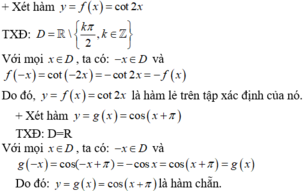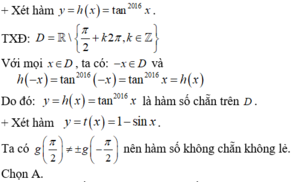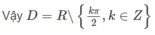Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


a, Hàm số xác định khi: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}cos\dfrac{x}{2}\ne3\\tanx\ne\sqrt{3}\\cosx\ne0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x\ne\dfrac{\pi}{3}+k\pi\\x\ne\dfrac{\pi}{2}+k\pi\end{matrix}\right.\)

a) Biểu thức \(\frac{{1 - \cos x}}{{\sin x}}\) có nghĩa khi \(\sin x \ne 0\), tức là \(x \ne k\pi \;\left( {k\; \in \;\mathbb{Z}} \right)\).
Vậy tập xác định của hàm số đã cho là \(\mathbb{R}/{\rm{\{ }}k\pi {\rm{|}}\;k\; \in \;\mathbb{Z}\} \;\)
b) Biểu thức \(\sqrt {\frac{{1 + \cos x}}{{2 - \cos x}}} \) có nghĩa khi \(\left\{ {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}}{\frac{{1 + \cos x}}{{2 - \cos x}} \ge 0}\\{2 - \cos x \ne 0}\end{array}} \right.\)
Vì \( - 1 \le \cos x \le 1 ,\forall x \in \mathbb{R}\)
Vậy tập xác định của hàm số là \(D = \mathbb{R}\)

Đáp án B
+ Xét hàm y = f(x) = cos (x + π)
TXĐ: D = R
Với mọi x ∈ D, ta có: -x ∈ D và f(-x) = cos (-x + π) = -cos x = cos (x + π) = f(x)
Do đó y = cos (x + π) là hàm số chẵn .
+ Xét hàm y = g(x) = tan2016x
TXĐ: D = R\{π/2 + kπ, k ∈ Z}
Với mọi x ∈ D, ta có: -x ∈ D và g(-x) = tan2016(-x) = (-tan x)2016 = tan2016x = g(x)
Do đó: y = tan2016x là hàm chẵn trên tập xác định của nó.
+Xét hàm y = cot2x
f(-x) = cot(-2x) = - cot 2x = -f(x) nên đây là hàm số lẻ.
+ Xét hàm số y = 1-sinx
f(-x) = 1- sin(-x) = 1+ sin x
Nên hàm số không chẵn không lẻ

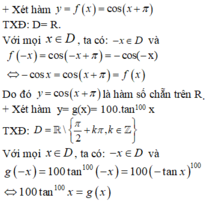
Do đó: y= 100 tan100x là hàm chẵn trên tập xác định của nó.
Đáp án B

ĐK: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}sin\left(x-\dfrac{\pi}{4}\right)\ne0\\sin^4x-cos^4x\ne0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x-\dfrac{\pi}{4}\ne k\pi\\\left(cos^2x-sin^2x\right)\left(cos^2x+sin^2x\right)\ne0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x\ne\dfrac{\pi}{4}+k\pi\\cos2x\ne0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x\ne\dfrac{\pi}{4}+k\pi\\2x\ne\dfrac{\pi}{2}+k\pi\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x\ne\dfrac{\pi}{4}+k\pi\\x\ne\dfrac{\pi}{4}+\dfrac{k\pi}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\ne\dfrac{\pi}{4}+\dfrac{k\pi}{2}\)