Cho biểu thức A = 3 x 2 − 2 x + 2 .
a) Tìm x để A đạt giá trị lớn nhất;
b) Tìm x để A ∈ Z.
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

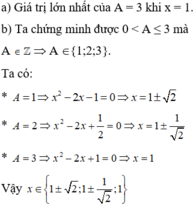

bài 2
Ta có:
\(A=\left|x-102\right|+\left|2-x\right|\Rightarrow A\ge\left|x-102+2-x\right|=-100\Rightarrow GTNNcủaAlà-100\)đạt được khi \(\left|x-102\right|.\left|2-x\right|=0\)
Trường hợp 1: \(x-102>0\Rightarrow x>102\)
\(2-x>0\Rightarrow x< 2\)
\(\Rightarrow102< x< 2\left(loại\right)\)
Trường hợp 2:\(x-102< 0\Rightarrow x< 102\)
\(2-x< 0\Rightarrow x>2\)
\(\Rightarrow2< x< 102\left(nhận\right)\)
Vậy GTNN của A là -100 đạt được khi 2<x<102.

a) \(A=\dfrac{3}{x-1}\)
Điều kiện \(|x-1|\ge0\)
\(\Rightarrow A=\dfrac{3}{x-1}\ge0\)
\(GTNN\left(A\right)=0\) \(\Rightarrow x-1=+\infty\Rightarrow x\rightarrow+\infty\)
b) \(GTLN\left(A\right)\) không có \(\left(A=\dfrac{3}{x-1}\ge0\right)\)

a: Ta có: \(x^2=3-2\sqrt{2}\)
nên \(x=\sqrt{2}-1\)
Thay \(x=\sqrt{2}-1\) vào A, ta được:
\(A=\dfrac{\left(\sqrt{2}+1\right)^2}{\sqrt{2}-1}=\dfrac{3+2\sqrt{2}}{\sqrt{2}-1}=7+5\sqrt{2}\)

\(A=0,6+\left|\dfrac{1}{2}-x\right|\\ Vì:\left|\dfrac{1}{2}-x\right|\ge\forall0x\in R\\ Nên:A=0,6+\left|\dfrac{1}{2}-x\right|\ge0,6\forall x\in R\\ Vậy:min_A=0,6\Leftrightarrow\left(\dfrac{1}{2}-x\right)=0\Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{1}{2}\)
\(B=\dfrac{2}{3}-\left|2x+\dfrac{2}{3}\right|\\ Vì:\left|2x+\dfrac{2}{3}\right|\ge0\forall x\in R\\ Nên:B=\dfrac{2}{3}-\left|2x+\dfrac{2}{3}\right|\le\dfrac{2}{3}\forall x\in R\\ Vậy:max_B=\dfrac{2}{3}\Leftrightarrow\left|2x+\dfrac{2}{3}\right|=0\Leftrightarrow x=-\dfrac{1}{3}\)

A = \(\dfrac{2x-1}{x+2}\)
a, A là phân số ⇔ \(x\) + 2 # 0 ⇒ \(x\) # -2
b, Để A là một số nguyên thì 2\(x-1\) ⋮ \(x\) + 2
⇒ 2\(x\) + 4 - 5 ⋮ \(x\) + 2
⇒ 2(\(x\) + 2) - 5 ⋮ \(x\) + 2
⇒ 5 ⋮ \(x\) + 2
⇒ \(x\) + 2 \(\in\) { -5; -1; 1; 5}
⇒ \(x\) \(\in\) { -7; -3; -1; 3}
c, A = \(\dfrac{2x-1}{x+2}\)
A = 2 - \(\dfrac{5}{x+2}\)
Với \(x\) \(\in\) Z và \(x\) < -3 ta có
\(x\) + 2 < - 3 + 2 = -1
⇒ \(\dfrac{5}{x+2}\) > \(\dfrac{5}{-1}\) = -5 ⇒ - \(\dfrac{5}{x+2}\)< 5
⇒ 2 - \(\dfrac{5}{x+2}\) < 2 + 5 = 7 ⇒ A < 7 (1)
Với \(x\) > -3; \(x\) # - 2; \(x\in\) Z ⇒ \(x\) ≥ -1 ⇒ \(x\) + 2 ≥ -1 + 2 = 1
\(\dfrac{5}{x+2}\) > 0 ⇒ - \(\dfrac{5}{x+2}\) < 0 ⇒ 2 - \(\dfrac{5}{x+2}\) < 2 (2)
Với \(x=-3\) ⇒ A = 2 - \(\dfrac{5}{-3+2}\) = 7 (3)
Kết hợp (1); (2) và(3) ta có A(max) = 7 ⇔ \(x\) = -3

Vì |x-2| \(\ge\) 0 với mọi x
=>\(\frac{1}{2}-\left|x-2\right|\le\frac{1}{2}\) với mọi x
=>MaxA=1/2
Dấu "=" xảy ra <=> \(\left|x-2\right|=0< =>x=2\)
Vậy..............