2 - 2x + 5 = 0
⇔ -x + 3 = 0
⇔ x = 3 (nhận)
*) Với x < 2, ta có:
(2) ⇔ 2 - x - 2x + 5 = 0
⇔ -3x + 7 = 0
⇔ 3x = 7
⇔ x = 7/3 (loại)
Vậy x = 3
1)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2+x+1=1^2=1\\ \Leftrightarrow x^2+x=0\\ \Leftrightarrow x\left(x+1\right)=0\\ \Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\x=-1\end{matrix}\right.\)
2) Do \(x^2+1>0\forall x\) nên \(x\in\varnothing\)
3)
\(\Leftrightarrow\sqrt{\left(x-5\right)^2}=7-2x\\ \Leftrightarrow\left|x-5\right|=7-2x\)
Nếu \(x\ge5\) thì
\(\Leftrightarrow x-5-7+2x=0\\ \Leftrightarrow3x-12=0\\ \Leftrightarrow3x=12\\ \Rightarrow x=4\)
=> Loại trường hợp này
Nếu \(x< 5\) thì
\(\Leftrightarrow5-x-7+2x=0\\ \Leftrightarrow x-2=0\\ \Rightarrow x=2\)
=> Nhận trường hợp này
Vậy x = 2
4)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x+5=5^2=25\\ \Leftrightarrow2x=25-5=20\\ \Rightarrow x=\dfrac{20}{2}=10\)
5)
\(\Leftrightarrow\sqrt{\left(x-2\right)^2}-2x+5=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left|x-2\right|-2x+5=0\)
Nếu \(x\ge2\) thì
\(\Leftrightarrow x-2-2x+5=0\\ \Leftrightarrow3-x=0\\ \Rightarrow x=3\)
=> Nhận trường hợp này
Nếu \(x< 2\) thì
\(\Leftrightarrow2-x-2x+5=0\\ \Leftrightarrow7-3x=0\\ \Leftrightarrow3x=7\\ \Rightarrow x=\dfrac{7}{3}\)
=> Loại trường hợp này
Vậy x = 3
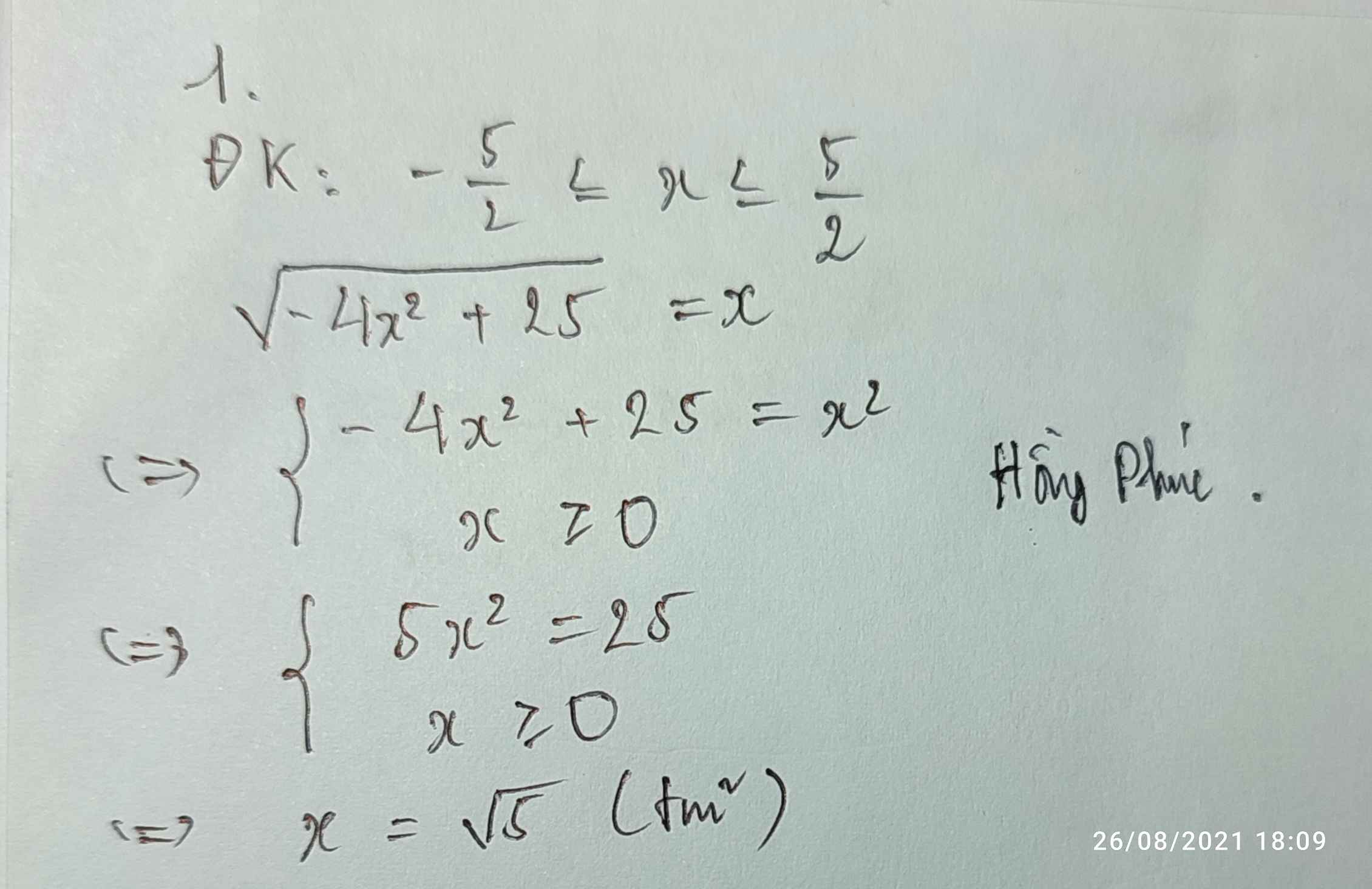
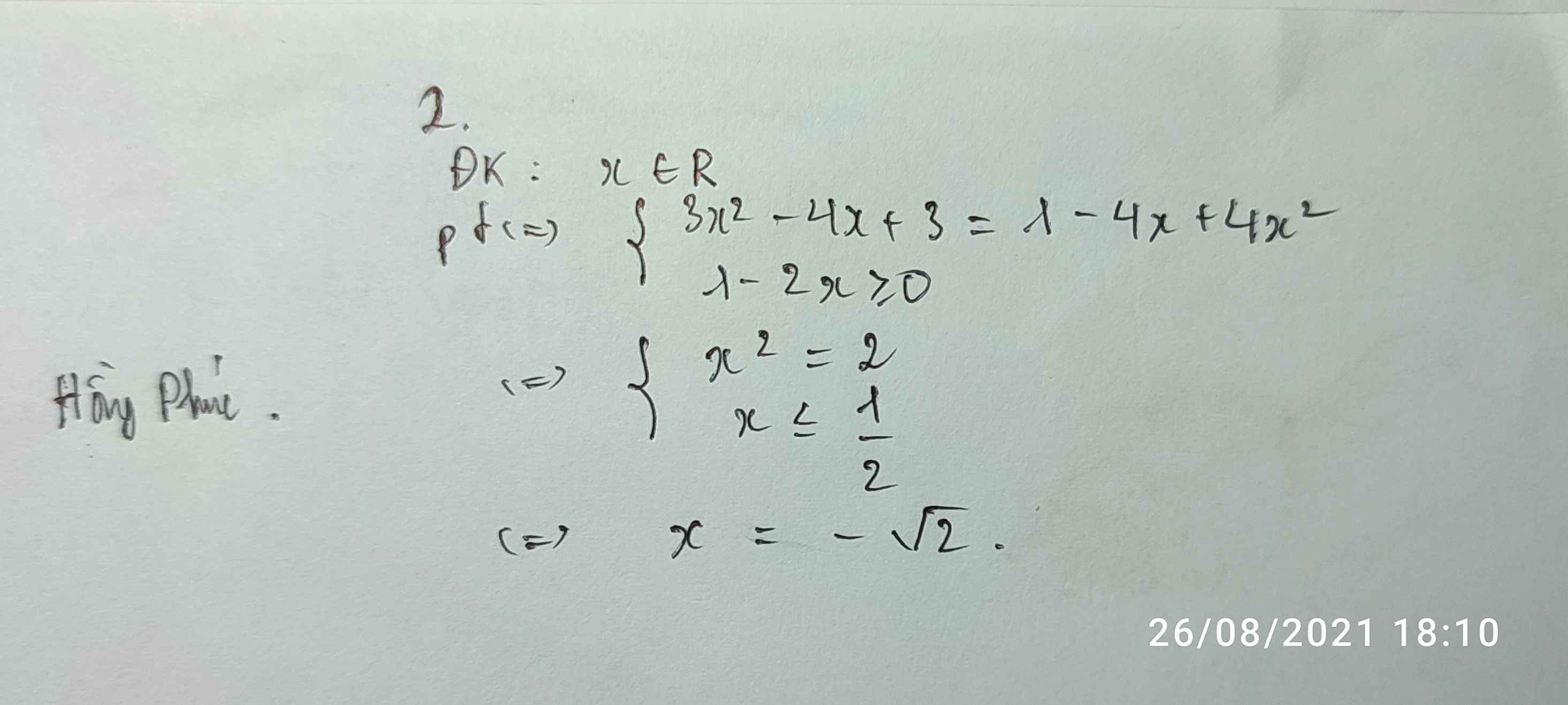
a.
\(\sqrt{x+2\sqrt{x-1}}=2\)
ĐKXĐ: \(x\ge1\)
\(\sqrt{x-1+2\sqrt{x-1}+1}=2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\sqrt{\left(\sqrt{x-1}+1\right)^2}=2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left|\sqrt{x-1}+1\right|=2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\sqrt{x-1}+1=2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\sqrt{x-1}=1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x-1=1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=2\)
b.
\(\sqrt{4x^2-20x+25}=5-2x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\sqrt{\left(2x-5\right)^2}=5-2x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left|5-2x\right|=5-2x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow5-2x\ge0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\le\dfrac{5}{2}\)
c.
ĐKXĐ: \(x\ge3\)
\(\sqrt{x^2-x-6}=\sqrt{x-3}\)
\(\Rightarrow x^2-x-6=x-3\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-2x-3=0\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-1\left(loại\right)\\x=3\end{matrix}\right.\)