
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


ĐKXĐ:\(x\ge0\)
Để \(\dfrac{2\sqrt{x}}{\sqrt{x}+3}\) nhận giá trị nguyên thì \(2\sqrt{x}⋮\sqrt{x}+3\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2\left(\sqrt{x}+3\right)-6⋮\sqrt{x}+3\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-6⋮\sqrt{x}+3hay\sqrt{x}+3\inƯ_{\left(-6\right)}\)
Vì \(\sqrt{x}\ge0\Rightarrow\sqrt{x}+3\ge3\)
TH1.\(\sqrt{x}+3=3\Leftrightarrow\sqrt{x}=0\Leftrightarrow x=0\left(tmĐKXĐ\right)\)
TH2.\(\sqrt{x}+3=6\Leftrightarrow\sqrt{x}=3\Leftrightarrow x=9\left(tmĐKXĐ\right)\)
Vậy,x={0;9}

Ta có: x + 1 x - 3 = x - 3 + 4 x - 3 = 1 + 4 x - 3
Để 1 + 4 x - 3 nhận giá trị nguyên thì 4 x - 3 phải có giá trị nguyên. Vì x nguyên nên √x là số nguyên hoặc số vô tỉ.
* Nếu x là số vô tỉ thì x - 3 là số vô tỉ nên 4 x - 3 không có giá trị nguyên. Trường hợp này không có giá trị nào của x để biểu thức nhận giá trị nguyên.
* Nếu
x
là số nguyên thì
x
- 3 là số nguyên. Vậy để 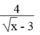 nguyên thì
x
- 3 phải là ước của 4.
nguyên thì
x
- 3 phải là ước của 4.
Đồng thời x ≥ 0 suy ra: x ≥ 0
Ta có: W(4) = {-4; -2; -1; 1; 2; 4}
Suy ra: x - 3 = -4 ⇒ x = -1 (loại)
x - 3 = -2 ⇒ x = 1 ⇒ x = 1
x - 3 = -1 ⇒ x = 2 ⇒ x = 4
x - 3 = 1 ⇒ x = 4 ⇒ x = 16
x - 3 = 2 ⇒ x = 5 ⇒ x = 25
x - 3 = 4 ⇒ x = 7 ⇒ x = 49
Vậy với x ∈ {1; 4; 16; 25; 49} thì biểu thức x + 1 x - 3 nhận giá trị nguyên.

\(\dfrac{\sqrt{x}+1}{\sqrt{x}+3}\left(x\ge0;x\ne9\right)=\dfrac{\sqrt{x}+3-2}{\sqrt{x}+3}=1-\dfrac{2}{\sqrt{x}+3}\)
Để \(\dfrac{\sqrt{x}+1}{\sqrt{x}+3}\in Z\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{2}{\sqrt{x}+3}\in Z\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2⋮\sqrt{x}+3\\ \Leftrightarrow\sqrt{x}+3\inƯ\left(2\right)=\left\{-2;-1;1;2\right\}\\ \Leftrightarrow\sqrt{x}\in\left\{-5;-4;-2;-1\right\}\\ \Leftrightarrow x\in\left\{1;4;16;25\right\}\)
Vậy \(x\in\left\{1;4;16;25\right\}\) thì \(\dfrac{\sqrt{x}+1}{\sqrt{x}+3}\in Z\)
Tick plz
ĐKXĐ: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x\ge0\\\sqrt{x}+3\ne0\end{matrix}\right.\)\(\Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x\ge0\\\sqrt{x}\ne-3\left(loại\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)\(\Rightarrow x\ge0\)
\(x\in Z\Rightarrow\dfrac{\sqrt{x}+1}{\sqrt{x}+3}\in Z\Rightarrow\left(\sqrt{x}+1\right)⋮\left(\sqrt{x}+3\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow\left(\sqrt{x}+3-2\right)⋮\left(\sqrt{x}+3\right)\)
Vì \(\Rightarrow\left(\sqrt{x}+3\right)⋮\left(\sqrt{x}+3\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow2⋮\left(\sqrt{x}+3\right)\Rightarrow\sqrt{x}+3\inƯ\left(2\right)=\left\{\pm1;\pm2\right\}\)
Ta có bảng:
| \(\sqrt{x}+3\) | -1 | -2 | 1 | 2 |
| \(x\) | \(\sqrt{x}=-4\left(loại\right)\) | \(\sqrt{x}=-5\left(loại\right)\) | \(\sqrt{x}=-2\left(loại\right)\) | \(\sqrt{x}=-1\left(loại\right)\) |
Vậy không có x nguyên thỏa mãn đề bài

Ta có
\(1D=\frac{\sqrt{x}-2}{\sqrt{x}-3}=1+\frac{1}{\sqrt{x}-3}\)
Để cho D nguyên thì \(\sqrt{x}-3\)phải là ước của 1
\(\Rightarrow\sqrt{x}-3=\left(-1;1\right)\)
=> x = (4; 16)
=> D = (0; 2)
1/ Để N nhận giá trị nguyên thì trước hết \(\sqrt{x}-2\)phải là ước của 3
\(\sqrt{x}-2=\left(-3;-1;1;3\right)\)
Thế vào ta tìm được x = (1; 9; 25)
=> N = (- 3; 3;1)

\(P\in Z\Rightarrow3P\in Z\Rightarrow\dfrac{3\sqrt{x}+15}{3\sqrt{x}+1}\in Z\)
\(\Rightarrow1+\dfrac{14}{3\sqrt{x}+1}\in Z\)
\(\Rightarrow3\sqrt{x}+1=Ư\left(14\right)=\left\{1;2;7;14\right\}\) (do \(3\sqrt{x}+1\ge1\))
\(3\sqrt{x}+1=1\Rightarrow x=0\)
\(3\sqrt{x}+1=2\Rightarrow x=\dfrac{1}{9}\notin Z\) (loại)
\(3\sqrt{x}+1=7\Rightarrow x=4\)
\(3\sqrt{x}+1=14\Rightarrow x=\dfrac{169}{9}\notin Z\) (loại)
Thế \(x=\left\{0;4\right\}\) vào P đều thỏa mãn
Vậy ....

a,\(P=\frac{7}{\sqrt{x}+3}\Rightarrow\sqrt{x}+3\inƯ\left(7\right)=\left\{1;7\right\}\)
| \(\sqrt{x}+3\) | 1 | 7 |
| x | loại | 16 |
b, Ta có : \(\sqrt{x}\ge0\Rightarrow\sqrt{x}+3\ge3>0\Rightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}\frac{7}{\sqrt{x}+3}\le\frac{7}{3}\\\frac{7}{\sqrt{x}+3}>0\end{cases}}\)
\(\Rightarrow0< P\le\frac{7}{3}\)mà \(P\in Z\)=> \(P\in\left\{1;2\right\}\)
Với \(P=\frac{7}{\sqrt{x}+3}=1\Rightarrow7=\sqrt{x}+3\Leftrightarrow x=16\)( tm )
Với \(P=\frac{7}{\sqrt{x}+3}=2\Rightarrow7=2\sqrt{x}+6\Leftrightarrow\sqrt{x}=\frac{1}{2}\Leftrightarrow x=\frac{1}{4}\)( ktm )

Ta có: \(P=\dfrac{4\sqrt{x}+3}{x+\sqrt{x}}+\dfrac{\sqrt{x}}{\sqrt{x}+1}\)
\(=\dfrac{4\sqrt{x}+3}{\sqrt{x}\left(\sqrt{x}+1\right)}+\dfrac{x}{\sqrt{x}\left(\sqrt{x}+1\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{x+4\sqrt{x}+3}{\sqrt{x}\left(\sqrt{x}+1\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{\left(\sqrt{x}+1\right)\left(\sqrt{x}+3\right)}{\sqrt{x}\left(\sqrt{x}+1\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{\sqrt{x}+3}{\sqrt{x}}\)
Để P nguyên thì \(\sqrt{x}+3⋮\sqrt{x}\)
mà \(\sqrt{x}⋮\sqrt{x}\)
nên \(3⋮\sqrt{x}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\sqrt{x}\inƯ\left(3\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\sqrt{x}\in\left\{1;-1;3;-3\right\}\)
mà \(\sqrt{x}>0\forall x\) thỏa mãn ĐKXĐ
nên \(\sqrt{x}\in\left\{1;3\right\}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\in\left\{1;9\right\}\)
Kết hợp ĐKXĐ, ta được: \(x\in\left\{1;9\right\}\)
Vậy: Để P nguyên thì \(x\in\left\{1;9\right\}\)

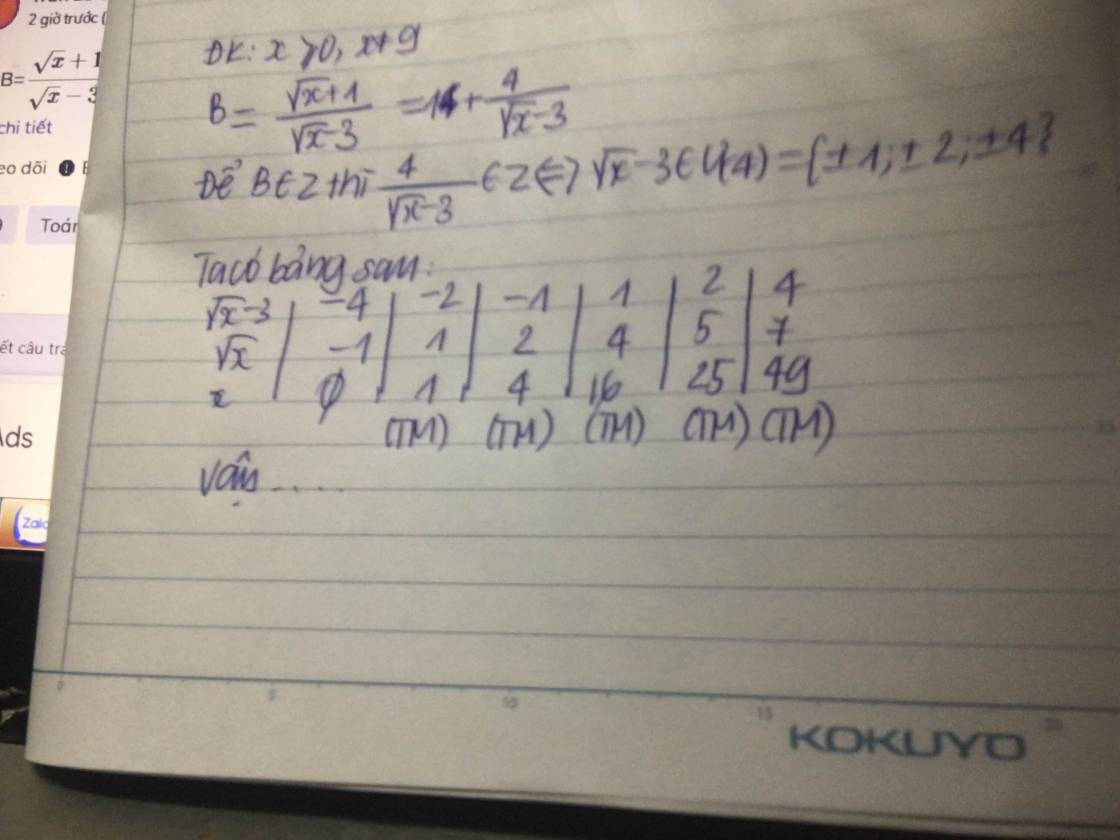

Ta có:
\(\dfrac{3-x}{3+x}=\dfrac{-x+3}{x+3}=\dfrac{-\left(x+3\right)+6}{x+3}=-1+\dfrac{6}{x+3}\)
Để biểu thức nhận giá trị nguyên thì: 6 ⋮ x + 3
=> x + 3 ∈ Ư(6) = {1; -1; 2; -2; 3; -3; 6; -6}
=> x ∈ {-2; -4; -1; -5; 0; -6; 3; -9}