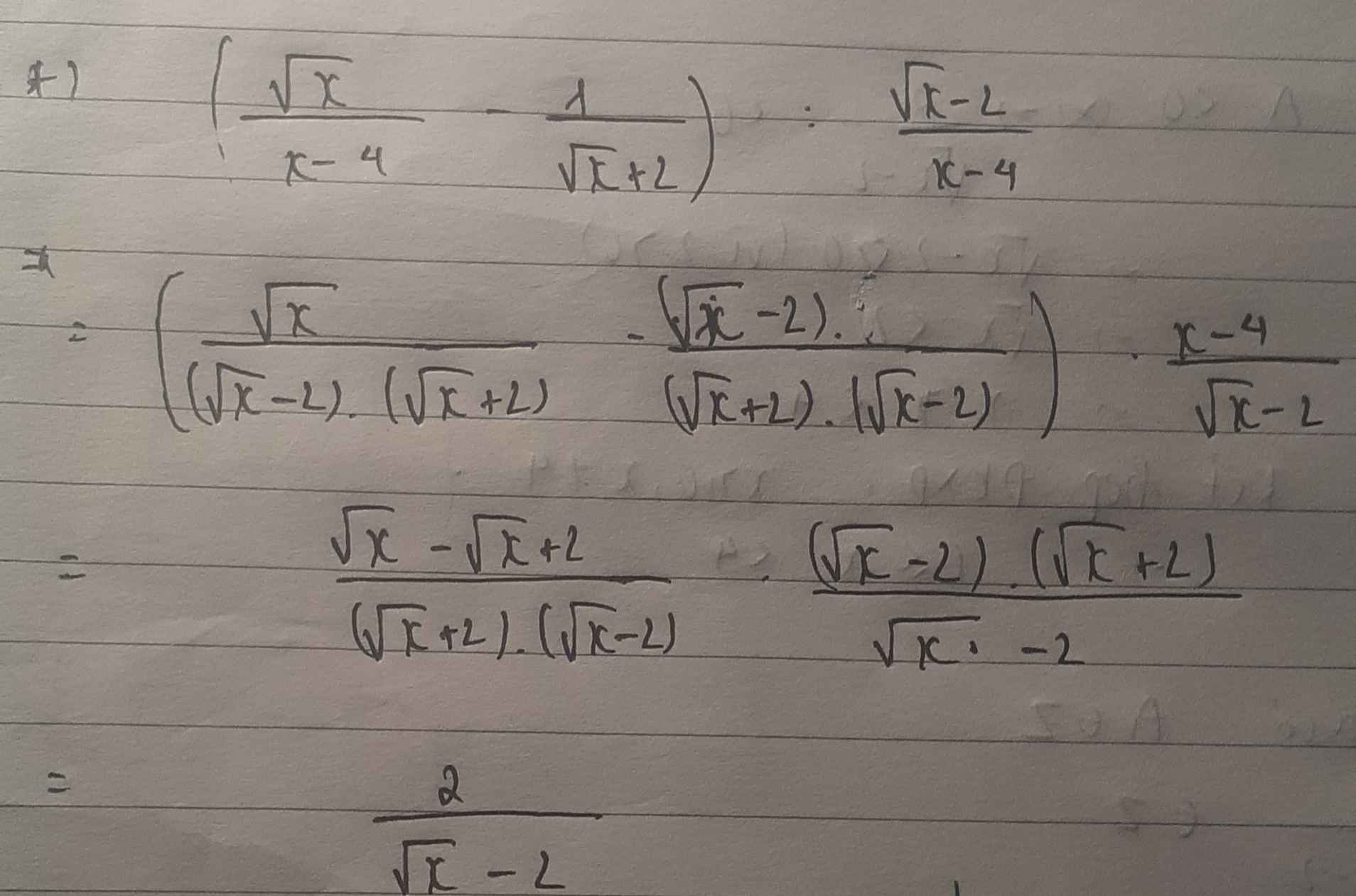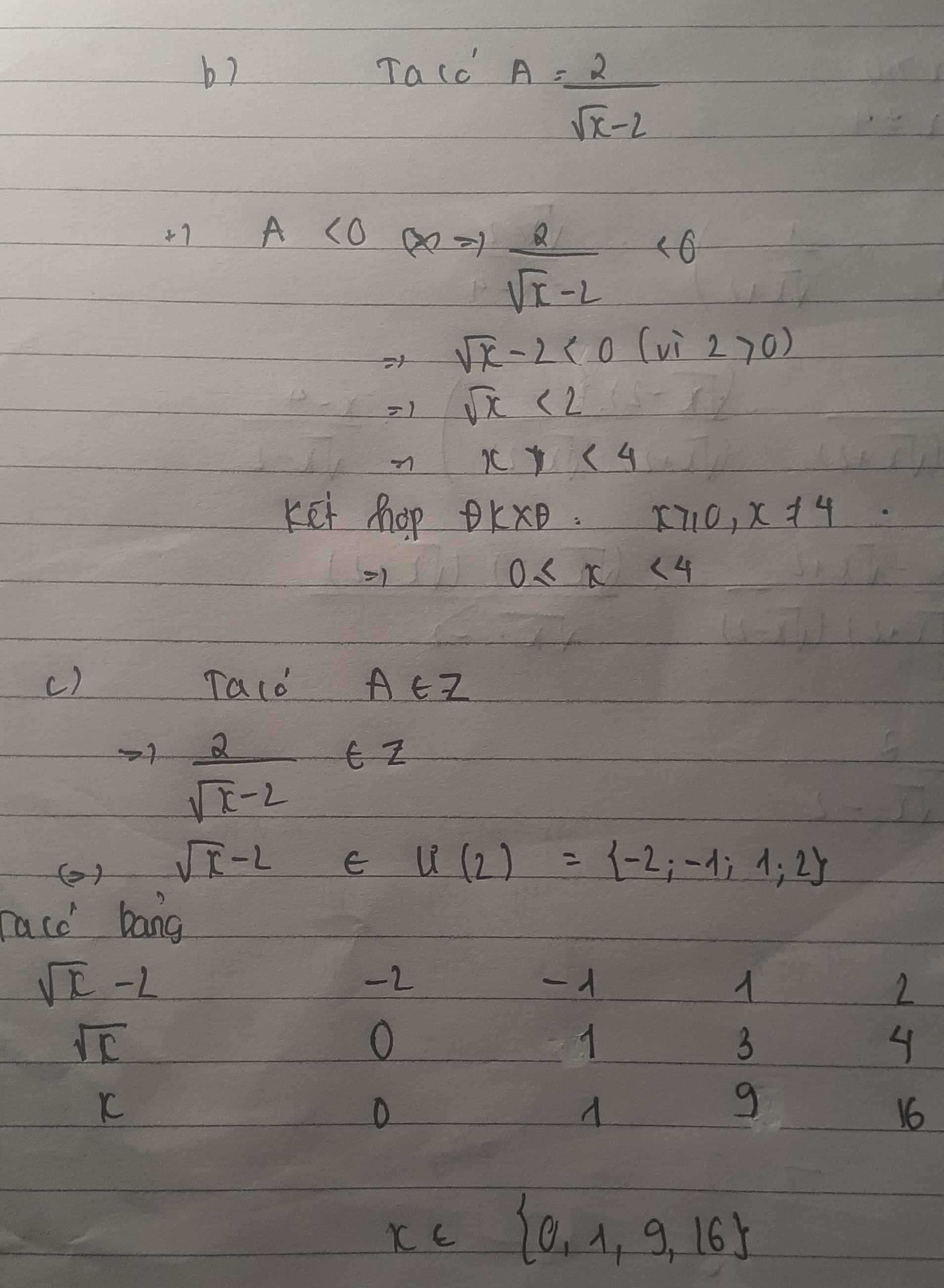Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

\(B+1=\dfrac{2\sqrt{x}-1}{\sqrt{x}+3}+1=\dfrac{3\sqrt{x}+2}{\sqrt{x}+3}>0\Rightarrow B>-1\)
\(B-2=\dfrac{2\sqrt{x}-1}{\sqrt{x}+3}-2=\dfrac{-7}{\sqrt{x}+3}< 0\Rightarrow B< 2\)
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}B=0\\B=1\end{matrix}\right.\)
- Với \(B=0\Rightarrow\sqrt{x}=\dfrac{1}{2}\Rightarrow x=\dfrac{1}{4}\notin Z\) (loại)
- Với \(B=1\Rightarrow2\sqrt{x}-1=\sqrt{x}+3\Leftrightarrow\sqrt{x}=4\Rightarrow x=16\)

Bài 5:
\(C=\frac{2\sqrt{x}-3}{\sqrt{x}-2}=\frac{2(\sqrt{x}-2)+1}{\sqrt{x}-2}=2+\frac{1}{\sqrt{x}-2}\)
Để $C$ nguyên nhỏ nhất thì $\frac{1}{\sqrt{x}-2}$ là số nguyên nhỏ nhất.
$\Rightarrow \sqrt{x}-2$ là ước nguyên âm lớn nhất
$\Rightarrow \sqrt{x}-2=-1$
$\Leftrightarrow x=1$ (thỏa mãn đkxđ)
Bài 6:
$D(\sqrt{x}+1)=x-3$
$D^2(x+2\sqrt{x}+1)=(x-3)^2$
$2D^2\sqrt{x}=(x-3)^2-D^2(x+1)$ nguyên
Với $x$ nguyên ta suy ra $\Rightarrow D=0$ hoặc $\sqrt{x}$ nguyên
Với $D=0\Leftrightarrow x=3$ (tm)
Với $\sqrt{x}$ nguyên:
$D=\frac{(x-1)-2}{\sqrt{x}+1}=\sqrt{x}-1-\frac{2}{\sqrt{x}+1}$
$D$ nguyên khi $\sqrt{x}+1$ là ước của $2$
$\Rightarrow \sqrt{x}+1\in\left\{1;2\right\}$
$\Leftrightarrow x=0; 1$
Vì $x\neq 1$ nên $x=0$.
Vậy $x=0; 3$

\(P=\dfrac{B}{A}\\ =\dfrac{\sqrt{x}+2}{\sqrt{x}-1}:\dfrac{\sqrt{x}+2}{\sqrt{x}-3}\\ =\dfrac{\sqrt{x}+2}{\sqrt{x}-1}\cdot\dfrac{\sqrt{x}-3}{\sqrt{x}+2}\\ =\dfrac{\sqrt{x}-3}{\sqrt{x}-1}\\ =\dfrac{\sqrt{x}-1-2}{\sqrt{x}-1}\\ =1-\dfrac{2}{\sqrt{x}-1}\)
Để \(P=\dfrac{B}{A}\) có giá trị nguyên
Thì \(2⋮\left(\sqrt{x}-1\right)\Rightarrow\left(\sqrt{x}-1\right)\inƯ\left(2\right)=\left\{2;-2;1;-1\right\}\)
| \(\sqrt{x}-1\) | 2 | -2 | 1 | -1 |
| \(x\) | 9 | ∅ | 4 | 0 |
| Nhận - Loại | nhận | loại | nhận | nhận |
Vậy \(x\in\left\{9;4;0\right\}\) thì \(x\) nguyên và \(P\) có giá trị nguyên

`C=(sqrtx+3)/(sqrtx-2)=(sqrtx-2+5)/(sqrtx-2)=1+5/(sqrtx-2)`
Ta cần tìm `max(5/(sqrtx-2))`
Nếu `0<=x<4` thì `5/(sqrtx-2)<0`
Nếu `x>4` thì `5/(sqrtx-2)>0`
Do đó ta chỉ xét `x>4` hay `x>=5(` Do `x` nguyên `)`
`=>sqrtx-2>=sqrt5-2`
`=>5/(sqrtx-2)<=5/(sqrt5-2)`
`=>C<=1+5/(sqrt5-2)=11+sqrt5`
Vậy `C_(max)=11+sqrt5<=>x=5`

a) \(P=\left(\dfrac{\sqrt{x}}{\sqrt{x}+1}+\dfrac{\sqrt{x}-4}{x-1}\right)\cdot\dfrac{\sqrt{x}+1}{\sqrt{x}-2}\left(dkxd:x\ge0;x\ne1;x\ne4\right)\)
\(=\left[\dfrac{\sqrt{x}\left(\sqrt{x}-1\right)}{\left(\sqrt{x}-1\right)\left(\sqrt{x}+1\right)}+\dfrac{\sqrt{x}-4}{\left(\sqrt{x}-1\right)\left(\sqrt{x}+1\right)}\right]\cdot\dfrac{\sqrt{x}+1}{\sqrt{x}-2}\)
\(=\dfrac{x-\sqrt{x}+\sqrt{x}-4}{\left(\sqrt{x}-1\right)\left(\sqrt{x}+1\right)}\cdot\dfrac{\sqrt{x}+1}{\sqrt{x}-2}\)
\(=\dfrac{x-4}{\sqrt{x}-1}\cdot\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{x}-2}\)
\(=\dfrac{\left(\sqrt{x}-2\right)\left(\sqrt{x}+2\right)}{\left(\sqrt{x}-1\right)\left(\sqrt{x}-2\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{\sqrt{x}+2}{\sqrt{x}-1}\)
b) Với \(x\ge0;x\ne1;x\ne4\):
Thay \(x=3+2\sqrt{2}\) vào \(P\), ta được:
\(P=\dfrac{\sqrt{3+2\sqrt{2}}+2}{\sqrt{3+2\sqrt{2}}-1}\)
\(=\dfrac{\sqrt{\left(\sqrt{2}\right)^2+2\cdot\sqrt{2}\cdot1+1^2}+2}{\sqrt{\left(\sqrt{2}\right)^2+2\cdot\sqrt{2}\cdot1+1^2}-1}\)
\(=\dfrac{\sqrt{\left(\sqrt{2}+1\right)^2}+2}{\sqrt{\left(\sqrt{2}+1\right)^2}-1}\)
\(=\dfrac{\sqrt{2}+1+2}{\sqrt{2}+1-1}\)
\(=\dfrac{\sqrt{2}+3}{\sqrt{2}}\)
\(=\dfrac{2+3\sqrt{2}}{2}\)
c) Với \(x\ge0;x\ne1;x\ne4\),
\(P=\dfrac{\sqrt{x}+2}{\sqrt{x}-1}=\dfrac{\sqrt{x}-1+3}{\sqrt{x}-1}=1+\dfrac{3}{\sqrt{x}-1}\)
Để \(P\) có giá trị nguyên thì \(\dfrac{3}{\sqrt{x}-1}\) có giá trị nguyên
\(\Rightarrow 3\vdots\sqrt x-1\\\Rightarrow \sqrt x-1\in Ư(3)\)
\(\Rightarrow\sqrt{x}-1\in\left\{1;3;-1;-3\right\}\)
\(\Rightarrow\sqrt{x}\in\left\{2;4;0;-2\right\}\) mà \(\sqrt{x}\ge0\)
\(\Rightarrow\sqrt{x}\in\left\{2;4;0\right\}\)
\(\Rightarrow x\in\left\{4;16;0\right\}\)
Kết hợp với ĐKXĐ của \(x\), ta được:
\(x\in\left\{0;16\right\}\)
Vậy: ...
\(\text{#}Toru\)