Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

y'= \(4x^3-4\left(m-1\right)x\)
Để hàm số đồng biến trên khoảng (1;3) thì \(y'\left(x\right)\ge0,\forall x\in\left(1;3\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-\left(m-1\right)\ge0,\forall x\in\left(1;3\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow m-1\le x^2,\forall x\in\left(1;3\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow m-1\le1\Leftrightarrow m\le2\)
Vậy \(m\in\) (−\(\infty\);2]

1.
\(y'=m-3cos3x\)
Hàm đồng biến trên R khi và chỉ khi \(m-3cos3x\ge0\) ; \(\forall x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow m\ge3cos3x\) ; \(\forall x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow m\ge\max\limits_{x\in R}\left(3cos3x\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow m\ge3\)
2.
\(y'=1-m.sinx\)
Hàm đồng biến trên R khi và chỉ khi:
\(1-m.sinx\ge0\) ; \(\forall x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow1\ge m.sinx\) ; \(\forall x\)
- Với \(m=0\) thỏa mãn
- Với \(m< 0\Rightarrow\dfrac{1}{m}\le sinx\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{1}{m}\le\min\limits_R\left(sinx\right)=-1\)
\(\Rightarrow m\ge-1\)
- Với \(m>0\Rightarrow\dfrac{1}{m}\ge sinx\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{1}{m}\ge\max\limits_R\left(sinx\right)=1\)
\(\Rightarrow m\le1\)
Kết hợp lại ta được: \(-1\le m\le1\)

Xét
\(y'=4x^3-4\left(m-1\right)x=0\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=0\\x^2=m-1\end{cases}}\)
TH1:
\(m-1\le0\) thì hàm số đồng biến trên R
TH2: \(m-1>0\Rightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=\sqrt{m-1}\\x=-\sqrt{m-1}\end{cases}}\)
Khi đó khoảng đồng biến của hàm số là \(\left(-\infty,-\sqrt{m-1}\right)\text{ và }\left(0,\sqrt{m-1}\right)\)
Muốn hàm số đồng biến trên (1,3) thì \(\left(1,3\right)\subset\left(0,\sqrt{m-1}\right)\Leftrightarrow3\le\sqrt{m-1}\Leftrightarrow m\ge10\)
Vậy \(\orbr{\begin{cases}m\le1\\m\ge10\end{cases}}\)

Đáp án B
Phương pháp:
Hàm số y = f(x) nghịch biến trên (-∞;+∞) khi và chỉ khi f'(x) ≤ 0, ∀ x ∈ (-∞;+∞), f'(x) = 0 tại hữu hạn điểm.
Cách giải:
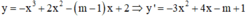
Hàm số đã cho nghịch biến trên khoảng (-∞;+∞)
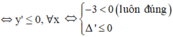
![]()
![]()
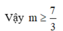
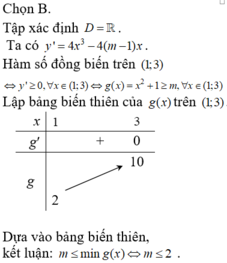


Chọn B.
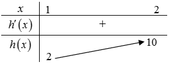
Tập xác định D = R.
Dựa vào bảng biến thiên, kết luận: m ≤ min g(x) ⇔ m ≤ 2