giải phương trình
2(x2+x+1)2-7(x-1)2=13(x2-1)
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


a)
( x − 3 ) 2 + ( x + 4 ) 2 = 23 − 3 x ⇔ x 2 − 6 x + 9 + x 2 + 8 x + 16 = 23 − 3 x ⇔ x 2 − 6 x + 9 + x 2 + 8 x + 16 + 3 x − 23 = 0 ⇔ 2 x 2 + 5 x + 2 = 0
Có a = 2; b = 5; c = 2 ⇒ Δ = 5 2 – 4 . 2 . 2 = 9 > 0
⇒ Phương trình có hai nghiệm:
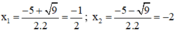
Vậy phương trình có tập nghiệm 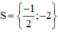
b)
x 3 + 2 x 2 − ( x − 3 ) 2 = ( x − 1 ) x 2 − 2 ⇔ x 3 + 2 x 2 − x 2 − 6 x + 9 = x 3 − x 2 − 2 x + 2 ⇔ x 3 + 2 x 2 − x 2 + 6 x − 9 − x 3 + x 2 + 2 x − 2 = 0 ⇔ 2 x 2 + 8 x − 11 = 0
Có a = 2; b = 8; c = -11 ⇒ Δ ’ = 4 2 – 2 . ( - 11 ) = 38 > 0
⇒ Phương trình có hai nghiệm:
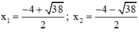
Vậy phương trình có tập nghiệm 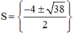
c)
( x − 1 ) 3 + 0 , 5 x 2 = x x 2 + 1 , 5 ⇔ x 3 − 3 x 2 + 3 x − 1 + 0 , 5 x 2 = x 3 + 1 , 5 x ⇔ x 3 + 1 , 5 x − x 3 + 3 x 2 − 3 x + 1 − 0 , 5 x 2 = 0 ⇔ 2 , 5 x 2 − 1 , 5 x + 1 = 0
Có a = 2,5; b = -1,5; c = 1
⇒ Δ = ( - 1 , 5 ) 2 – 4 . 2 , 5 . 1 = - 7 , 75 < 0
Vậy phương trình vô nghiệm.
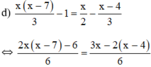
⇔ 2 x ( x − 7 ) − 6 = 3 x − 2 ( x − 4 ) ⇔ 2 x 2 − 14 x − 6 = 3 x − 2 x + 8 ⇔ 2 x 2 − 14 x − 6 − 3 x + 2 x − 8 = 0 ⇔ 2 x 2 − 15 x − 14 = 0
Có a = 2; b = -15; c = -14
⇒ Δ = ( - 15 ) 2 – 4 . 2 . ( - 14 ) = 337 > 0
⇒ Phương trình có hai nghiệm:
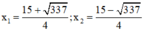
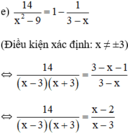
⇔ 14 = ( x - 2 ) ( x + 3 ) ⇔ 14 = x 2 - 2 x + 3 x - 6 ⇔ x 2 + x - 20 = 0
Có a = 1; b = 1; c = -20
⇒ Δ = 1 2 – 4 . 1 . ( - 20 ) = 81 > 0
Phương trình có hai nghiệm:
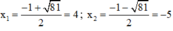
Cả hai nghiệm đều thỏa mãn điều kiện xác định.
Vậy phương trình có tập nghiệm S = {-5; 4}.
f) Điều kiện: x≠-1;x≠4

Ta có: a= 1, b = -7, c = - 8
∆ = ( - 7 ) 2 – 4 . 1 . ( - 8 ) = 81
=> Phương trình có hai nghiệm:
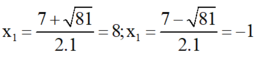
Kết hợp với diều kiện, nghiệm của phương trình đã cho là x = 8

a) \(\left(3x-2\right)\left(4x+5\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}3x-2=0\\4x+5=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{2}{3}\\x=-\dfrac{5}{4}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy: \(S=\left\{\dfrac{2}{3};-\dfrac{5}{4}\right\}\)
b) \(\left(2,3x-6,9\right)\left(0,1x+2\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}2,3x-6,9=0\\0,1x+2=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=3\\x=-20\end{matrix}\right.\)
c) \(\left(4x+2\right)\left(x^2+1\right)=0\)
Vì \(x^2+1\ge1>0\forall x\)
\(\Rightarrow4x+2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=-\dfrac{1}{2}\)
Vậy: \(S=\left\{-\dfrac{1}{2}\right\}\)
d) \(\left(2x+7\right)\left(x-5\right)\left(5x+1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}2x+7=0\\x-5=0\\5x+1=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-\dfrac{7}{2}\\x=5\\x=-\dfrac{1}{5}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy: \(S=\left\{-\dfrac{7}{2};5;-\dfrac{1}{5}\right\}\)
e) \(\left(x-1\right)\left(2x+7\right)\left(x^2+2\right)=0\)
Vì \(x^2+2\ge2>0\forall x\)
\(\Rightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left(2x+7\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-1=0\\2x+7=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=1\\x=-\dfrac{7}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
f) \(\left(3x+2\right)\left(x^2-1\right)=\left(9x^2-4\right)\left(x+1\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(3x+2\right)\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)-\left(3x-2\right)\left(3x+2\right)\left(x+1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[\left(3x+2\right)\left(x+1\right)\right].\left(x-1-3x+2\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(3x^2+5x+2\right)\left(-2x+1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(3x^2+3x+2x+2\right)\left(-2x+1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[3x\left(x+1\right)+2\left(x+1\right)\right]\left(-2x+1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+1\right)\left(3x+2\right)\left(-2x+1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x+1=0\\3x+2=0\\-2x+1=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-1\\x=-\dfrac{2}{3}\\x=\dfrac{1}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy: \(S=\left\{-1;-\dfrac{2}{3};\dfrac{1}{2}\right\}\)

`a)x^2>4`
`<=>sqrtx^2>sqrt4`
`<=>|x|>2`
`<=>` \(\left[ \begin{array}{l}x>2\\x<-2\end{array} \right.\)
`b)x^2<9`
`<=>\sqrtx^2<sqrt9`
`<=>|x|<3`
`<=>-3<x<3`
`c)(x-1)^2>=4`
`<=>\sqrt{(x-1)^2}>=sqrt4`
`<=>|x-1|>=2`
`<=>` \(\left[ \begin{array}{l}x-1 \ge 2\\x-1 \le -2\end{array} \right.\)
`<=>` \(\left[ \begin{array}{l}x \ge 3\\x \le -1\end{array} \right.\)
`d)(1-2x)^2<=0,09`
`<=>\sqrt{(1-2x)^2}<=sqrt{0,09}`
`<=>|2x-1|<=0,3`
`<=>-0,3<=2x-1<=0,3`
`<=>0,7<=2x<=1,3`
`<=>0,35<=x<=0,65`
`e)x^2+6x-7>0`
`<=>x^2-x+7x-7>0`
`<=>x(x-1)+7(x-1)>0`
`<=>(x-1)(x+7)>0`
TH1:
\(\left[ \begin{array}{l}x-1>0\\x+7>0\end{array} \right.\)
`<=>` \(\left[ \begin{array}{l}x>1\\x>-7\end{array} \right.\)
`<=>x>1`
TH2"
\(\left[ \begin{array}{l}x-1<0\\x+7<0\end{array} \right.\)
`<=>` \(\left[ \begin{array}{l}x<1\\x<-7\end{array} \right.\)
`<=>x<-7`
`f)x^2-x<2`
`<=>x^2-x-2<0`
`<=>x^2-2x+x-2<0`
`<=>x(x-2)+x-2<0`
`<=>(x-2)(x+1)<0`
`<=>` \(\begin{cases}x-2<0\\x+1>0\\\end{cases}\)
`<=>` \(\begin{cases}x<2\\x>-1\\\end{cases}\)
`<=>-1<x<2`
a) x2 > 4
<=> \(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x>2\\x< -2\end{matrix}\right.\)
b) \(x^2< 9\)
<=> \(-3< x< 3\)
c) \(\left(x-1\right)^2\ge4\)
<=> \(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-1\ge2< =>x\ge3\\x-1\le-2< =>x\le-1\end{matrix}\right.\)
d) \(\left(1-2x\right)^2\le0,09\)
<=> \(-0,3\le1-2x\le0,3\)
<=> \(1,3\ge2x\ge0,7\)
<=> \(0,65\ge x\ge0,35\)
e) \(x^2+6x-7>0\)
<=> \(\left(x+7\right)\left(x-1\right)>0\)
<=> \(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-1>0< =>x>1\\x+7< 0< =>x< -7\end{matrix}\right.\)
f) \(x^2-x< 2\)
<=> \(x^2-x-2< 0\)
<=> \(\left(x-2\right)\left(x+1\right)< 0\)
<=> \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x+1>0< =>x>-1\\x-2< 0< =>x< 2\end{matrix}\right.\)
<=> -1 < x < 2
g) \(4x^2-12x\le\dfrac{-135}{16}\)
<=> \(64x^2-192x+135\le0\)
<=> (8x - 15)(8x - 9) \(\le0\)
<=> \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}8x-15\le0< =>x\le\dfrac{15}{8}\\8x-9\ge0< =>x\ge\dfrac{9}{8}\end{matrix}\right.\)
<=> \(\dfrac{9}{8}\le x\le\dfrac{15}{8}\)

\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x^2-2x\right)^2+x^2-2x+1-13=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x^2-2x\right)^2+x^2-2x-12=0\)
Đặt \(x^2-2x=t\Rightarrow t^2+t-12=0\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}t=3\\t=-4\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x^2-2x=3\\x^2-2x=-4\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x^2-2x-3=0\\x^2-2x+4=0\left(vô-nghiệm\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-1\\x=3\end{matrix}\right.\)

1. Đặt $x^2+x=a$ thì pt trở thành:
$a^2+4a=12$
$\Leftrightarrow a^2+4a-12=0$
$\Leftrightarrow (a-2)(a+6)=0$
$\Leftrightarrow a-2=0$ hoặc $x+6=0$
$\Leftrightarrow x^2+x-2=0$ hoặc $x^2+x+6=0$
Dễ thấy $x^2+x+6=0$ vô nghiệm.
$\Rightarrow x^2+x-2=0$
$\Leftrightarrow (x-1)(x+2)=0$
$\Leftrightarrow x=1$ hoặc $x=-2$
2.
$x(x-1)(x+1)(x+2)=24$
$\Leftrightarrow [x(x+1)][(x-1)(x+2)]=24$
$\Leftrightarrow (x^2+x)(x^2+x-2)=24$
$\Leftrightarrow a(a-2)=24$ (đặt $x^2+x=a$)
$\Leftrightarrow a^2-2a-24=0$
$\Leftrightarrow (a+4)(a-6)=0$
$\Leftrightarrow a+4=0$ hoặc $a-6=0$
$\Leftrightarrow x^2+x+4=0$ hoặc $x^2+x-6=0$
Nếu $x^2+x+4=0$
$\Leftrightarrow (x+\frac{1}{2})^2=\frac{1}{4}-4<0$ (vô lý - loại)
Nếu $x^2+x-6=0$
$\Leftrightarrow (x-2)(x+3)=0$
$\Leftrightarrow x-2=0$ hoặc $x+3=0$
$\Leftrightarrow x=2$ hoặc $x=-3$