Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

1.
PT $\Leftrightarrow 2^{x^2-5x+6}+2^{1-x^2}-2^{7-5x}-1=0$
$\Leftrightarrow (2^{x^2-5x+6}-2^{7-5x})-(1-2^{1-x^2})=0$
$\Leftrightarrow 2^{7-5x}(2^{x^2-1}-1)-(2^{x^2-1}-1)2^{1-x^2}=0$
$\Leftrightarrow (2^{x^2-1}-1)(2^{7-5x}-2^{1-x^2})=0$
$\Rightarrow 2^{x^2-1}-1=0$ hoặc $2^{7-5x}-2^{1-x^2}=0$
Nếu $2^{x^2-1}=1\Leftrightarrow x^2-1=0$
$\Leftrightarrow x^2=1\Leftrightarrow x=\pm 1$
$2^{7-5x}-2^{1-x^2}=0$
$\Leftrightarrow 7-5x=1-x^2\Leftrightarrow x^2-5x+6=0$
$\Leftrightarrow (x-2)(x-3)=0\Leftrightarrow x=2; x=3$
2. Đặt $\sin ^2x=a$ thì $\cos ^2x=1-a$. PT trở thành:
$16^a+16^{1-a}=10$
$\Leftrightarrow 16^a+\frac{16}{16^a}=10$
$\Leftrightarrow (16^a)^2-10.16^a+16=0$
Đặt $16^a=x$ thì:
$x^2-10x+16=0$
$\Leftrightarrow (x-2)(x-8)=0$
$\Leftrightarrow x=2$ hoặc $x=8$
$\Leftrightarrow 16^a=2$ hoặc $16^a=8$
$\Leftrightarrow 2^{4a}=2$ hoặc $2^{4a}=2^3$
$\Leftrightarroww 4a=1$ hoặc $4a=3$
$\Leftrightarrow a=\frac{1}{4}$ hoặc $a=\frac{3}{4}$
Nếu $a=\frac{1}{4}\Leftrightarrow \sin ^2x=\frac{1}{4}$
$\Leftrightarrow \sin x=\pm \frac{1}{2}$
Nếu $a=\sin ^2x=\frac{3}{4}\Rightarrow \sin x=\pm \frac{\sqrt{3}}{2}$
Đến đây thì đơn giản rồi.

Tính \(I=\int_0^{\dfrac{\pi}{2}}\dfrac{cos^{2017}x}{sin^{2017}x+cos^{2017}}dx\left(1\right)\)
Đặt \(t=cosx\Rightarrow sinx=\sqrt{1-cos^2x}\)
\(\Rightarrow dt=-sinx.dx\)
\(\Rightarrow I=\int_0^1\dfrac{t^{2017}.}{\sqrt{1-t^2}.\left(\left(\sqrt{1-t^2}\right)^{2017}+t^{2017}\right)}dt\)
Đặt: \(t=siny\Rightarrow\sqrt{1-t^2}=cosy\)
\(\Rightarrow dt=cosy.dy\)
\(\Rightarrow I=\int_0^{\dfrac{\pi}{2}}\dfrac{sin^{2017}y.cosy}{cosy\left(cos^{2017}y+sin^{2017}y\right)}dy=\int_0^{\dfrac{\pi}{2}}\dfrac{sin^{2017}y}{\left(cos^{2017}y+sin^{2017}y\right)}\)
\(\Rightarrow I=\int_0^{\dfrac{\pi}{2}}\dfrac{sin^{2017}x}{\left(cos^{2017}x+sin^{2017}x\right)}\left(2\right)\)
Cộng (1) và (2) ta được
\(2I=\int_0^{\dfrac{\pi}{2}}\dfrac{sin^{2017}x+cos^{2017}x}{sin^{2017}x+cos^{2017}x}dx=\int_0^{\dfrac{\pi}{2}}1dx\)
\(=x|^{\dfrac{\pi}{2}}_0=\dfrac{\pi}{2}\)
\(\Rightarrow I=\dfrac{\pi}{4}\)
Thế lại bài toán ta được
\(\dfrac{\pi}{4}+t^2-6t+9-\dfrac{\pi}{4}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow t^2-6t+9=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow t=3\)
Chọn đáp án C
mỗi trắc nghiệm thoy mà lm dài ntn s @@
chắc lên đó khó lắm ag

a.
\(y'=\dfrac{2-x}{2x^2\sqrt{x-1}}=0\Rightarrow x=2\)
\(y\left(1\right)=0\) ; \(y\left(2\right)=\dfrac{1}{2}\) ; \(y\left(5\right)=\dfrac{2}{5}\)
\(\Rightarrow y_{min}=y\left(1\right)=0\)
\(y_{max}=y\left(2\right)=\dfrac{1}{2}\)
b.
\(y'=\dfrac{1-3x}{\sqrt{\left(x^2+1\right)^3}}< 0\) ; \(\forall x\in\left[1;3\right]\Rightarrow\) hàm nghịch biến trên [1;3]
\(\Rightarrow y_{max}=y\left(1\right)=\dfrac{4}{\sqrt{2}}=2\sqrt{2}\)
\(y_{min}=y\left(3\right)=\dfrac{6}{\sqrt{10}}=\dfrac{3\sqrt{10}}{5}\)
c.
\(y=1-cos^2x-cosx+1=-cos^2x-cosx+2\)
Đặt \(cosx=t\Rightarrow t\in\left[-1;1\right]\)
\(y=f\left(t\right)=-t^2-t+2\)
\(f'\left(t\right)=-2t-1=0\Rightarrow t=-\dfrac{1}{2}\)
\(f\left(-1\right)=2\) ; \(f\left(1\right)=0\) ; \(f\left(-\dfrac{1}{2}\right)=\dfrac{9}{4}\)
\(\Rightarrow y_{min}=0\) ; \(y_{max}=\dfrac{9}{4}\)
d.
Đặt \(sinx=t\Rightarrow t\in\left[-1;1\right]\)
\(y=f\left(t\right)=t^3-3t^2+2\Rightarrow f'\left(t\right)=3t^2-6t=0\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}t=0\\t=2\notin\left[-1;1\right]\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(f\left(-1\right)=-2\) ; \(f\left(1\right)=0\) ; \(f\left(0\right)=2\)
\(\Rightarrow y_{min}=-2\) ; \(y_{max}=2\)

\(\Leftrightarrow\frac{3^{\sin^2x}+3}{3^{\sin^2x}}-4=2^{2.\frac{x}{2}}+2^{2.\frac{-x}{2}}-2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\frac{\left(3^{\sin^2x}-1\right)\left(3^{\sin^2x}-3\right)}{3^{\sin^2x}}=\left(2^{\frac{x}{2}}-2^{\frac{-x}{2}}\right)^2\)
Vì 0 \(\le\sin^2x\)\(\le1\) nên 1 \(\le3\sin^2x\)\(\le3\) . Suy ra Vế trái \(\le0\)\(\le\) vế phải và phương trình tương đương với hệ :
\(\begin{cases}\left(3^{\sin^2x}-1\right)\left(3^{\sin^2x}-3\right)=0\\2^{\frac{x}{2}}-2^{\frac{-x}{2}}=0\end{cases}\)
Từ phương trình thứ 2, dễ dàng suy ra x=0 (thỏa mãn). Vậy x=0 là nghiệm duy nhất của phương trình đã cho.

ĐKXĐ: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x\ne-\dfrac{\pi}{2}+k2\pi\\x\ne\dfrac{\pi}{6}+\dfrac{k2\pi}{3}\\\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\dfrac{cosx-2sinx.cosx}{2cos^2x-1-sinx}=\sqrt{3}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{cosx-sin2x}{cos2x-sinx}=\sqrt{3}\)
\(\Rightarrow cosx-sin2x=\sqrt{3}cos2x-\sqrt{3}sinx\)
\(\Leftrightarrow cosx+\sqrt{3}sinx=\sqrt{3}cos2x+sin2x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{1}{2}cosx+\dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{2}sinx=\dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{2}cos2x+\dfrac{1}{2}sin2x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow cos\left(x-\dfrac{\pi}{3}\right)=cos\left(2x-\dfrac{\pi}{6}\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}2x-\dfrac{\pi}{6}=x-\dfrac{\pi}{3}+k2\pi\\2x-\dfrac{\pi}{6}=\dfrac{\pi}{3}-x+k2\pi\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-\dfrac{\pi}{6}+k2\pi\\x=\dfrac{\pi}{6}+\dfrac{k2\pi}{3}\left(loại\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy \(x=-\dfrac{\pi}{6}+k2\pi\)

\(f\left(1-x\right)+f\left(x\right)=\dfrac{9^{1-x}}{9^{1-x}+3}+\dfrac{9^x}{9^x+3}=\dfrac{9}{9+3.9^x}+\dfrac{9^x}{9^x+3}=\dfrac{3}{9^x+3}+\dfrac{9^x}{9^x+3}=1\)
\(\Rightarrow f\left(x\right)=1-f\left(1-x\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow f\left(cos^2x\right)=1-f\left(sin^2x\right)\)
Do đó:
\(f\left(3m+\dfrac{1}{4}sinx\right)+f\left(cos^2x\right)=1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow f\left(3m+\dfrac{1}{4}sinx\right)=f\left(sin^2x\right)\) (1)
Hàm \(f\left(x\right)=\dfrac{9^x}{9^x+3}\) có \(f'\left(x\right)=\dfrac{3.9^x.ln9}{\left(9^x+3\right)^2}>0\Rightarrow f\left(x\right)\) đồng biến trên R
\(\Rightarrow\left(1\right)\Leftrightarrow3m+\dfrac{1}{4}sinx=sin^2x\)
Đến đây chắc dễ rồi, biện luận để pt \(sin^2x-\dfrac{1}{4}sinx=3m\) có 8 nghiệm trên khoảng đã cho



Chọn C
Ta có: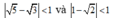 nên (1) và (2) có nghiệm.
nên (1) và (2) có nghiệm.
Cách 1:
Xét: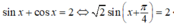
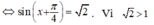 nên (3) vô nghiệm.
nên (3) vô nghiệm.
Cách 2:
Điều kiện có nghiệm của phương trình: sin x + cos x = 2 là: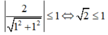
(vô lý) nên (3) vô nghiệm.
Cách 3:
Vì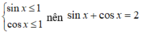
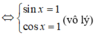
nên (3) vô nghiệm.