
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


\(2x+\frac{\pi}{6}=\frac{\pi}{2}+k\pi\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x=\frac{\pi}{3}+k\pi\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=\frac{\pi}{6}+\frac{k\pi}{2}\)

Khi tịnh tiến đường thẳng \(\left(d\right)\)thì sẽ thu được đường thẳng song song hoặc trùng với nó nên \(\left(d'\right)\)có dạng
\(2x+y+c=0\).
Lấy \(A\left(0,-3\right)\in\left(d\right)\).
Tịnh tiến điểm \(A\)theo vector \(v\left(1,2\right)\)được \(A'=\left(1,-1\right)\in\left(d'\right)\).
Suy ra \(2.1-1+c=0\Leftrightarrow c=-1\).
Vậy \(\left(d'\right):2x+y-1=0\).



Bài 2:
Sửa đề: \(y=f\left(x\right)=\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{2x^2+3x-5}{x-1}nếux\ne1\\2a+1nếux=1\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow1}f\left(x\right)=\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow1}\dfrac{2x^2+3x-5}{x-1}\)
\(=\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow1}\dfrac{\left(2x+5\right)\left(x-1\right)}{x-1}=\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow1}2x+5=2+5=7\)
f(1)=2a+1
Để hàm số liên tục khi x=1 thì \(f\left(1\right)=\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow1}f\left(x\right)\)
=>2a+1=7
=>2a=6
=>a=3

ĐK: `x \ne kπ`
`cot(x-π/4)+cot(π/2-x)=0`
`<=>cot(x-π/4)=-cot(π/2-x)`
`<=>cot(x-π/4)=cot(x-π/2)`
`<=> x-π/4=x-π/2+kπ`
`<=>0x=-π/4+kπ` (VN)
Vậy PTVN.
 Giải bài này hộ mình với!!!
Giải bài này hộ mình với!!! Ai giải chi tiết cái này hộ mình với
Ai giải chi tiết cái này hộ mình với
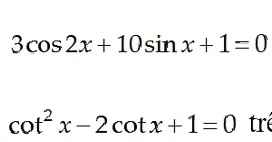

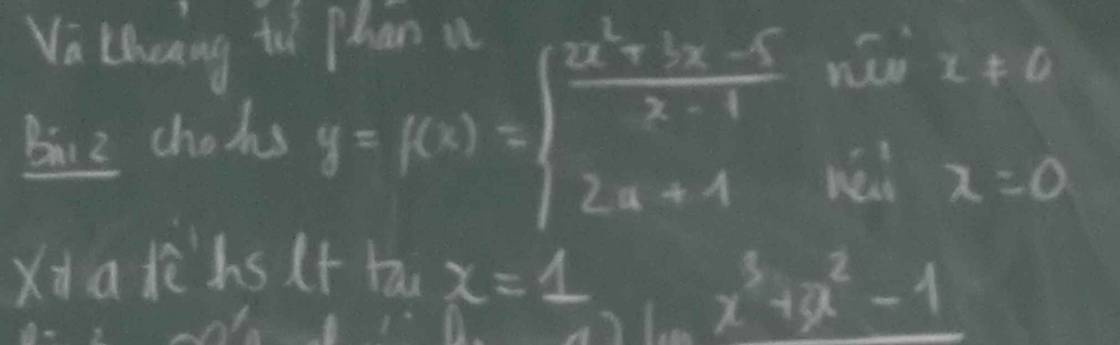

Bài 1 :
a) \(sin4x=sin\dfrac{\pi}{5}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}4x=\dfrac{\pi}{5}+k2\pi\\4x=\pi-\dfrac{\pi}{5}+k2\pi\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{\pi}{20}+k\dfrac{\pi}{2}\\x=\dfrac{\pi}{5}+k\dfrac{\pi}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
e) \(2sin\dfrac{x}{2}+\sqrt[]{3}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow sin\dfrac{x}{2}=-\dfrac{\sqrt[]{3}}{2}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow sin\dfrac{x}{2}=sin\left(-\dfrac{\pi}{3}\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{x}{2}=-\dfrac{\pi}{3}+k2\pi\\\dfrac{x}{2}=\pi+\dfrac{\pi}{3}+k2\pi\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-\dfrac{2\pi}{3}+k2\pi\\x=\dfrac{8\pi}{3}+k2\pi\end{matrix}\right.\)
m) \(\sqrt[]{3}tan2x-3=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow tan2x=\sqrt[]{3}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow tan2x=tan\dfrac{\pi}{3}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x=\dfrac{\pi}{3}+k\pi\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{\pi}{6}+\dfrac{k\pi}{2}\)