
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


a, Câu này dễ quá bỏ qua nha :)
b, Ta có : \(\Delta^,=b^{,2}-ac=\left(-2\right)^2-\left(m+1\right)=4-m-1=3-m\)
- Để phương trình có 2 nghiệm phân biết thì \(\Delta^,>0\)
=> \(m< 3\)
- Theo vi ét : \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x_1+x_2=-\frac{b}{a}=4\\x_1x_2=\frac{c}{a}=m+1\end{matrix}\right.\)
- Để \(x^2_1+x^2_2=3\left(x_1+x_2\right)\)
<=> \(\left(x_1+x_2\right)^2-2x_1x_2=3\left(x_1+x_2\right)\)
<=> \(4^2-2\left(m+1\right)=3.4=12\)
<=> \(-2\left(m+1\right)=-4\)
<=> \(m+1=2\)
<=> \(m=1\left(TM\right)\)
Vậy ....

ĐKXĐ: \(x\ge1\)
\(pt\Leftrightarrow\sqrt{\left(2x-1\right)^2}=x-1\Leftrightarrow\left|2x-1\right|=x-1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x-1=x-1\left(do.x\ge1\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=0\left(ktm\right)\)
Vậy \(S=\varnothing\)

Gọi đường thẳng cần tìm là d1
d1 có dạng y=ax+b
Vì d1 vuông với d
=> a.(-2)=-1=> a=1/2
Mà d1 qua A(-1, 3)
=> 3=\(\frac{1}{2}.\left(-1\right)+b\)=> b=7/2
=> d1: y=\(\frac{1}{2}x+\frac{7}{2}\)

\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}2\left(x+y\right)+\sqrt{x+1}=4\\\left(x+y\right)-3\sqrt{x+1}=-5\end{matrix}\right.\left(x\ge-1\right)\)
Đặt \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}a=x+y\\b=\sqrt{x+1}\end{matrix}\right.\left(b\ge0\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}2a+b=4\\a-3b=-5\end{matrix}\right.\Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}2a+b=4\left(1\right)\\2a-6b=-10\left(2\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
Lấy \(\left(1\right)-\left(2\right)\Rightarrow7b=14\Rightarrow b=2\Rightarrow2a=4-2=2\Rightarrow a=1\)
\(\Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x+y=1\\\sqrt{x+1}=2\end{matrix}\right.\Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=-2\\x=3\end{matrix}\right.\)

a/ Bạn tự giải
b/ \(\Delta'=\left(m-1\right)^2-2\left(m-1\right)=m^2-4m+3\)
Biểu thức này có thể nhận giá trị âm với \(1< m< 3\) nên đề bài sai

a) \(\sqrt{1-4x+4x^2}=5\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\sqrt{\left(1-2x\right)^2}=5\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left|1-2x\right|=5\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x-1=5\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x=6\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=3\)
b) \(\sqrt{x^2+6x+9}=3x-1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\sqrt{\left(x+3\right)^2=3x-1}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left|x+3\right|=3x-1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x+3=3x-1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x=4\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=2\)
\(a,\sqrt{1-4x+4x^2}=5\\ \Leftrightarrow\sqrt{\left(1-2x\right)^2}=5\\ \Leftrightarrow\left|1-2x\right|=5\)
\(TH_1:x\le\dfrac{1}{2}\)
\(1-2x=5\\ \Leftrightarrow x=-2\left(tm\right)\)
\(TH_2:x\ge\dfrac{1}{2}\)
\(-1+2x=5\\ \Leftrightarrow x=3\left(tm\right)\)
Vậy \(S=\left\{-2;3\right\}\)
\(b,\sqrt{x^2+6x+9}=3x-1\\ \Leftrightarrow\sqrt{\left(x+3\right)^2}=3x-1\\ \Leftrightarrow\left|x+3\right|=3x-1\)
\(TH_1:x\ge-3\\ x+3=3x-1\\ \Leftrightarrow-2x=-4\Leftrightarrow x=2\left(tm\right)\)
\(TH_2:x< 3\\ -x-3=3x-1\\ \Leftrightarrow-4x=2\\ \Leftrightarrow x=-\dfrac{1}{2}\left(tm\right)\)
Vậy \(S=\left\{2;-\dfrac{1}{2}\right\}\)

Lời giải:
ĐKXĐ: \(x\geq \frac{5}{3}\)
Ta có: \(4\sqrt{3x-5}-8=0\Leftrightarrow 4\sqrt{3x-5}=8\Leftrightarrow \sqrt{3x-5}=2\)
\(\Rightarrow 3x-5=4\Rightarrow x=\frac{4+5}{3}=3\) (thỏa mãn)
Vậy $x=3$

Đk: \(x\ge-\frac{1}{4}\)
pt <=> \(4x^2+4x+2=2\sqrt{4x-1}\)
<=> \(\left(2x+1\right)^2+1=2\sqrt{2\left(2x+1\right)-1}\)
Đặt \(\sqrt{2\left(2x+1\right)-1}=a\left(a\ge0\right)\)
Ta có hệ \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\left(2x+1\right)^2+1=2a\left(1\right)\\a^2+1=2\left(2x+1\right)\left(2\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
Từ (1),(2)=> \(\left(2x+1\right)^2-a^2=2a-2\left(2x+1\right)\)
<=> \(\left(2x+1-a\right)\left(2x+1+a\right)=-2\left(2x+1-a\right)\)
<=> \(\left(2x+1-a\right)\left(2x+1+a\right)+2\left(2x+1-a\right)=0\)
<=> \(\left(2x+1-a\right)\left(2x+a+3\right)=0\)( *)
vì \(x\ge-\frac{1}{4}\) và \(a\ge0\)=> \(2x+a+3\ge2.\frac{-1}{4}+0+3=\frac{5}{2}>0\)
(*) => \(2x+1-a=0\)
<=> \(2x+1=a\)
<=> \(2x+1=\sqrt{2\left(2x+1\right)-1}\)
=> \(4x^2+4x+1=2\left(2x+1\right)-1\)
<=> \(4x^2+4x+1-4x-1=0\)
<=> \(4x^2=0\)
<=> x=0 (t/m)
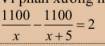
\(\dfrac{1100}{x}-\dfrac{1100}{x+5}=2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{1105-1100}{x+5}=2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{5}{x-5}=2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow5=2\left(x-5\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow5=2x-10\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x=15\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{15}{2}=7,5\)
\(\dfrac{1100}{x}-\dfrac{1100}{x+5}=2\left(ĐK:x\ne0;x\ne-5\right)\\ \Leftrightarrow\dfrac{1100\left(x+5\right)-1100x}{x\left(x+5\right)}=\dfrac{2x\left(x+5\right)}{x\left(x+5\right)}\\ \Leftrightarrow2x^2+10x-5500=0\\ \Leftrightarrow2x^2-100x+110x-5500=0\\ \Leftrightarrow2x.\left(x-50\right)+110.\left(x-50\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(2x+110\right).\left(x-50\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}2x+110=0\\x-50=0\end{matrix}\right.\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-55\left(TM\right)\\x=50\left(TM\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy: S={-55;50}