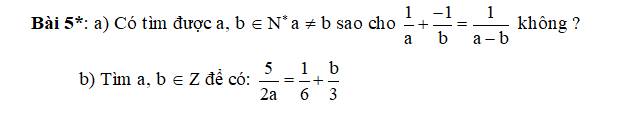 Giúp mình với . Cảm ơn rất nhiều !
Giúp mình với . Cảm ơn rất nhiều !
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


120 dm2 x 5 + 4m2 = 600 dm2 + 4 m2 = 6 m2 + 4m2 = 10 m2

Gọi điện trở ampe kế là Ra
Hiệu điện thế hai đầu ampe kế A2 là:
\(UA2=I2.Ra=1.Ra=Ra\)
Mà ta lại có: \(UA2=UA3+IA3.2r=IA3.Ra+IA3.2r=0.5Ra+0.5.2r=0.5Ra+r\)
=> \(Ra=0.5Ra+r\)
=> \(r=0.5Ra\)
Ta có: \(IMP=IA2+IA3=1+0.5=1.5\left(A\right)\)
=>\(UMP=IMP.r=1.5r=1,5.0.5Ra=0.75Ra\)
=>\(UMQ=UMP+UA2=0.75Ra+Ra=1.75Ra\)
=> Cường độ dong điện chạy qua ampe kế A1 là:
\(IA1=\dfrac{UMQ}{Ra}=\dfrac{1.75Ra}{Ra}=1.75\left(A\right)\)




Bài 1 :
Thay x = 2 ; y = -1/2 ta được
\(B=-8+2.4\left(-\dfrac{1}{2}\right)-4.2.\left(\dfrac{1}{4}\right)+2\left(-\dfrac{1}{2}\right)-3\)
\(=-8-4-2-1-3=-18\)

a) Ta có: \(\left(2x-3\right)\left(3x+4\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}2x-3=0\\3x+4=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}2x=3\\3x=-4\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{3}{2}\\x=-\dfrac{4}{3}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy: \(S=\left\{\dfrac{3}{2};-\dfrac{4}{3}\right\}\)
b) Ta có: \(x^3-3x^2+3x-1=\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)^3-\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left[x^2-2x+1-x-1\right]=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left(x^2-3x\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\left(x-1\right)\left(x-3\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\x-1=0\\x-3=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\x=1\\x=3\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy: S={0;1;3}
c) Ta có: \(x^2+x=2x+2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\left(x+1\right)-2\left(x+1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+1\right)\left(x-2\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x+1=0\\x-2=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-1\\x=2\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy: S={-1;2}
d) Ta có: \(\left(x-1\right)^2=2\left(x^2-1\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)^2-2\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left(x-1-2x-2\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left(-x-3\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-1=0\\-x-3=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=1\\-x=3\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=1\\x=-3\end{matrix}\right.\)Vậy: S={1;-3}
e) Ta có: \(2\left(x+2\right)^2-x^3-8=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2\left(x+2\right)^2-\left(x^3+8\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2\left(x+2\right)\cdot\left(x+2\right)-\left(x+2\right)\left(x^2-2x+4\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+2\right)\left(2x+4-x^2+2x-4\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+2\right)\cdot\left(-x^2+4x\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-x\left(x+2\right)\left(x-4\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\x+2=0\\x-4=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\x=-2\\x=4\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy: S={0;-2;4}

a: \(P=-\left|5-x\right|+2019\le2019\forall x\)
Dấu '=' xảy ra khi x=5
 ai giúp mình với ạ, mình cảm ơn rất nhiều
ai giúp mình với ạ, mình cảm ơn rất nhiều




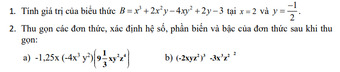


Lời giải:
a.
$\frac{1}{a}+\frac{-1}{b}=\frac{1}{a-b}$
$\Rightarrow \frac{b-a}{ab}=\frac{1}{a-b}$
$\Rightarrow (b-a)(a-b)=ab$
$\Rightarrow -(a-b)^2=ab$
Với $a,b\in\mathbb{N}^*$, $ab>0$ còn $-(a-b)^2\leq 0$
Do đó $-(a-b)^2\neq ab$
$\Rightarrow$ không tồn tại $a,b\in\mathbb{N}^*$ thỏa mãn điều kiện đề.
b.
$\frac{5}{2a}=\frac{1}{6}+\frac{b}{3}$
$\frac{15}{6a}=\frac{1+2b}{6}=\frac{a+2ab}{6a}$
$\Rightarrow a+2ab=15$
$\Rightarrow a(1+2b)=15$
Do $a,b$ nguyên nên $a, 1+2b$ nguyên. Mà tích $a(1+2b)=15$ nên xét các TH sau:
TH1: $a=1, 2b+1=15\Rightarrow a=1; b=7$
TH2: $a=-1, 2b+1=-15\Rightarrow a=-1; b=-8$
TH3: $a=15, 2b+1=1\Rightarrow a=15; b=0$
TH4: $a=-15; 2b+1=-1\Rightarrow a=-15; b=-1$
TH5: $a=3, 2b+1=5\Rightarrow a=3; b=2$
TH6: $a=-3, 2b+1=-5\Rightarrow a=-3; b=-3$
TH7: $a=5; 2b+1=3\Rightarrow a=5; b=1$
TH8: $a=-5; 2b+1=-3\Rightarrow a=-5; b=-2$
e cảm ơn